FRONTAL BONE AR ATLAS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FRONTAL BONE AR ATLAS
AR Figure 23 – Frontal Bone: Disarticulated view, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
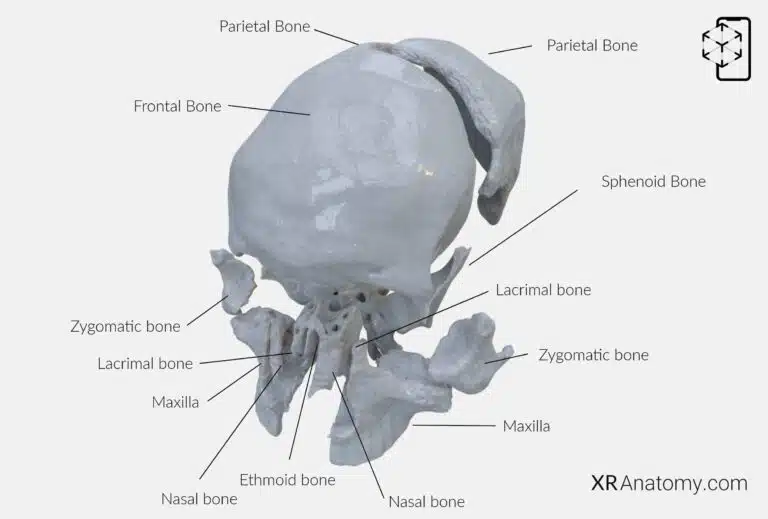
The frontal bone is a major component of the cranium, forming the forehead, the roofs of the orbits (eye sockets), and the anterior portion of the cranial floor. It , including the sphenoid, ethmoid, two parietals, two nasals, two maxillae, two lacrimals, and two zygomatic bones, contributing to the complex structure of the skull.
SQUAMOUS PART OF FRONTAL BONE
AR Figure 24 – Frontal Bone: Squamous part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
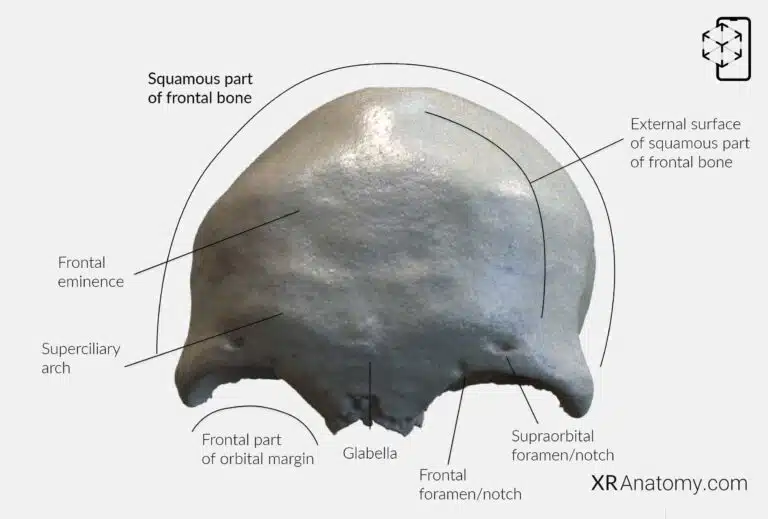
, forms the forehead's vertical, flat region. is smooth and convex, facing outward toward the scalp. Approximately 3 cm above the , on either side of the midline, are —rounded elevations that contribute to the forehead's shape. Just above the lie the , two elevations that enhance the brow's prominence. Between these arches is the , a smooth elevation located along the midline.
The lower boundary of the is known as , which separates the from the . Along this margin, on the medial aspect, is the . In some individuals, this notch is a complete hole called the supraorbital foramen. Medial to the supraorbital notch is the , which can also present as a hole termed the frontal foramen when fully enclosed. These openings allow the passage of nerves and blood vessels to the forehead and scalp.
EXTERNAL SURFACE OF SQUAMOUS PART OF FRONTAL BONE

AR Figure 24 – Frontal Bone: Squamous part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
, The external surface of the squamous part of the frontal bone is smooth and convex, forming the prominent forehead area. , frontal eminences, which are rounded elevations located about 3 cm above the , supraorbital margin on either side of the midline. Above the supraorbital margin are , the superciliary arches, enhancing the contour of the brow region. Centrally located between these arches is , the glabella, a slight elevation on the midline. The frontal part of the orbital margin serves as the lower boundary of the squama, demarcating it from the orbital part below. , The supraorbital notch or foramen is found on the medial aspect of , allowing passage for nerves and vessels. Medial to this is the , which similarly permits neurovascular structures to reach the forehead.
THE TEMPORAL SURFACE OF THE FRONTAL BONE
AR Figure 25 – Frontal Bone: Temporal surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
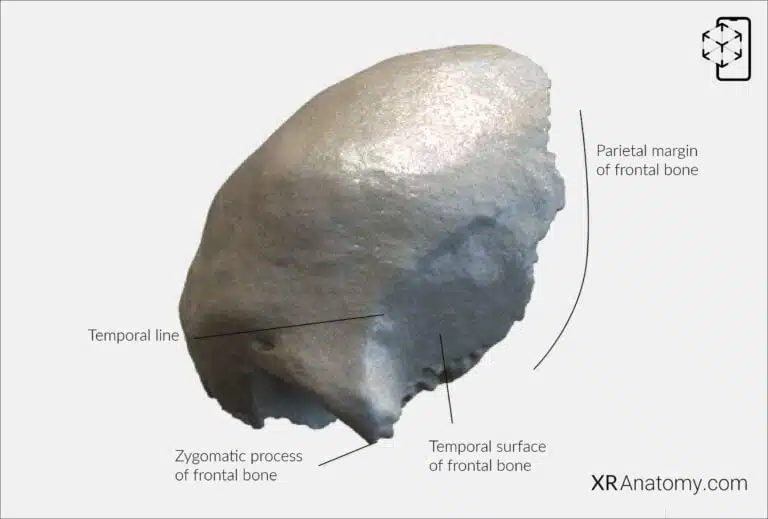
,is the lateral aspect that contributes to the formation of the temple region. Posteriorly, it connects to the parietal bones via the . The is a prominent projection at the lateral end of the , articulating with the zygomatic bone and contributing to the lateral wall and rim of the orbit. Extending upward and backward from the is the , which divides into upper and lower temporal lines and serves as an attachment point for the temporalis muscle and temporal fascia.
INTERNAL SURFACE OF THE SQUAMOUS PART OF THE FRONTAL BONE
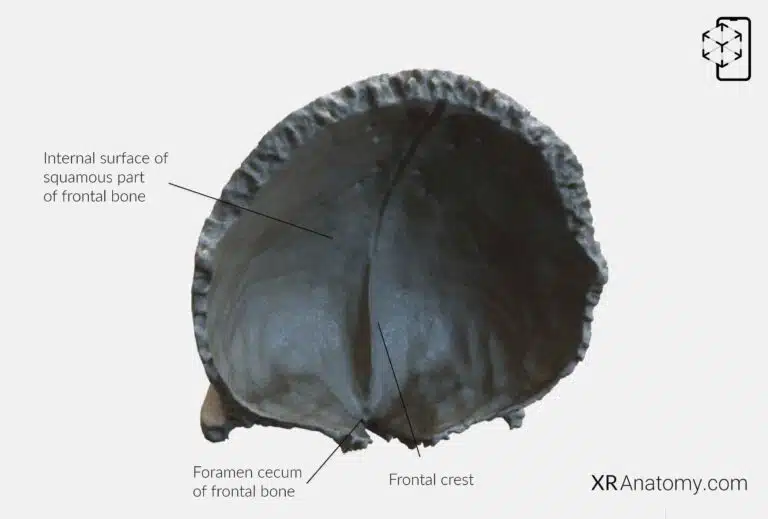

AR Figure 26 – Frontal Bone: Internal surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The internal surface of the squamous part of the frontal bone faces the cranial cavity and features the , a ridge formed by the union of the edges of the sagittal sulcus at the midline's lower end. At the inferior end of the frontal crest lies the , which is formed by a small notch that unites with the ethmoid bone. This foramen allows passage for small veins connecting the nasal cavity with the superior sagittal sinus.
THE NASAL PART OF THE FRONTAL BONE

AR Figure 27 – Frontal Bone: Nasal part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The nasal part of the frontal bone is a downward extension located between the supraorbital margins. It includes the , a bony projection that extends downward from the center of the nasal part and articulates with the nasal bones and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The forms the lower border of this part and articulates with the upper borders of the nasal bones, contributing to the formation of the nasal bridge.
THE ORBITAL PART OF THE FRONTAL BONE
AR Figure 28 – Frontal Bone: Orbital part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
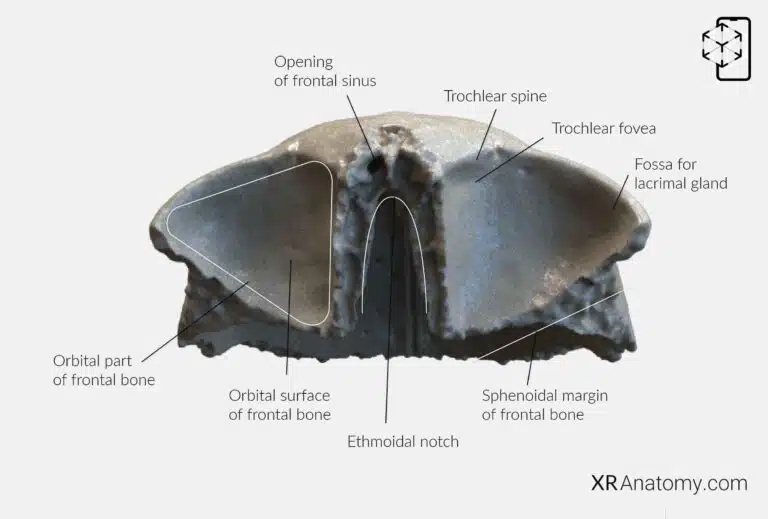
The orbital part of the frontal bone consists of two horizontal, triangular plates known as the , which form the roofs of the orbits and the floor of the anterior cranial fossa. These plates are separated by the , a gap that accommodates the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. The of each plate faces downward into the orbit and includes important features such as the —a small depression medially near the nasal part, which serves as the attachment for the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle. Lateral to this is the , a shallow depression that houses the lacrimal gland within the orbit. The of the frontal bone articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone, completing the anterior cranial fossa's formation.
FRONTAL SINUS
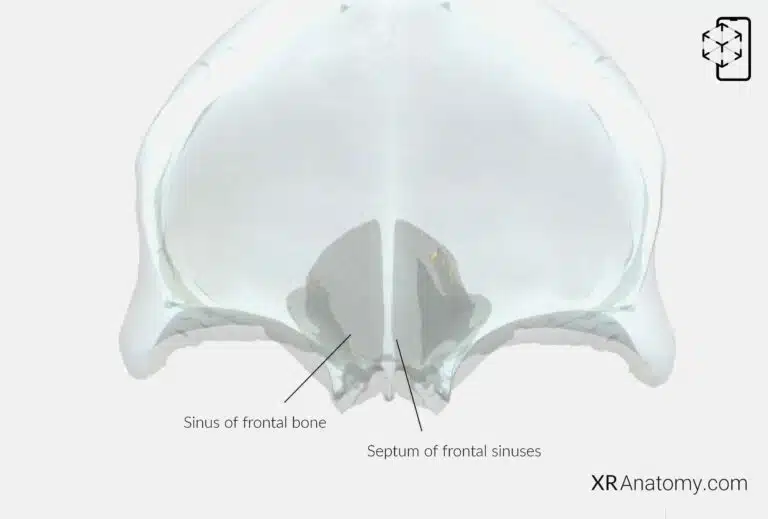
AR Figure 29 – Frontal Bone: Frontal sinus, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The are two irregular cavities located within the frontal bone, situated above the orbits and behind the superciliary arches. They are separated by a thin bony septum known as the , which varies in position and can result in asymmetrical sinuses. Each sinus opens into the nasal cavity on either side of the nasal spine, just anterior to the ethmoidal notch. These openings allow mucus drainage from the sinuses into the nasal passages. The frontal sinuses play roles in humidifying inhaled air, enhancing voice resonance, and reducing the skull's weight.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Sampson HW, Montgomery JL, Henryson GL. Atlas of the human skull. College Station: Texas A & M University Press; 2007.
4. Saylam C, Özer MA, Ozek C, Gurler T. Anatomical Variations of the Frontal and Supraorbital Transcranial Passages. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2003;14(1):10–2.
5. Hosemann W, Gross R, Goede U, Kuehnel T. Clinical anatomy of the nasal process of the frontal bone (spina nasalis interna). Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. 2001;125(1):60–5.
6. Steele DG, Bramblett CA. The anatomy and biology of human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press; 1988.
7. Tersigni-Tarrant MTA, Shirley NR. Human osteology. Vol. 4, Forensic Anthropology: An Introduction. 2012. 33–68 p.
8. Monjas-Cánovas I, García-Garrigós E, Arenas-Jiménez JJ, Abarca-Olivas J, Sánchez-Del Campo F, Gras-Albert JR. Radiological Anatomy of the Ethmoidal Arteries: CT Cadaver Study. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition). 2011;62(5):367–74.
9. Pereira G, Lopes P, Santos A, Krebs. Morphometric aspects of the jugular foramen in dry skulls of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. Vol. 27, J. Morphol. Sci. 2010.
12. Kunc V, Fabik J, Kubickova B, Kachlik D. Vermian fossa or median occipital fossa revisited: Prevalence and clinical anatomy. Annals of Anatomy. 2020 May 1;229:151458.
14. Standring S. The skull. In: Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2021st ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. p. 558–73.
15. Rhoton AL. Chapter 1 Overview of Temporal Bone. Neurosurgery. 2007;
17. Tóth M, Moser G, Patonay L, Oláh I. Development of the anterior chordal canal. Annals of Anatomy. 2006;
18. Carpenter G, Knipe H. Tympanic part of temporal bone. Radiopaedia.org. 2014 Mar 23;
19. Eckerdal O. The petrotympanic fissure: A link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio – Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1991;9(1):15–22.
21. Singh R, Kishore Gupta N, Kumar R. Morphometry and Morphology of Foramen Petrosum in Indian Population. Basic Sciences of Medicine. 2020;2020(1):8–9.
23. Piagkou M, Xanthos T, Anagnostopoulou S, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Piagkos G, et al. Anatomical variation and morphology in the position of the palatine foramina in adult human skulls from Greece. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 2012 Oct 1;40(7):e206–10.