MAXILLA
MAXILLA AR ATLAS
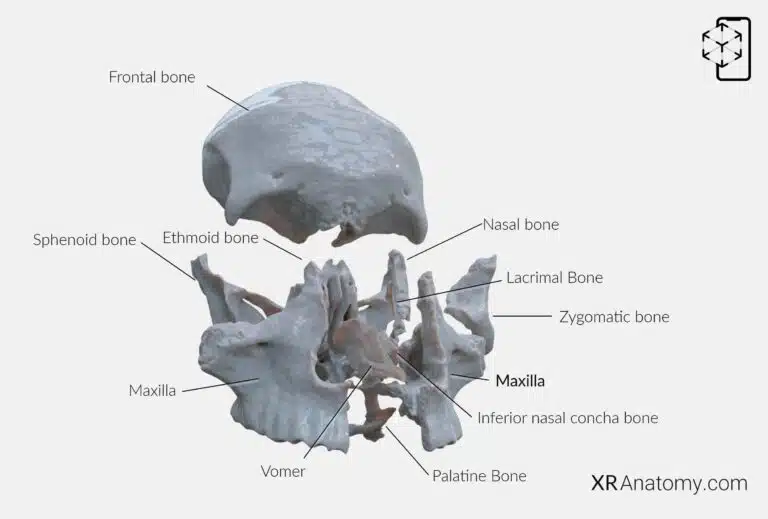
AR Figure 51 – Maxilla: Disarticulated View, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is a fundamental bone of the facial skeleton, forming the upper jaw and playing a critical role in the architecture of the face. It contributes to the formation of the roof of the mouth, the floor of the orbit, and the sides and floor of the nasal cavity. The maxilla articulates with several bones, creating a complex and interwoven structure that supports various functions such as mastication, speech, and facial expression. The the following bones: The frontal bone, The ethmoid bone, The nasal bone, The zygomatic bone, The lacrimal bone, The inferior nasal concha, The palatine bone, The vomer, The opposite maxilla.
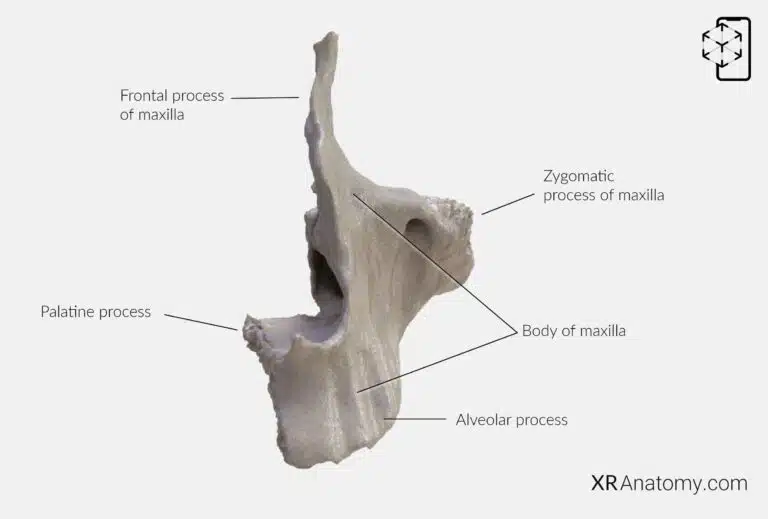
AR Figure 52 – Maxilla: Anterior View, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
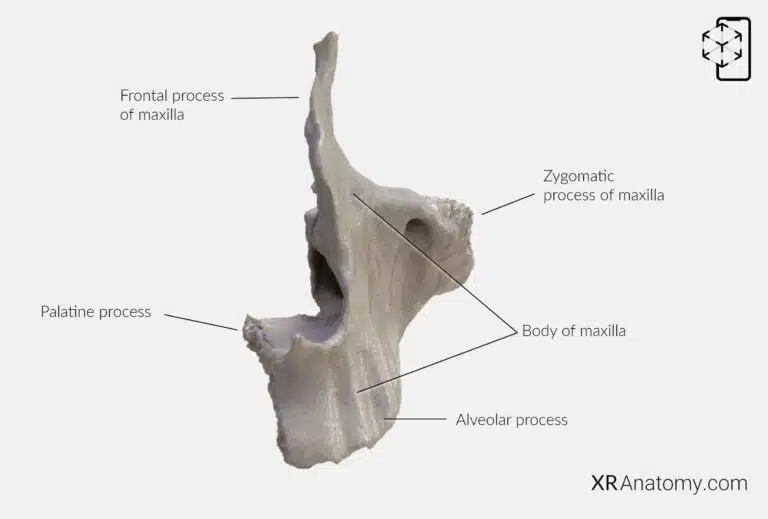
Structurally, the maxilla consists of a and four distinct processes: the , the , the , and the . Each process serves a specific function and contributes to the maxilla's overall role in the facial skeleton.
BODY OF MAXILLA
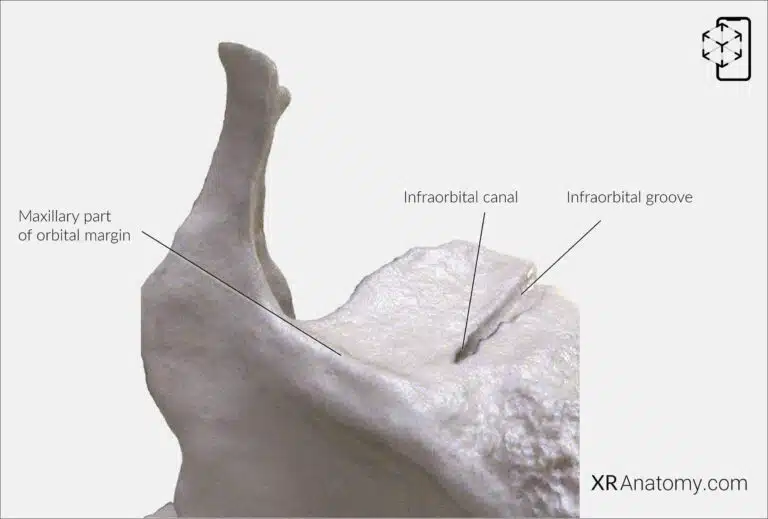
AR Figure 53 – Maxilla: Orbital surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The serves as the central hub of the bone, enclosing the large , which is a significant air-filled cavity contributing to the lightness of the skull and resonance of the voice. The body features four surfaces, each oriented in different directions and associated with various anatomical landmarks.
The , located superiorly, forms a substantial part of the floor of the orbit. This surface is smooth and triangular, providing support for the eye and associated structures. Notably, it contains the , which begins at the posterior border and continues as the . This canal transmits the infra-orbital nerve and vessels, which emerge onto the face through the to supply the mid-facial region.
The contributes to the inferior rim of the orbit, offering structural integrity and forming a boundary between the orbital cavity and the facial surface.
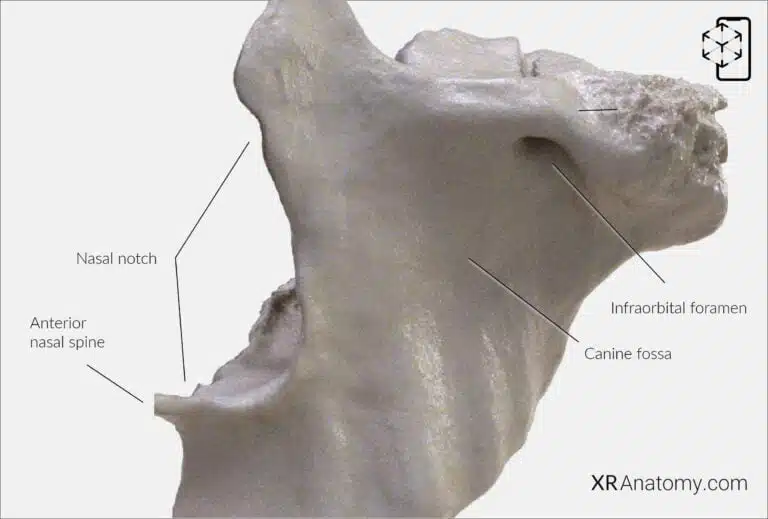
AR Figure 54 – Maxilla: Anterior Surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The faces forward and slightly laterally, forming part of the facial structure. This surface is marked by the , a depression situated below the and above the roots of the canine teeth. The inferior portion displays corresponding to the tooth roots. The , located here, allows the infra-orbital nerve and vessels to emerge onto the face.
The is a deep concavity on the anterior surface that contributes to the formation of the piriform aperture—the pear-shaped opening of the nasal cavity. At the inferior end of the nasal notch, the left and right maxillae unite to form the sharp , providing attachment for the nasal septum cartilage.
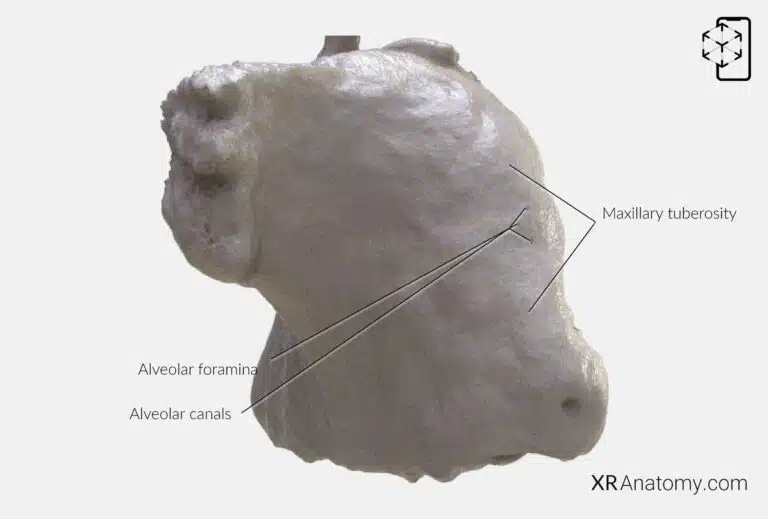
AR Figure 55 – Maxilla: Infratemporal surface of maxilla, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
Facing posteriorly, the contributes to the formation of the infratemporal and pterygopalatine fossae. This surface features the , a rounded prominence posterior to the last molar tooth, which serves as an attachment point for muscles and is significant in dental procedures.
The and are located on this surface, allowing passage of the posterior superior alveolar nerves and vessels to the molar teeth, thereby supplying essential innervation and blood flow.
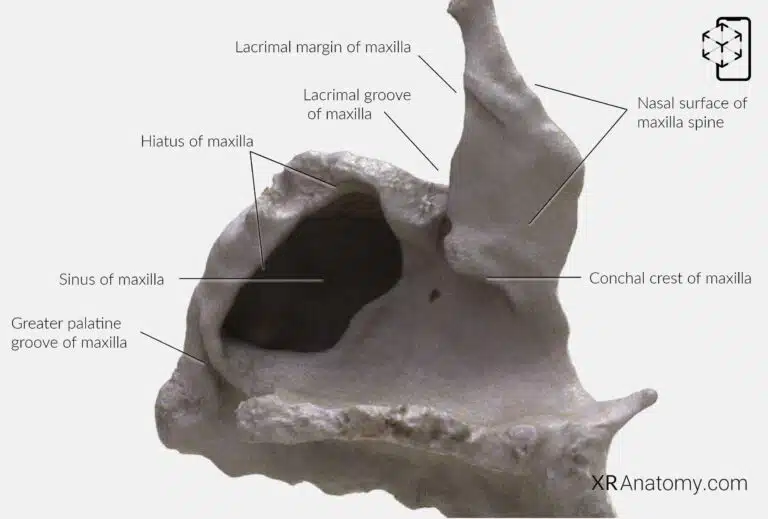
AR Figure 56 – Maxilla: Nasal Surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The , or medial surface, contributes to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. A prominent feature here is the , a deep groove that, together with the lacrimal bone, forms the nasolacrimal canal. This canal transmits the nasolacrimal duct, which drains tears from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity.
The is a ridge that articulates with the inferior nasal concha, aiding in the formation of the nasal cavity's lateral wall. The articulates with the lacrimal bone, contributing to the medial wall of the orbit.
The large, irregular on this surface leads into the . In life, this opening is mostly covered by adjacent bones and mucous membrane, regulating airflow and drainage within the sinus.
Near the posterior border, the forms, along with the palatine bone, the greater palatine canal. This canal transmits the greater palatine nerve and vessels to the hard palate.
FRONTAL PROCESS OF THE MAXILLA
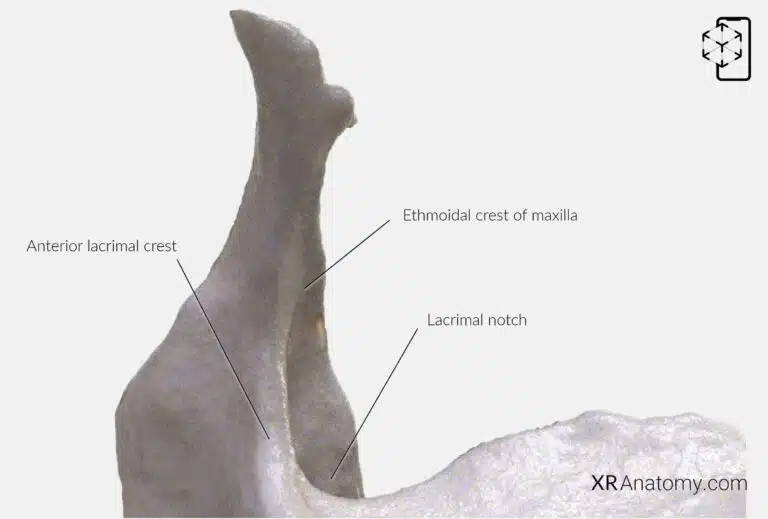
AR Figure 57 – Maxilla: Frontal process, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is an upward projection that articulates with the frontal bone. It contributes to the formation of the lateral boundary of the nose and the medial wall of the orbit, playing a role in the structure of the face and the protection of the eye.
A prominent feature of this process is the , a vertical ridge that provides attachment for the lacrimal sac and the medial palpebral ligament, which are integral to the lacrimal apparatus responsible for tear drainage.
The , situated posteriorly, articulates with the lacrimal bone, completing the lacrimal fossa that houses the lacrimal sac. The is an oblique ridge on the frontal process that articulates with the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid bone, contributing to the nasal cavity's structure.
ZYGOMATIC PROCESS OF MAXILLA
AR Figure 58 – Maxilla: Zygomatic process, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The extends laterally to articulate with the zygomatic bone, forming part of the infraorbital rim and contributing to the prominence of the cheek. This articulation is essential in maintaining the facial contour and providing attachment points for muscles of facial expression.
PALATINE PROCESS
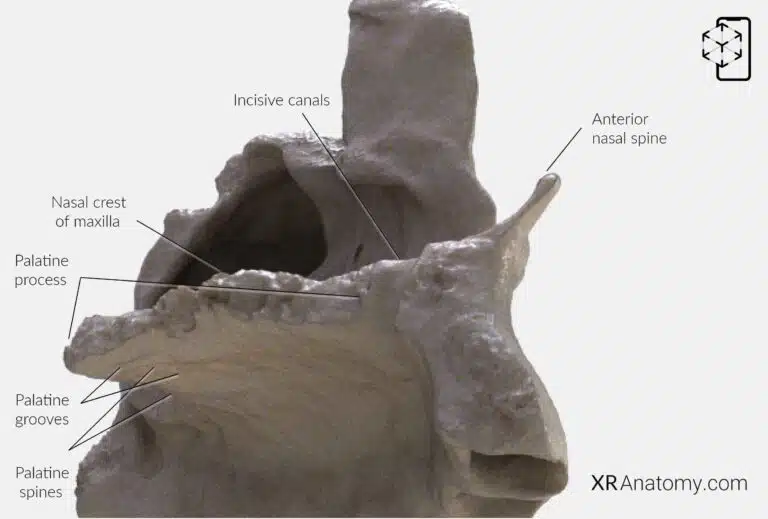
AR Figure 59 – Maxilla: Palatine process, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The projects medially from the maxilla and forms the anterior three-quarters of the hard palate, separating the oral and nasal cavities. This bony plate provides structural support for the upper teeth and serves as the floor of the nasal cavity and the roof of the mouth.
Along the midline of the palatine process is the , a bony ridge where the left and right maxillae meet, providing attachment for the vomer bone that forms part of the nasal septum.
At the anterior end, the pass through the palatine process, transmitting the nasopalatine nerves and branches of the greater palatine arteries. These canals open inferiorly at the , located just posterior to the incisor teeth.
The inferior surface of the palatine process features the and , which accommodate and support the mucous membrane of the hard palate.
ALVEOLAR PROCESS
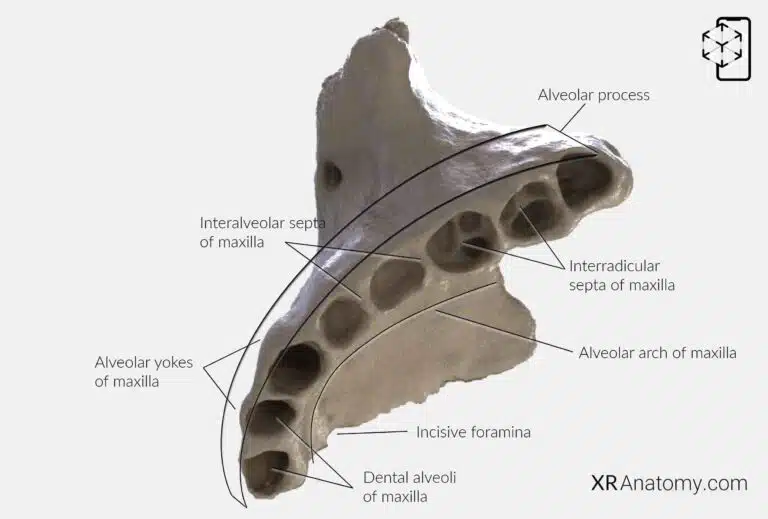
AR Figure 60 – Maxilla: Alveolar process, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is the inferior portion of the maxilla that contains the , the sockets that house the roots of the upper teeth. This process is essential for tooth support and plays a significant role in mastication and speech.
The refers to the curved free margin of the alveolar process, following the contour of the dental arcade. Between the dental alveoli are the , bony partitions that separate adjacent tooth sockets.
In the case of multirooted teeth, the alveoli are further divided by the , which provide additional support and stability for the tooth roots.
Externally, the alveolar process displays the , which are bony prominences corresponding to the positions of the tooth roots. These contribute to the characteristic contour of the upper jaw.
The are located on the midline just posterior to the incisor teeth in the articulated skull. They serve as important anatomical landmarks and are involved in the passage of neurovascular structures supplying the anterior palate.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Sampson HW, Montgomery JL, Henryson GL. Atlas of the human skull. College Station: Texas A & M University Press; 2007.
4. Saylam C, Özer MA, Ozek C, Gurler T. Anatomical Variations of the Frontal and Supraorbital Transcranial Passages. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2003;14(1):10–2.
5. Hosemann W, Gross R, Goede U, Kuehnel T. Clinical anatomy of the nasal process of the frontal bone (spina nasalis interna). Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. 2001;125(1):60–5.
6. Steele DG, Bramblett CA. The anatomy and biology of human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press; 1988.
7. Tersigni-Tarrant MTA, Shirley NR. Human osteology. Vol. 4, Forensic Anthropology: An Introduction. 2012. 33–68 p.
8. Monjas-Cánovas I, García-Garrigós E, Arenas-Jiménez JJ, Abarca-Olivas J, Sánchez-Del Campo F, Gras-Albert JR. Radiological Anatomy of the Ethmoidal Arteries: CT Cadaver Study. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition). 2011;62(5):367–74.
9. Pereira G, Lopes P, Santos A, Krebs. Morphometric aspects of the jugular foramen in dry skulls of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. Vol. 27, J. Morphol. Sci. 2010.
12. Kunc V, Fabik J, Kubickova B, Kachlik D. Vermian fossa or median occipital fossa revisited: Prevalence and clinical anatomy. Annals of Anatomy. 2020 May 1;229:151458.
14. Standring S. The skull. In: Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2021st ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. p. 558–73.
15. Rhoton AL. Chapter 1 Overview of Temporal Bone. Neurosurgery. 2007;
17. Tóth M, Moser G, Patonay L, Oláh I. Development of the anterior chordal canal. Annals of Anatomy. 2006;
18. Carpenter G, Knipe H. Tympanic part of temporal bone. Radiopaedia.org. 2014 Mar 23;
19. Eckerdal O. The petrotympanic fissure: A link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio – Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1991;9(1):15–22.
21. Singh R, Kishore Gupta N, Kumar R. Morphometry and Morphology of Foramen Petrosum in Indian Population. Basic Sciences of Medicine. 2020;2020(1):8–9.
23. Piagkou M, Xanthos T, Anagnostopoulou S, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Piagkos G, et al. Anatomical variation and morphology in the position of the palatine foramina in adult human skulls from Greece. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 2012 Oct 1;40(7):e206–10.