HEART SURFACES AND BORDERS
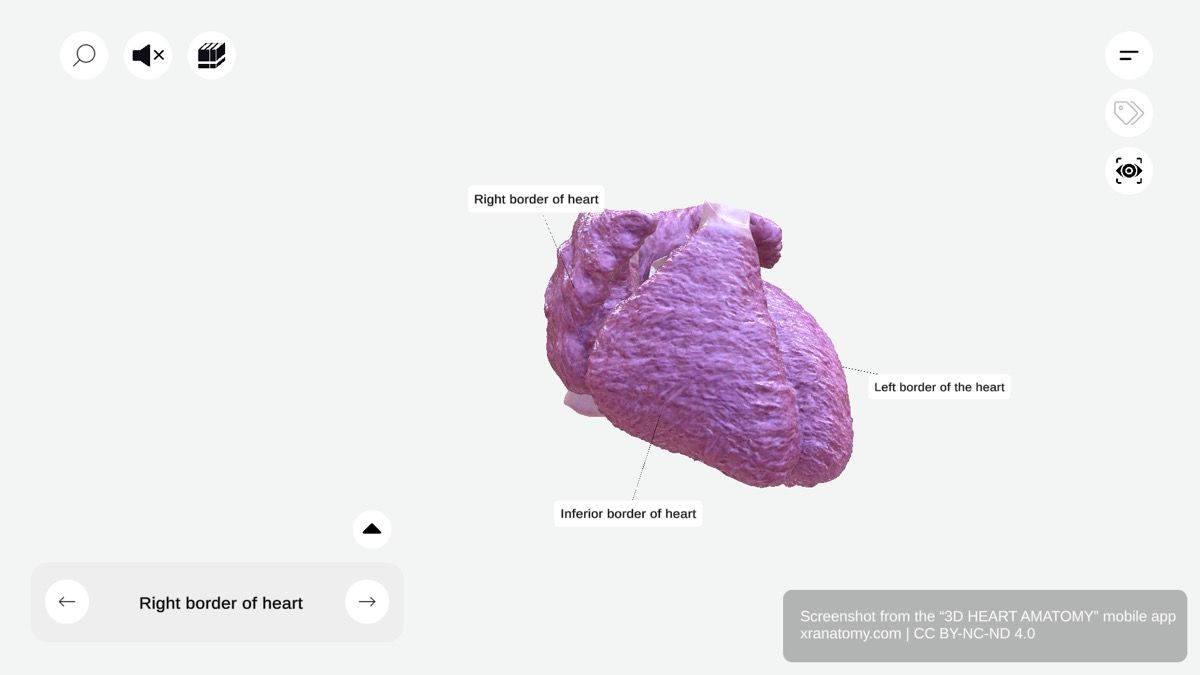
Heart Borders - Right Border, Preview from the app.
WHY THIS MATTERS
Your heart sits in a precise orientation inside your chest, and each of its surfaces, borders, and sulci relates directly to surrounding structures. Knowing which chambers form each surface and border helps you interpret chest radiographs, locate coronary vessels, and understand patterns of myocardial infarction.
BORDERS OF THE HEART
Your heart has three main borders. The right border faces your right lung and is formed by the superior vena cava and right atrium. The inferior border rests on your diaphragm and is primarily formed by the right ventricle. The left border faces your left lung and is formed by the aortic arch, pulmonary trunk, left auricle, and left ventricle.
Right Border
The right border of your heart is formed by two structures: the superior vena cava superiorly and the right atrium inferiorly. It faces your right lung. Clinicians use this border in radiography to assess right atrial enlargement.
Inferior Border
The inferior border is nearly horizontal in orientation. It is primarily formed by the right ventricle and rests on your diaphragm. This border separates the anterior surface from the diaphragmatic surface.
Left Border
The left border outlines the left side of your heart and faces your left lung. It is formed by multiple structures: the aortic arch, pulmonary trunk, left auricle, and left ventricle extending to the apex. This border is important for evaluating left ventricular size and shape.
SURFACES OF THE HEART
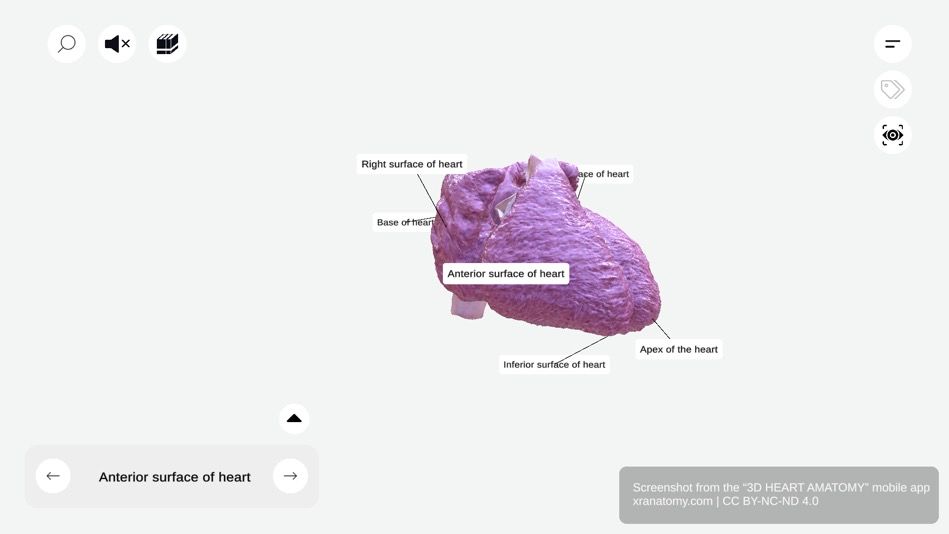
Heart Surfaces - Anterior Surface, Preview from the app.
Your heart has four surfaces, each facing a different direction. The anterior surface (sternocostal) faces your sternum and ribs. The left surface (pulmonary) faces your left lung. The right surface faces your right lung. The inferior surface (diaphragmatic) rests on your diaphragm.
Anterior Surface
The anterior surface is also called the sternocostal surface. It faces anteriorly toward your sternum and ribs. Three chambers compose it: the right atrium, the right ventricle (which makes the major contribution), and the left ventricle (a small contribution).
Left Surface
The left surface is also called the pulmonary surface. It is directed toward your left lung. The left ventricle mainly forms this surface, with the left atrium contributing partly.
Right Surface
The right surface faces your right lung. It is formed mainly by the right atrium and extends between the superior and inferior vena cava. This surface is relevant in right-sided cardiac conditions.
Inferior Surface
The inferior surface is also called the diaphragmatic surface. It faces downward and rests on your diaphragm. The left ventricle makes the major contribution, while the right ventricle contributes partially. This surface is clinically significant in inferior wall myocardial infarctions.
BASE OF THE HEART
The base is the posterior aspect of your heart. It is oriented posteriorly and to the right. The left atrium mainly forms the base. It receives the pulmonary veins carrying oxygenated blood.
APEX OF THE HEART
The apex is the tip of the left ventricle. It points anteriorly, downward, and to the left. You can locate it in your fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line. The apex serves as an important landmark for cardiac auscultation and is the site for listening to mitral valve sounds.
SULCI OF THE HEART
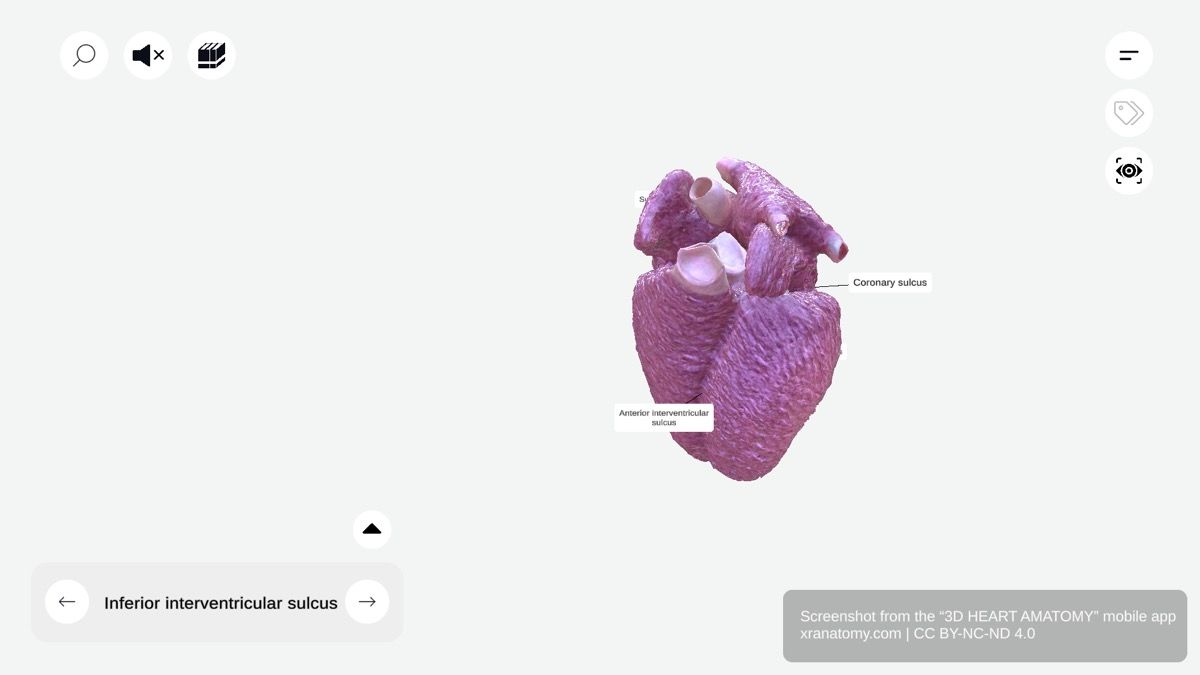
Heart Sulci - Interventricular Sulcus, Preview from the app.
The sulci are surface grooves on your heart that contain cardiac vessels. The coronary sulcus encircles the heart and separates atria from ventricles. The sulcus terminalis runs vertically along the right atrium. The anterior interventricular sulcus marks the junction between ventricles on the front, while the inferior interventricular sulcus marks the same junction on the diaphragmatic surface.
Coronary Sulcus
The coronary sulcus is also called the atrioventricular groove. It encircles your heart and demarcates the atria from the ventricles. It contains important cardiac vessels.
Sulcus Terminalis
The sulcus terminalis is a groove on the right atrium. It runs vertically along the right atrium, extending from the right side of the superior vena cava to the right side of the inferior vena cava. Its internal correspondence is the crista terminalis. It marks an important junction in the right atrial wall.
Anterior Interventricular Sulcus
The anterior interventricular sulcus is a groove on the anterior surface of your heart. It marks the junction between the right and left ventricles. This sulcus contains the anterior interventricular artery (left anterior descending) and the great cardiac vein.
Inferior Interventricular Sulcus
The inferior interventricular sulcus is a groove on the diaphragmatic surface. It marks the junction between the ventricles on the inferior surface. This sulcus contains the posterior interventricular artery, usually a branch of the right coronary artery, and the middle cardiac vein.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Which structures form the right border of your heart?
Reveal Answer
The superior vena cava superiorly and the right atrium inferiorly.
2. Name the four surfaces of the heart and which chamber mainly forms each one.
Reveal Answer
The anterior (sternocostal) surface is mainly formed by the right ventricle. The left (pulmonary) surface is mainly formed by the left ventricle. The right surface is mainly formed by the right atrium. The inferior (diaphragmatic) surface is mainly formed by the left ventricle.
3. What vessels does the anterior interventricular sulcus contain?
Reveal Answer
The anterior interventricular artery (left anterior descending) and the great cardiac vein.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you know the external surfaces, borders, and sulci, the next page explores the Myocardium and Conducting System. You will study the cardiac muscle layer and the specialized network that generates and transmits electrical impulses, including the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, and Purkinje fibres.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Gray H, Lewis W. Angiology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. p. 526–542.
2. Gosling JA, Harris PF, Humpherson JR, Whitmore I, Willan PLT. Human anatomy: color atlas and textbook. 6th ed. 2017. 45–58 p.
3. Anderson RH, Spicer DE, Hlavacek AM, Cook AC, Backer CL. (2013). Anatomy of the cardiac chambers. In Wilcox’s Surgical Anatomy of the Heart (4th ed., pp. 13–50). Cambridge University Press.
4. Fritsch H, Kuehnel W. Color Atlas of Human Anatomy. Vol. Volume 2, Color Atlas and Textbook of Human Anatomy. 2005. 10–42 p.
5. Moore K, Dalley A, Agur A. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Vol. 7ed, Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2014. 132–151 p.
6. Ho SYen. Anatomy for Cardiac Electrophysiologists: A Practical Handbook. Cardiotext Pub; 2012. 5–27 p.
7. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
8. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.