PALATINE BONE
PALATINE BONE AR ATLAS
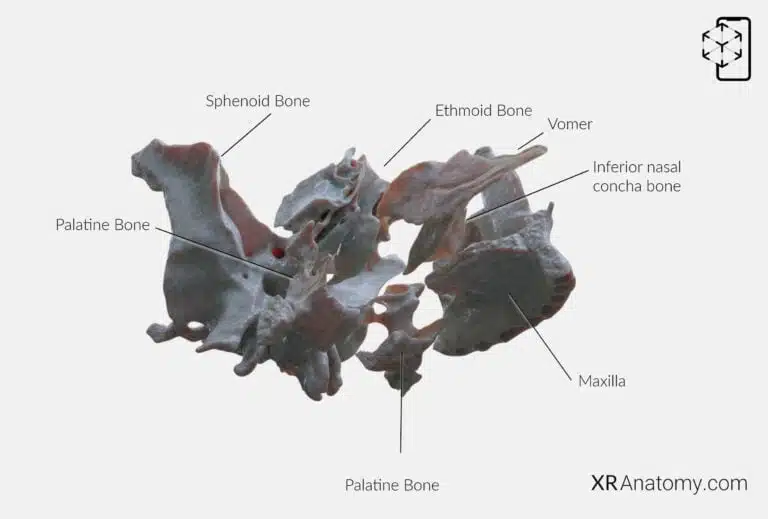
AR Figure 61 – Palatine bone: Disarticulated view, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is a complex structure located at the back part of the nasal cavity and the hard palate. It plays a crucial role in forming the nasal cavity, the orbit, and the hard palate by , including: The sphenoid bone, The ethmoid bone, The maxilla, The inferior nasal concha, The vomer, The opposite palatine bone.
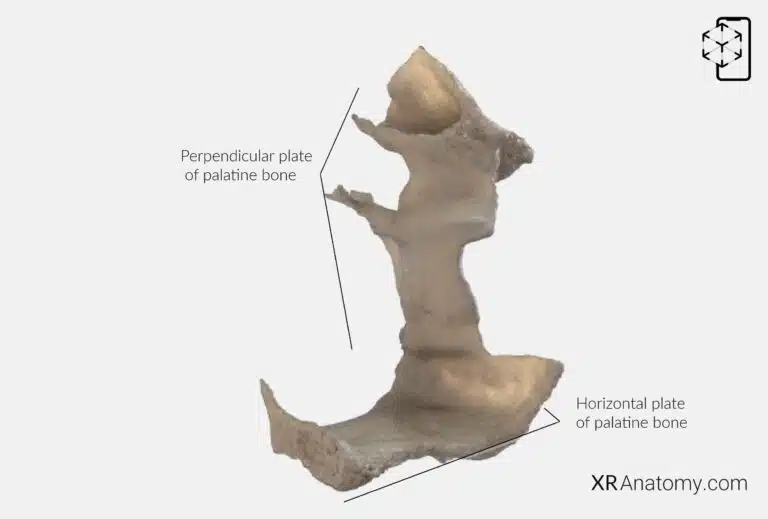
AR Figure 62 – Palatine bone, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
Structurally, the consists of a , a , and multiple processes. These components work together to contribute to the architecture of the skull.
PERPENDICULAR PLATE OF PALATINE BONE
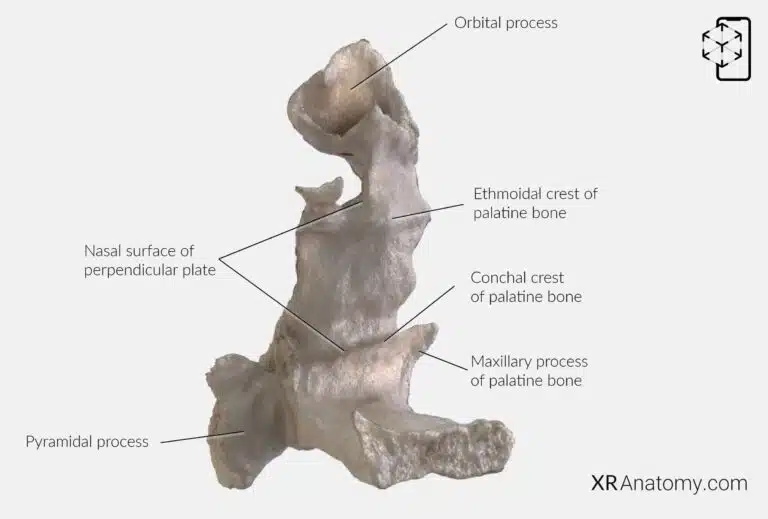
AR Figure 63 – Palatine bone: Perpendicular plate, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is the vertical part of the , extending upward from the horizontal plate. It plays a significant role in forming parts of the nasal cavity and the maxillary sinuses. The contributes to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity, providing structural support and articulation points for other bones.
At the junction where the lateral plate meets the perpendicular plate, the projects posterolaterally. This process fills the space between the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone and contains the . These canals transmit nerves and vessels to the soft palate, emerging through the lesser palatine foramina on the inferior surface.
The is a ridge that articulates with the inferior nasal concha, aiding in the formation of the nasal cavity's structure. The extends to articulate with the maxilla. Additionally, the serves as a ridge that articulates with the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid bone.
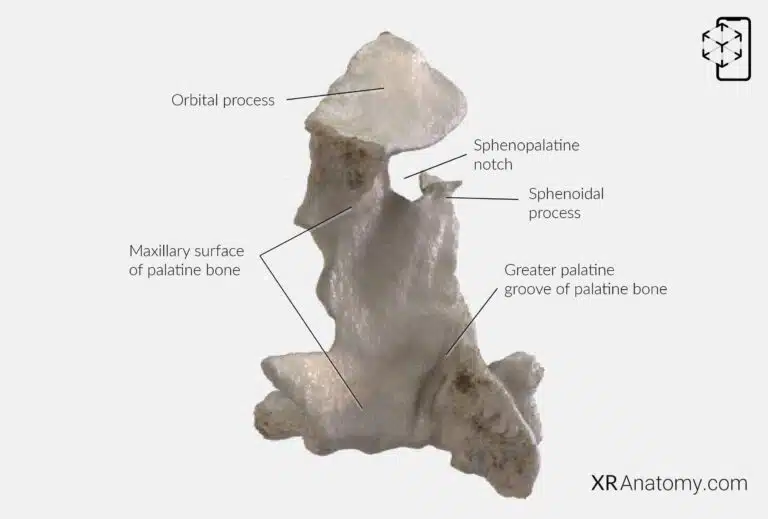
AR Figure 64 – Palatine bone: Perpendicular plate, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The , located where the orbital process meets the sphenoidal process, becomes the sphenopalatine foramen when articulated with the sphenoid bone. This opening allows communication between the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa, transmitting nerves and vessels. The of the palatine bone runs along the posterior part of the maxillary surface. When the articulates with the maxilla, this groove forms the greater palatine canal, which carries the greater palatine nerve and vessels to the hard palate.
The of the palatine bone is the lateral aspect of the perpendicular plate, contributing to the walls of the maxillary sinus. The , located at the superior end of the vertical plate, extends superolaterally to articulate with the maxilla, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones, forming part of the floor of the orbit.
The projects horizontally to articulate with the sphenoid bone, specifically its body and vaginal process, aiding in the formation of the nasal cavity's roof.
HORIZONTAL PLATE OF PALATINE BONE
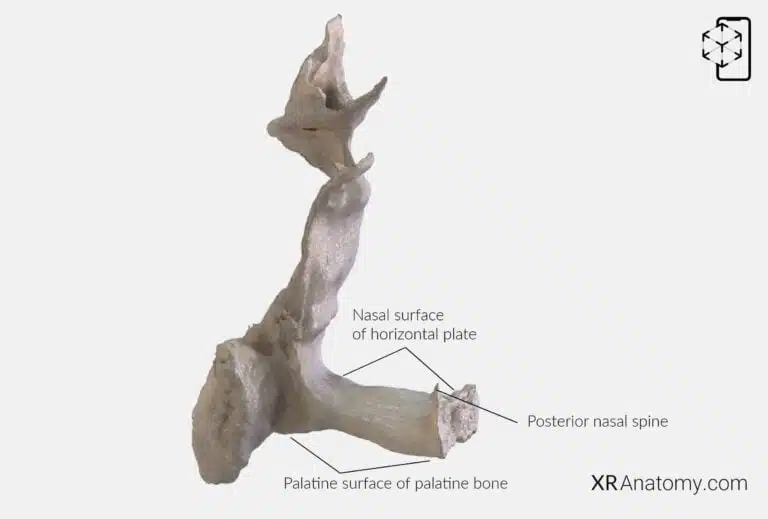
AR Figure 65 – Palatine bone: Horizontal plate, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is a flat, rectangular component that forms the posterior one-third of the hard palate, meeting its counterpart from the opposite side at the midline. The faces superiorly, contributing to the floor of the nasal cavity, while the inferior surface forms part of the roof of the oral cavity.
Located on the posterior region of the pyramidal process are the , small openings that transmit the lesser palatine nerves and vessels to the soft palate. The , a bony projection at the back of the horizontal plate, provides attachment for muscles, playing.
The of the palatine bone is part of the bone that forms the posterior one-third of the hard palate.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Sampson HW, Montgomery JL, Henryson GL. Atlas of the human skull. College Station: Texas A & M University Press; 2007.
4. Saylam C, Özer MA, Ozek C, Gurler T. Anatomical Variations of the Frontal and Supraorbital Transcranial Passages. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2003;14(1):10–2.
5. Hosemann W, Gross R, Goede U, Kuehnel T. Clinical anatomy of the nasal process of the frontal bone (spina nasalis interna). Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. 2001;125(1):60–5.
6. Steele DG, Bramblett CA. The anatomy and biology of human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press; 1988.
7. Tersigni-Tarrant MTA, Shirley NR. Human osteology. Vol. 4, Forensic Anthropology: An Introduction. 2012. 33–68 p.
8. Monjas-Cánovas I, García-Garrigós E, Arenas-Jiménez JJ, Abarca-Olivas J, Sánchez-Del Campo F, Gras-Albert JR. Radiological Anatomy of the Ethmoidal Arteries: CT Cadaver Study. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition). 2011;62(5):367–74.
9. Pereira G, Lopes P, Santos A, Krebs. Morphometric aspects of the jugular foramen in dry skulls of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. Vol. 27, J. Morphol. Sci. 2010.
12. Kunc V, Fabik J, Kubickova B, Kachlik D. Vermian fossa or median occipital fossa revisited: Prevalence and clinical anatomy. Annals of Anatomy. 2020 May 1;229:151458.
14. Standring S. The skull. In: Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2021st ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. p. 558–73.
15. Rhoton AL. Chapter 1 Overview of Temporal Bone. Neurosurgery. 2007;
17. Tóth M, Moser G, Patonay L, Oláh I. Development of the anterior chordal canal. Annals of Anatomy. 2006;
18. Carpenter G, Knipe H. Tympanic part of temporal bone. Radiopaedia.org. 2014 Mar 23;
19. Eckerdal O. The petrotympanic fissure: A link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio – Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1991;9(1):15–22.
21. Singh R, Kishore Gupta N, Kumar R. Morphometry and Morphology of Foramen Petrosum in Indian Population. Basic Sciences of Medicine. 2020;2020(1):8–9.
23. Piagkou M, Xanthos T, Anagnostopoulou S, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Piagkos G, et al. Anatomical variation and morphology in the position of the palatine foramina in adult human skulls from Greece. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 2012 Oct 1;40(7):e206–10.