TEMPORAL BONE AR ATLAS
TEMPORAL BONE AR ATLAS
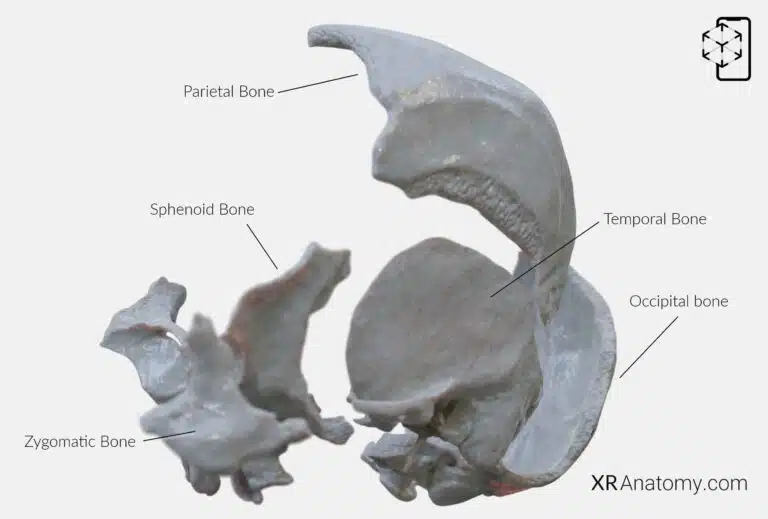
AR Figure 8 – Temporal Bone: Disarticulated view, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
is a complex structure located on the sides and base of the skull, adjacent to the ears. It supports the temples and houses structures vital for hearing and balance. Its intricate anatomy plays a crucial role in protecting the delicate organs of the inner ear and forming articulations with surrounding bones.
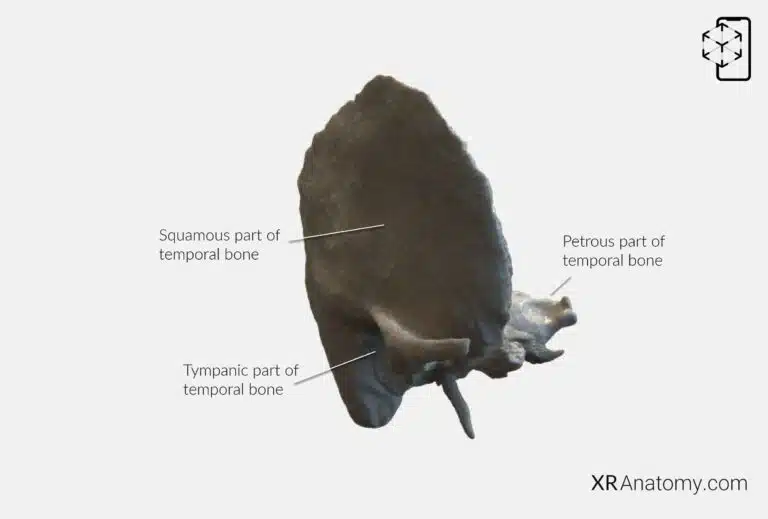
AR Figure 9 – Temporal Bone: Parts of Temporal bone, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
is irregular in shape and consists of multiple parts: the , the , the petromastoid part (which includes the and ). Each part contributes to the bone's overall function and forms important relationships with adjacent structures.
PETROUS PART OF THE TEMPORAL BONE
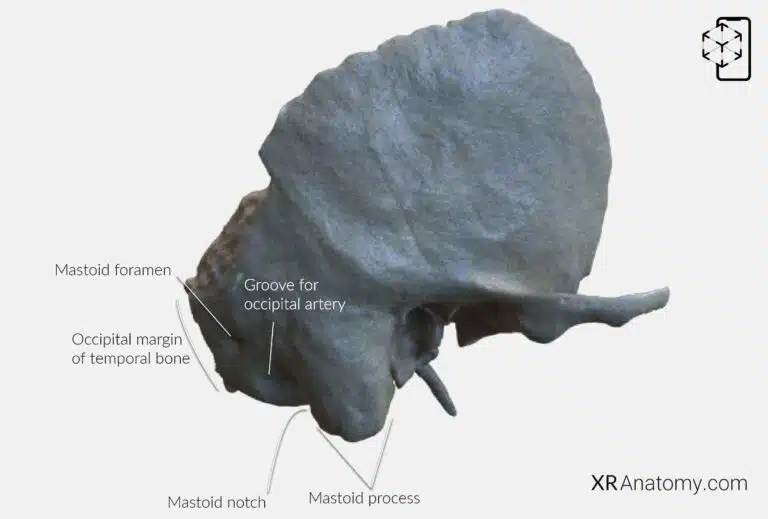
AR Figure 10 – Temporal Bone: Petrous part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
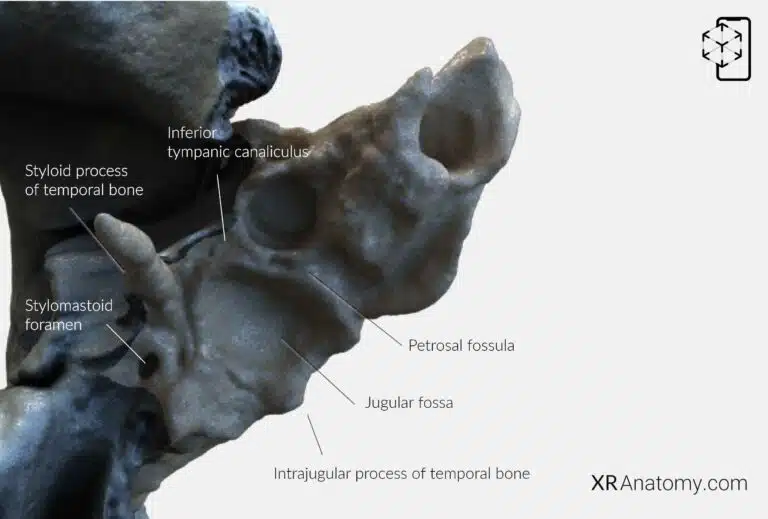
The is a pyramid-shaped region with an apex, three surfaces, and three borders. It is oriented with its base laterally and is one of the densest bones in the body, housing the structures of the inner ear. The posterior border, known as the , articulates with the occipital bone. The , a prominent bony projection on the outer surface of the posterior part, serves as an attachment point for neck muscles. Inferior to the mastoid process is the , a groove that provides attachment for the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. Posterior to the mastoid notch lies the , accommodating this vessel as it ascends the skull. The , located posterior to the mastoid process, allows passage for emissary veins connecting the sigmoid sinus to the posterior scalp.
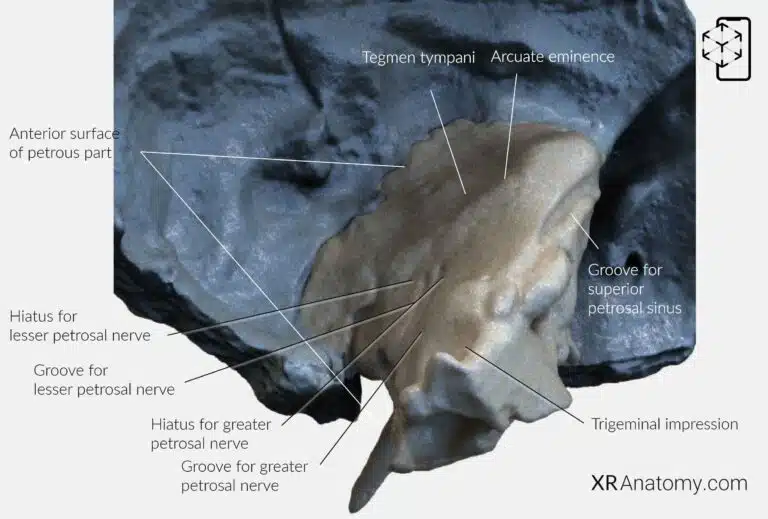
At the , it articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone. The is a significant feature that begins on the inferior surface of the petrous part and opens at the apex. It transmits the internal carotid artery into the cranial cavity, supplying blood to the brain. The is situated on the inferior surface medial to the jugular fossa, while the is located at the petrous apex.
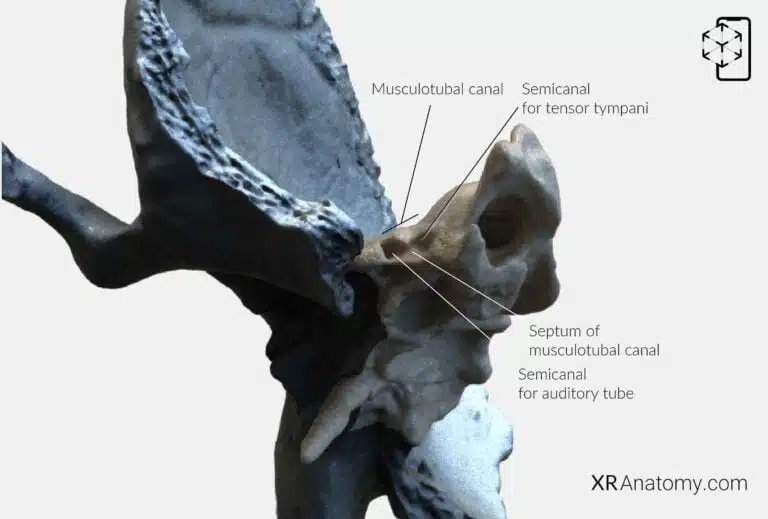
AR Figure 12 – Temporal Bone: Petrous part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is another important feature of the petrous part. It is divided into two semicanals by a thin bony septum. The . The lower (Eustachian tube), which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and helps equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane. The musculotubal canal opens into the tympanic cavity and is situated anterior to the external opening of the carotid canal.
TYMPANIC PART OF THE TEMPORAL BONE
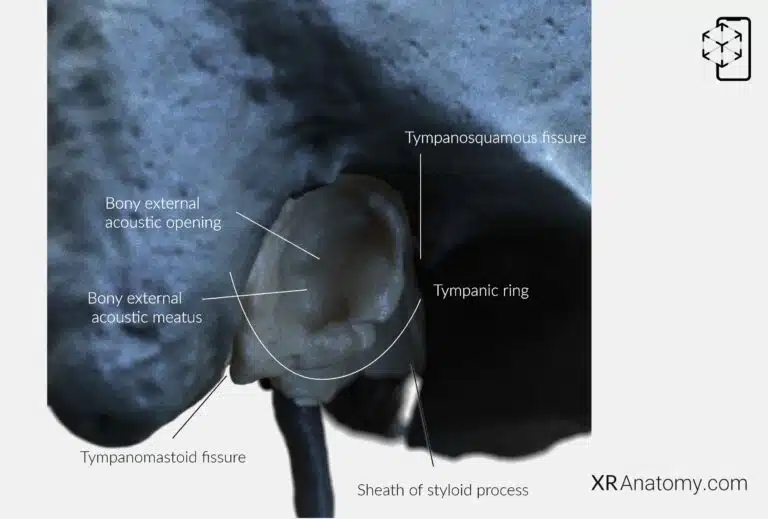
AR Figure 16 – Temporal Bone: Tympanic part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is a curved plate situated anterior to the mastoid process. It forms the anterior wall, floor, and part of the posterior wall of the (ear canal). Initially present as the tympanic ring in infants, it fuses with the squamous part shortly after birth and expands to form the tympanic part. The marks the entrance to the external acoustic meatus, an approximately 1 cm long oval canal formed by the tympanic and squamous parts. Inside the tympanic ring is the tympanic sulcus, a groove where the circumference of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) attaches. The tympanic notch is a deficiency in the superior part of the tympanic ring, allowing passage of the chorda tympani nerve. The greater and lesser tympanic spines are small bony projections on the anterior and posterior parts of the ring, respectively. The extends posteriorly from the carotid canal, encircling the styloid process—a slender projection that serves as an attachment for muscles and ligaments associated with the tongue and pharynx.
SQUAMOUS PART OF THE TEMPORAL BONE
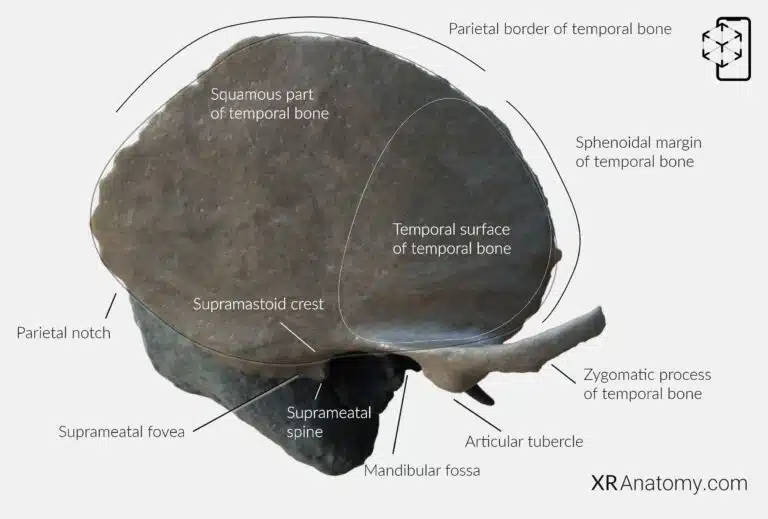
AR Figure 17 – Temporal Bone: Squamous Part, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The is the thin, flat, anterosuperior portion that forms part of the temporal fossa. It has two surfaces: the outer temporal surface and the inner cerebral surface. The superior border, or , articulates with the parietal bone, forming part of the squamous suture. Posteriorly, the is formed by the angle between the parietal border and the superior border of the mastoid part. The , located anteroinferiorly, articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
The is smooth and convex, providing attachment for the temporalis muscle. Extending from the lower part of the squamous portion is the , an arched projection that forms part of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone) by connecting with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone. The continues posteriorly from the root of the zygomatic process. The is a small depression between the posterior wall of the ** external acoustic meatus and the ** posterior root of the zygomatic process. The , located near the external acoustic meatus, is another important anatomical landmark.
The is a concave depression on the inferior surface of the squamous part, forming part of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) by articulating with the condyle of the mandible. The is the anterior portion that contacts the mandible, while the is a rounded eminence anterior to the fossa that prevents excessive backward movement of the mandible during mouth opening.
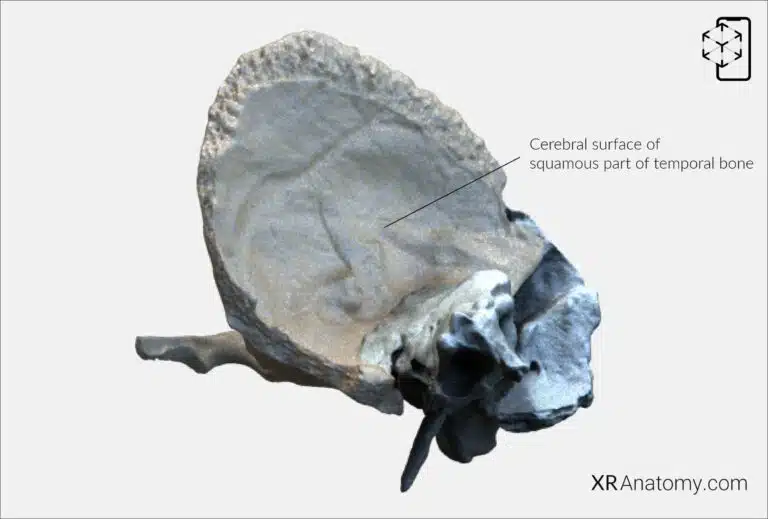
AR Figure 18 – Temporal Bone: Squamous Part, Cerebral Surface, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
The faces inward toward the brain and is concave to accommodate the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. It features grooves for the middle meningeal vessels and impressions corresponding to the gyri of the brain.
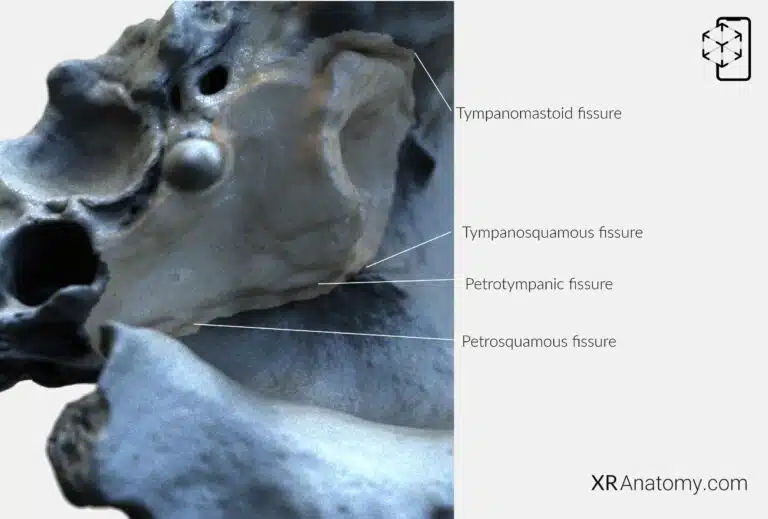
AR Figure 15 – Temporal Bone: Fissures, Augmented Illustration by B. Leahu – MD. This image is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0).
Several fissures in the temporal bone separate its different parts and allow the passage of nerves and vessels. The , located between the mandibular fossa and the tympanic part posterior to the petrosquamous fissure. The , situated anterior to the petrotympanic fissure, separates the petrous part from the squamous part. The continues the petrosquamous and petrotympanic fissures laterally, between the tympanic part and the squamous part. The , formed by the posterior edge of the tympanic part and the mastoid part.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Sampson HW, Montgomery JL, Henryson GL. Atlas of the human skull. College Station: Texas A & M University Press; 2007.
4. Saylam C, Özer MA, Ozek C, Gurler T. Anatomical Variations of the Frontal and Supraorbital Transcranial Passages. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 2003;14(1):10–2.
5. Hosemann W, Gross R, Goede U, Kuehnel T. Clinical anatomy of the nasal process of the frontal bone (spina nasalis interna). Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. 2001;125(1):60–5.
6. Steele DG, Bramblett CA. The anatomy and biology of human skeleton. Texas A&M University Press; 1988.
7. Tersigni-Tarrant MTA, Shirley NR. Human osteology. Vol. 4, Forensic Anthropology: An Introduction. 2012. 33–68 p.
8. Monjas-Cánovas I, García-Garrigós E, Arenas-Jiménez JJ, Abarca-Olivas J, Sánchez-Del Campo F, Gras-Albert JR. Radiological Anatomy of the Ethmoidal Arteries: CT Cadaver Study. Acta Otorrinolaringologica (English Edition). 2011;62(5):367–74.
9. Pereira G, Lopes P, Santos A, Krebs. Morphometric aspects of the jugular foramen in dry skulls of adult individuals in Southern Brazil. Vol. 27, J. Morphol. Sci. 2010.
12. Kunc V, Fabik J, Kubickova B, Kachlik D. Vermian fossa or median occipital fossa revisited: Prevalence and clinical anatomy. Annals of Anatomy. 2020 May 1;229:151458.
14. Standring S. The skull. In: Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 2021st ed. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. p. 558–73.
15. Rhoton AL. Chapter 1 Overview of Temporal Bone. Neurosurgery. 2007;
17. Tóth M, Moser G, Patonay L, Oláh I. Development of the anterior chordal canal. Annals of Anatomy. 2006;
18. Carpenter G, Knipe H. Tympanic part of temporal bone. Radiopaedia.org. 2014 Mar 23;
19. Eckerdal O. The petrotympanic fissure: A link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio – Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1991;9(1):15–22.
21. Singh R, Kishore Gupta N, Kumar R. Morphometry and Morphology of Foramen Petrosum in Indian Population. Basic Sciences of Medicine. 2020;2020(1):8–9.
23. Piagkou M, Xanthos T, Anagnostopoulou S, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Piagkos G, et al. Anatomical variation and morphology in the position of the palatine foramina in adult human skulls from Greece. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 2012 Oct 1;40(7):e206–10.