PALATINE BONE ANATOMY
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →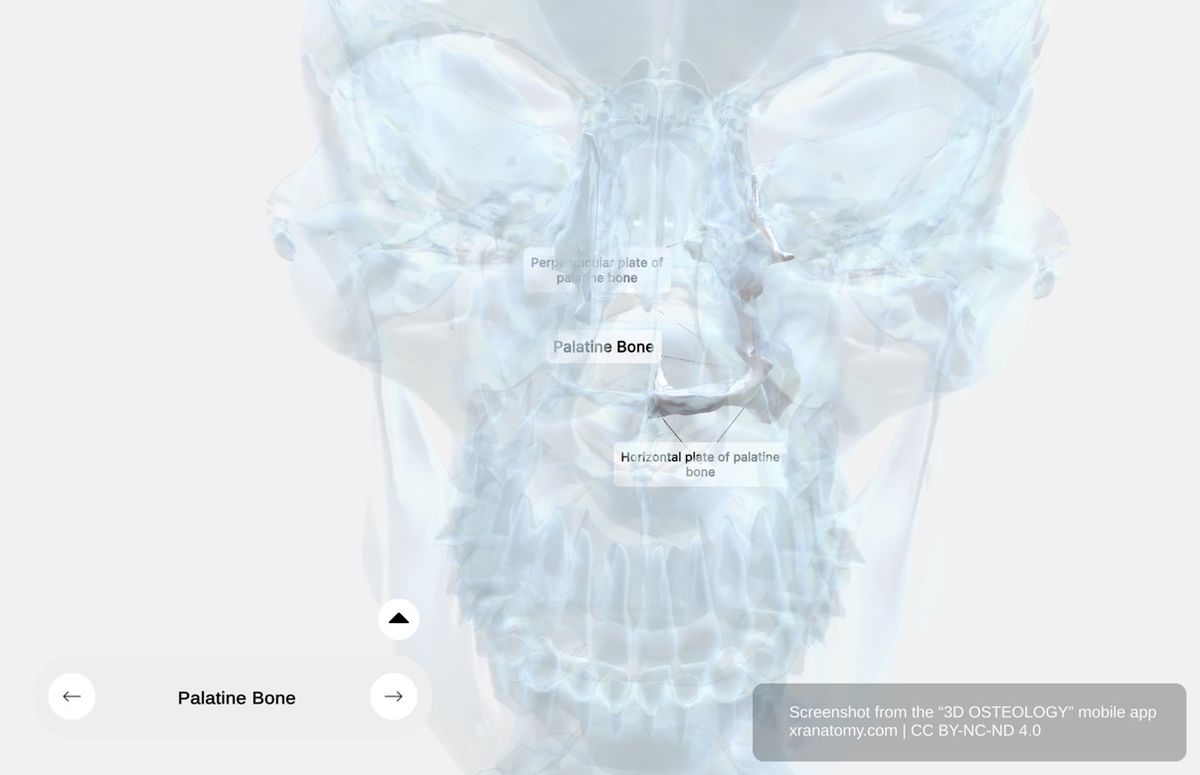
Palatine Bone - X-Ray View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The palatine bone is a small, L-shaped bone tucked deep inside your skull. Understanding its two plates, multiple processes, and foramina helps you see how it forms the posterior hard palate, contributes to your nasal cavity walls, and even reaches the floor of your orbit.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The palatine bone is an intricate paired bone situated posteriorly in your nasal cavity. It contributes to the hard palate formation and participates in constructing your nasal cavity walls, the orbital floor, and the posterior portion of the hard palate.
Articulations
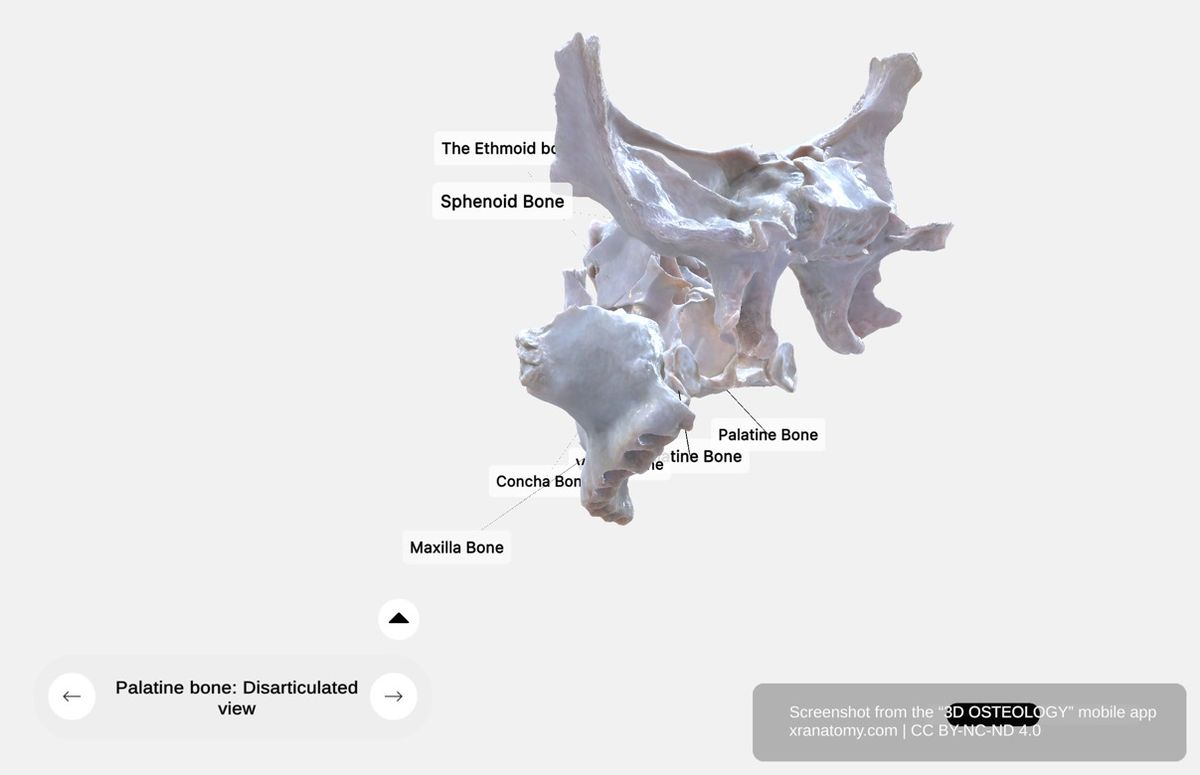
Palatine Bone - Disarticulated View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The palatine bone articulates with six bones: the sphenoid bone, the ethmoid bone, the maxilla, the inferior nasal concha, the vomer, and the contralateral palatine bone.
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS
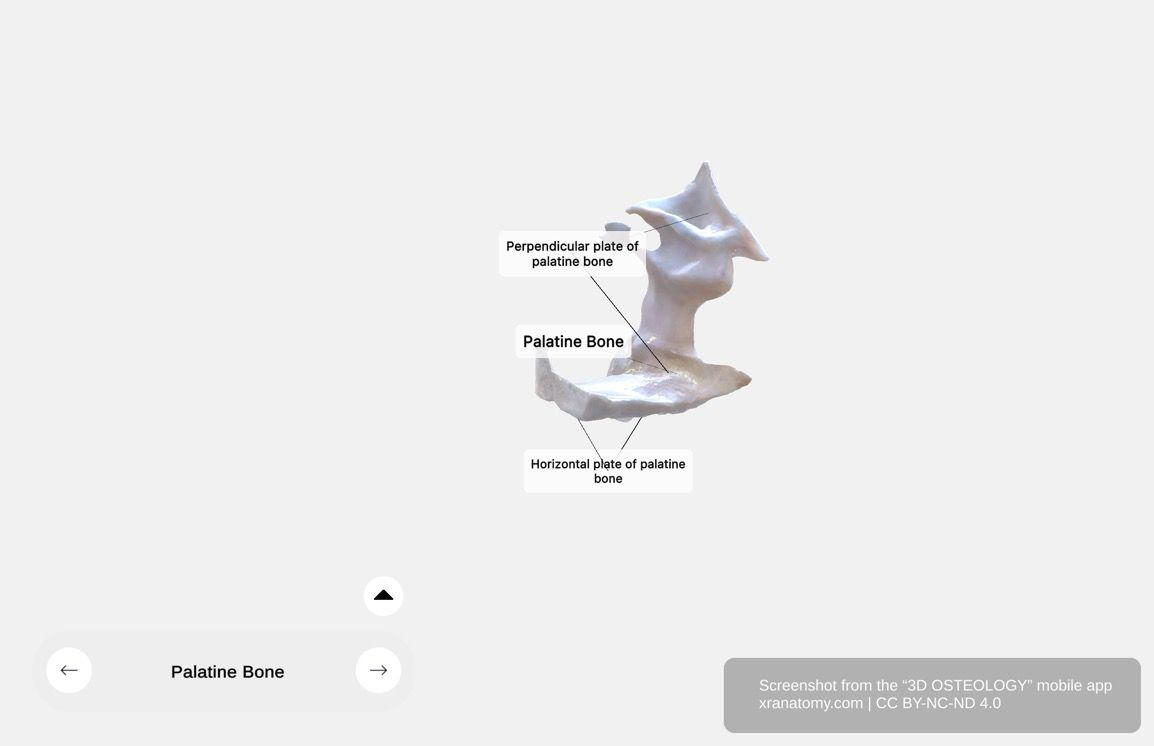
Palatine Bone - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The palatine bone is comprised of three main parts: the horizontal plate, the perpendicular (vertical) plate, and multiple processes.
PERPENDICULAR PLATE
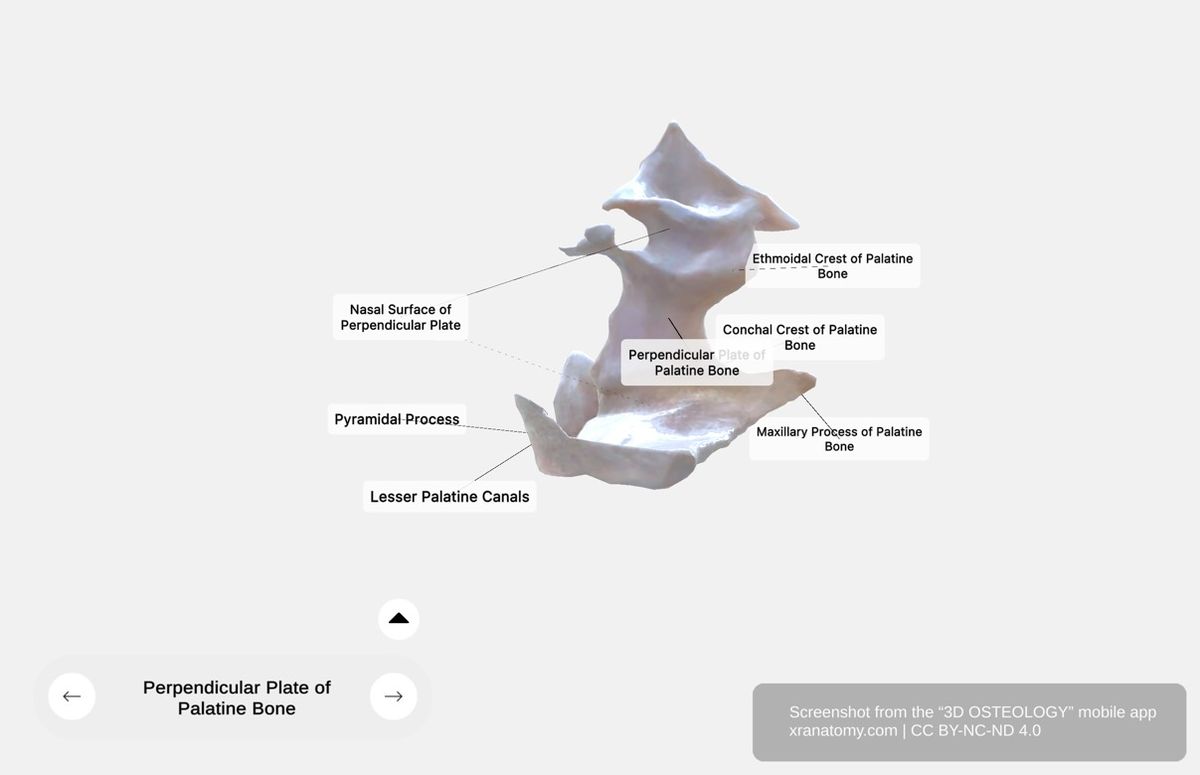
Perpendicular Plate of Palatine Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The perpendicular plate is the vertical portion that ascends from the horizontal plate. It forms part of your nasal cavity lateral wall, contributes to the maxillary sinus walls, and provides structural support. This section covers the plate's surfaces, crests, and the greater palatine groove.
Surfaces
The perpendicular plate has two surfaces. The nasal surface is the medial aspect that contributes to your lateral nasal cavity wall and provides articulation points for adjacent bones. The maxillary surface is the lateral aspect that forms part of your maxillary sinus walls.
Crests
Two horizontal ridges cross the perpendicular plate. The conchal crest articulates with the inferior nasal concha and assists in your nasal cavity structure formation. The ethmoidal crest articulates with the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid bone.
Greater Palatine Groove
The greater palatine groove is a vertical groove located on the posterior maxillary surface. When articulated with the maxilla, it forms the greater palatine canal. This canal transmits the greater palatine nerve and greater palatine vessels to your hard palate.
PROCESSES OF PALATINE BONE
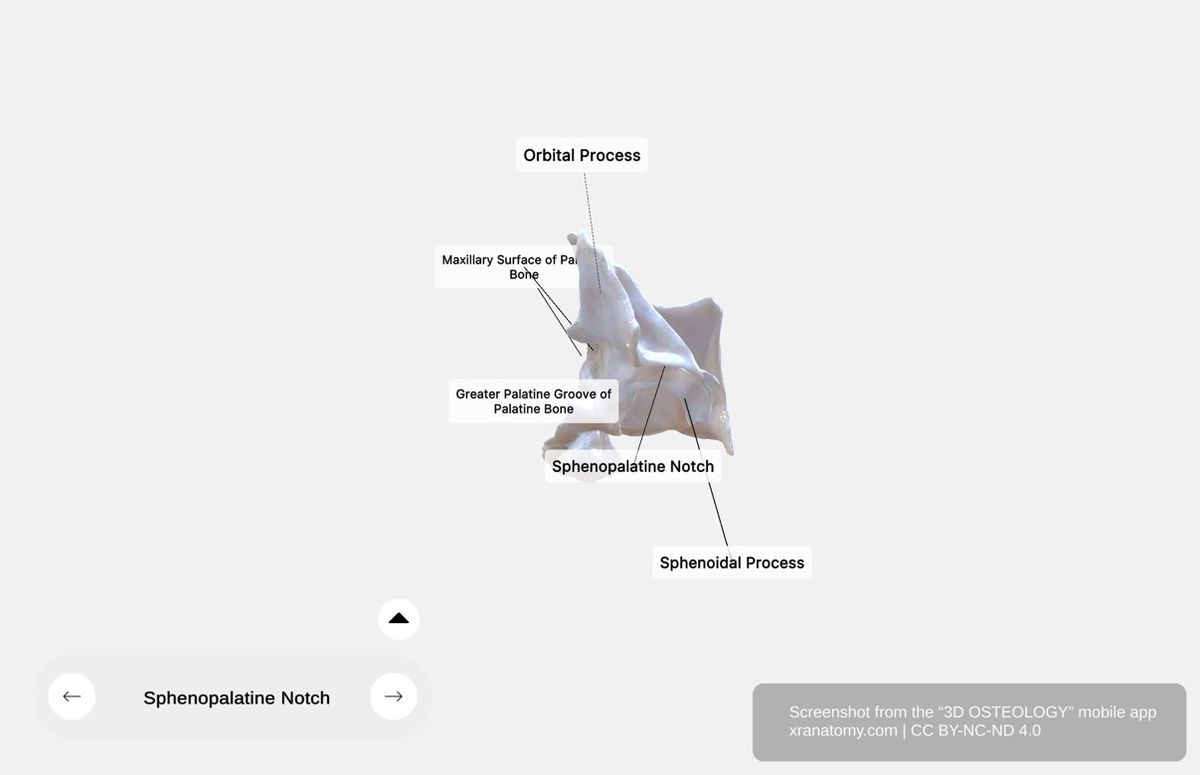
Processes of Palatine Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The palatine bone features three processes: the pyramidal process, the orbital process, and the sphenoidal process.
Pyramidal Process
The pyramidal process is a posterolateral projection located at the junction of the horizontal and perpendicular plates. It occupies the gap between the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid. It contains the lesser palatine canals, and the lesser palatine foramina open on its inferior surface.
Orbital Process
The orbital process is a superior projection located at the upper end of the perpendicular plate. It extends superolaterally and articulates with the maxilla, the sphenoid bone, and the ethmoid bone. It forms a portion of your orbital floor.
Sphenoidal Process
The sphenoidal process is a horizontal projection that articulates with the sphenoid body and the vaginal process of the sphenoid. It contributes to your nasal cavity roof formation.
Maxillary Process
The maxillary process is a lateral extension that articulates with the maxilla.
SPHENOPALATINE NOTCH AND FORAMEN
This section covers the sphenopalatine notch and the sphenopalatine foramen, which together connect your nasal cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa.
Sphenopalatine Notch
The sphenopalatine notch is located between the orbital and sphenoidal processes. It is converted to the sphenopalatine foramen upon articulation with the sphenoid.
Sphenopalatine Foramen
The sphenopalatine foramen is an opening formed by articulation with the sphenoid bone. It provides communication between your nasal cavity and pterygopalatine fossa and transmits neurovascular structures.
HORIZONTAL PLATE
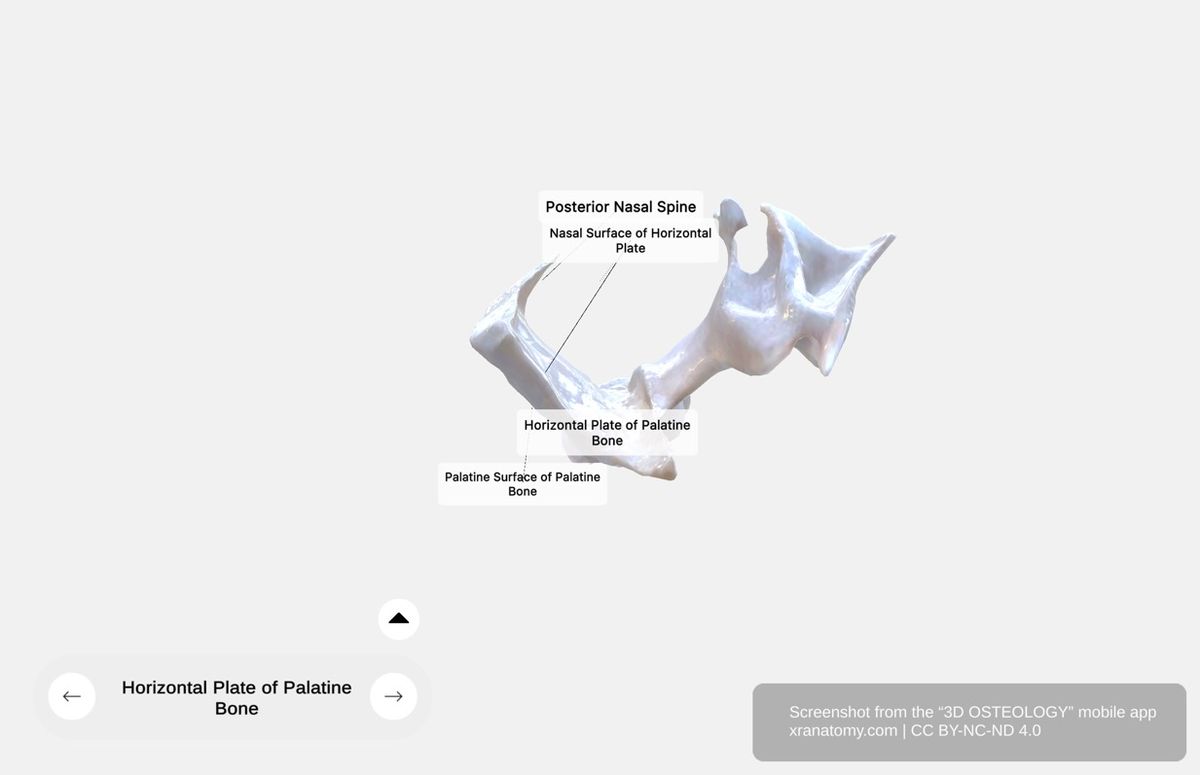
Horizontal Plate of Palatine Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The horizontal plate is a flat rectangular component that forms the posterior quarter of your hard palate. It meets the opposite palatine bone at the midline. This section covers the plate's surfaces, the lesser palatine foramina, and the posterior nasal spine.
Surfaces
The horizontal plate has two surfaces. The nasal surface is the superior aspect that contributes to your nasal cavity floor. The palatine surface is the inferior aspect that forms part of your oral cavity roof and constitutes the posterior quarter of your hard palate.
Lesser Palatine Foramina
The lesser palatine foramina are small openings located on the posterior pyramidal process region. They transmit the lesser palatine nerves and lesser palatine vessels to your soft palate.
Posterior Nasal Spine
The posterior nasal spine is a midline bony projection located at the posterior border of the horizontal plate. It provides a muscular attachment site.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What are the three main parts of the palatine bone?
Reveal Answer
The horizontal plate, the perpendicular (vertical) plate, and multiple processes (pyramidal, orbital, sphenoidal, and maxillary).
2. Name the two crests on the perpendicular plate and what each articulates with.
Reveal Answer
The conchal crest articulates with the inferior nasal concha. The ethmoidal crest articulates with the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid bone.
3. How does the sphenopalatine notch become the sphenopalatine foramen?
Reveal Answer
The sphenopalatine notch, located between the orbital and sphenoidal processes, is converted to the sphenopalatine foramen upon articulation with the sphenoid bone. This foramen connects the nasal cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the palatine bone and its plates, processes, and foramina, the next page focuses on the Inferior Nasal Concha. You will explore this delicate scroll-like bone that projects into the nasal cavity and plays a key role in directing airflow.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.