NAVICULAR BONE ANATOMY
WHY THIS MATTERS
The navicular bone is a keystone of your foot's medial longitudinal arch. It connects the talus to the three cuneiform bones and anchors the tibialis posterior tendon, the main muscle supporting your arch. Understanding its surfaces, tuberosity, and clinical significance helps you see how this small bone keeps your foot stable during movement.
GENERAL STRUCTURE
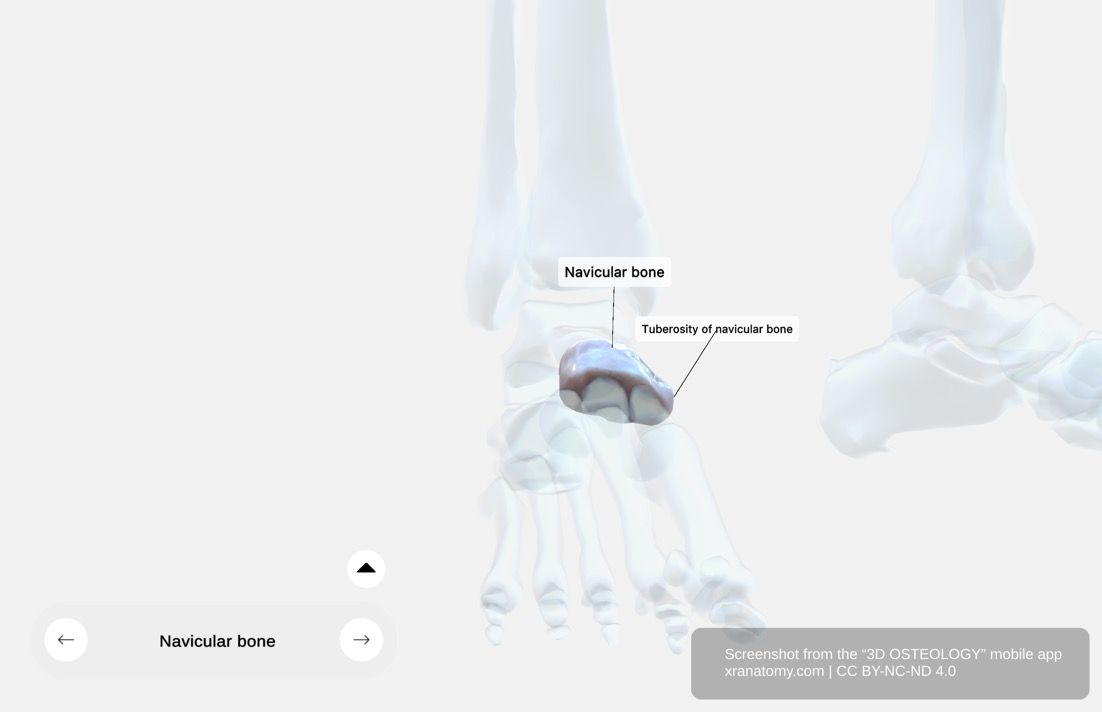
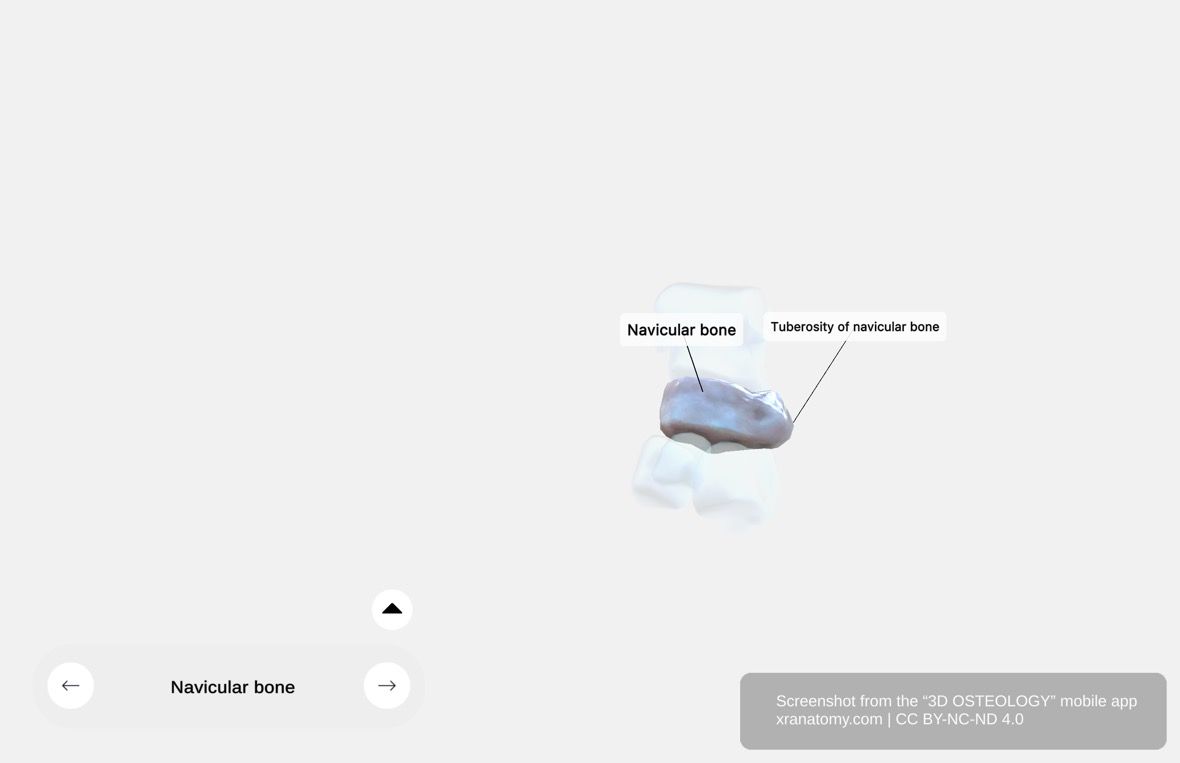
The navicular bone sits on the medial side of the tarsus, positioned between the talus behind and the three cuneiform bones in front. It connects these structures and maintains the integrity of your foot's arch. The name "navicular" derives from its boat-shaped appearance. This section covers its location and position, articular surfaces, dorsal surface, and plantar surface.
Location and Position
You will find the navicular on the medial side of your tarsus. It sits between the talus posteriorly and the three cuneiform bones anteriorly. It forms a key part of the medial longitudinal arch of your foot.
Articular Surfaces
The posterior surface is oval and concave, and it articulates with the head of the talus. The anterior surface is convex from side to side and divided into three facets that articulate with the medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bones. The lateral surface may present a small facet that occasionally articulates with the cuboid bone.
Dorsal Surface
The dorsal surface is convex and rough. It provides attachment for ligaments.
Plantar Surface
The plantar surface is irregular and rough. It provides attachment for portions of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament.
TUBEROSITY OF THE NAVICULAR
The tuberosity of the navicular bone is a prominent bony projection on the medial surface. It serves as an important attachment point for the tibialis posterior tendon, one of the main muscles supporting the medial longitudinal arch of your foot. This section covers the features of the tuberosity, tibialis posterior insertion, groove feature, and clinical significance.
Features of the Tuberosity
The tuberosity forms a rounded prominence on the medial surface of the navicular. You can easily palpate it through your skin, making it an important landmark in clinical examination.
Tibialis Posterior Insertion
The lower part of the tuberosity provides insertion for a large portion of the tendon of Tibialis posterior. This muscle supports your medial longitudinal arch and plays an important role in plantar flexion and inversion of your foot.
Groove Feature
A groove runs between the tuberosity and the plantar process. This groove lodges part of the tendon of Tibialis posterior and provides mechanical advantage for tendon function.
Clinical Significance
An accessory navicular bone may be present as an additional ossification center. It can cause pain with footwear pressure on your foot. Tibialis posterior dysfunction may lead to adult-acquired flatfoot deformity, and tenderness over the tuberosity is a clinical sign.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What bones does the navicular articulate with on its posterior and anterior surfaces?
Reveal Answer
The posterior surface articulates with the head of the talus. The anterior surface articulates with the medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bones.
2. Which tendon inserts on the tuberosity of the navicular, and what does it support?
Reveal Answer
The tibialis posterior tendon inserts on the tuberosity. It supports the medial longitudinal arch of your foot and plays a role in plantar flexion and inversion.
3. What is an accessory navicular bone, and what problem can it cause?
Reveal Answer
An accessory navicular bone is an additional ossification center that may be present. It can cause pain with footwear pressure on your foot.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, explore the Cuneiform Bones. You will study the three wedge-shaped tarsal bones (medial, intermediate, and lateral) that sit between the navicular and the first three metatarsals, forming the transverse arch of your foot.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.