TALUS ANATOMY
Talus - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The talus connects your foot to your leg and forms a crucial part of your ankle joint. Understanding its head, neck, body, and trochlea helps you see how your body weight transfers from the tibia and fibula down through the calcaneus and into your foot.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
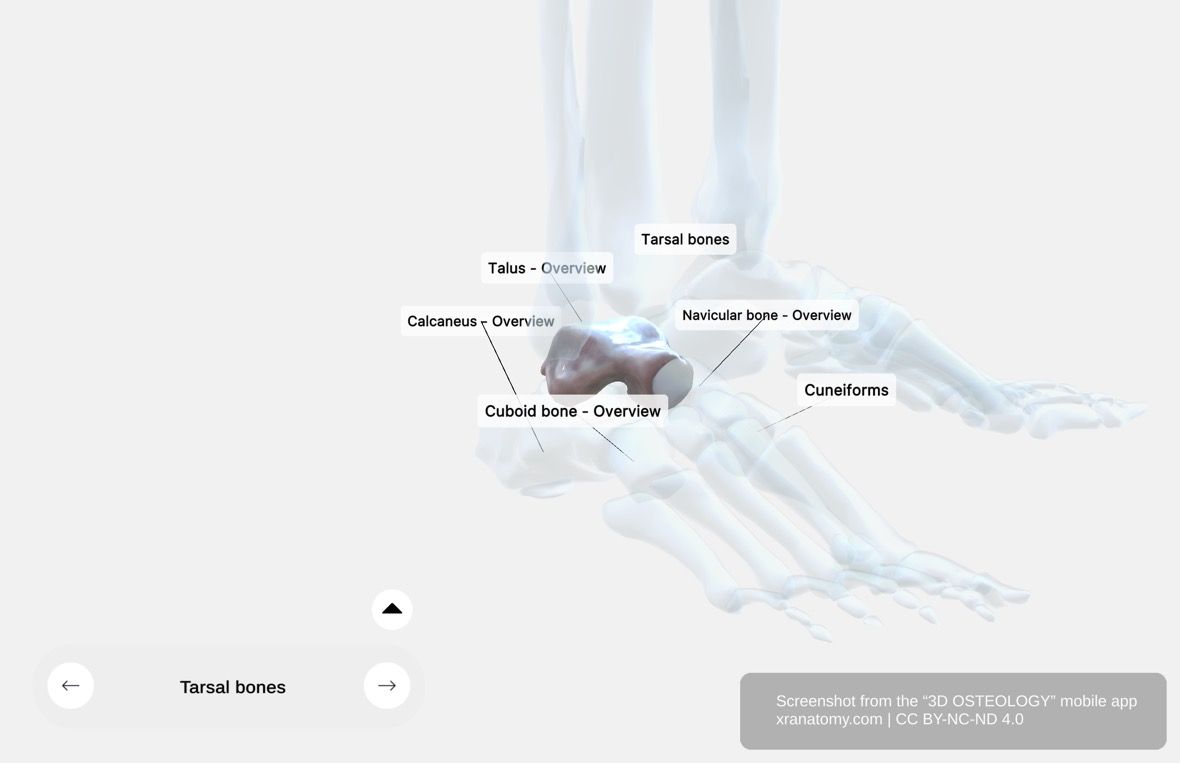
GENERAL STRUCTURE
The talus is the second-largest tarsal bone, supporting your tibia and resting on the calcaneus. It articulates with the navicular bone in front and the malleoli on either side, forming a crucial part of your ankle joint. Structurally, the talus divides into three main parts: the head, neck, and body. The trochlea is a prominent articular feature located on the superior surface of the body.
Head
The head of the talus points forwards and medialwards. It articulates with the navicular bone and contains multiple articular surfaces on its plantar surface.
Neck
The neck is the constricted part connecting the head with the body. Its dorsal and medial surfaces are rough and perforated by foramina for vessels. The plantar surface contains the sulcus tali.
Body
The body is the cuboidal posterior part of the bone. It features the trochlea on its dorsal surface and articulates with your tibia and fibula.
Trochlea
The trochlea is an articular eminence on the dorsal surface of the body. It is broader in front than behind and articulates with the tibia.
HEAD OF TALUS

Head of the Talus, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The head of the talus points forwards and medialwards, with its anterior surface articulating with the concavity of the navicular bone. It contributes significantly to your foot's tarsal structure. The plantar surface of the head contains three articular areas that enhance its role in joint articulation and foot stability: the navicular articular surface, the facet for the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament, and the anterior facet for the calcaneus. The neck connects the head to the body, and the sulcus tali runs along its plantar surface.
Navicular Articular Surface
The navicular articular surface sits on the anterior surface of the talus head. It is oval and convex in shape and articulates with the navicular bone, aligning with the concave surface of the navicular.
Facet for the Plantar Calcaneonavicular Ligament
This facet sits on the medial aspect of the talus. It supports the inferior calcaneonavicular ligament and helps stabilize your foot's arch.
Anterior Facet for the Calcaneus
The anterior calcaneal facet sits on the plantar surface of the talus. It is quadrilateral or irregularly oval in shape and articulates with the anterior part of the calcaneus.
Neck of Talus
The neck is the constricted part connecting the head with the body. Its dorsal and medial surfaces are rough and perforated by foramina for vessels. The dorsal surface provides attachment to the talonavicular ligament.
Sulcus Tali
The sulcus tali is a deep groove on the plantar surface of the talus. It is wide in front, narrow behind, and directed forwards and lateralwards. Together with the sulcus calcanei, it forms the sinus tarsi, which is filled with the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament.
BODY OF TALUS
Body of the Talus, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
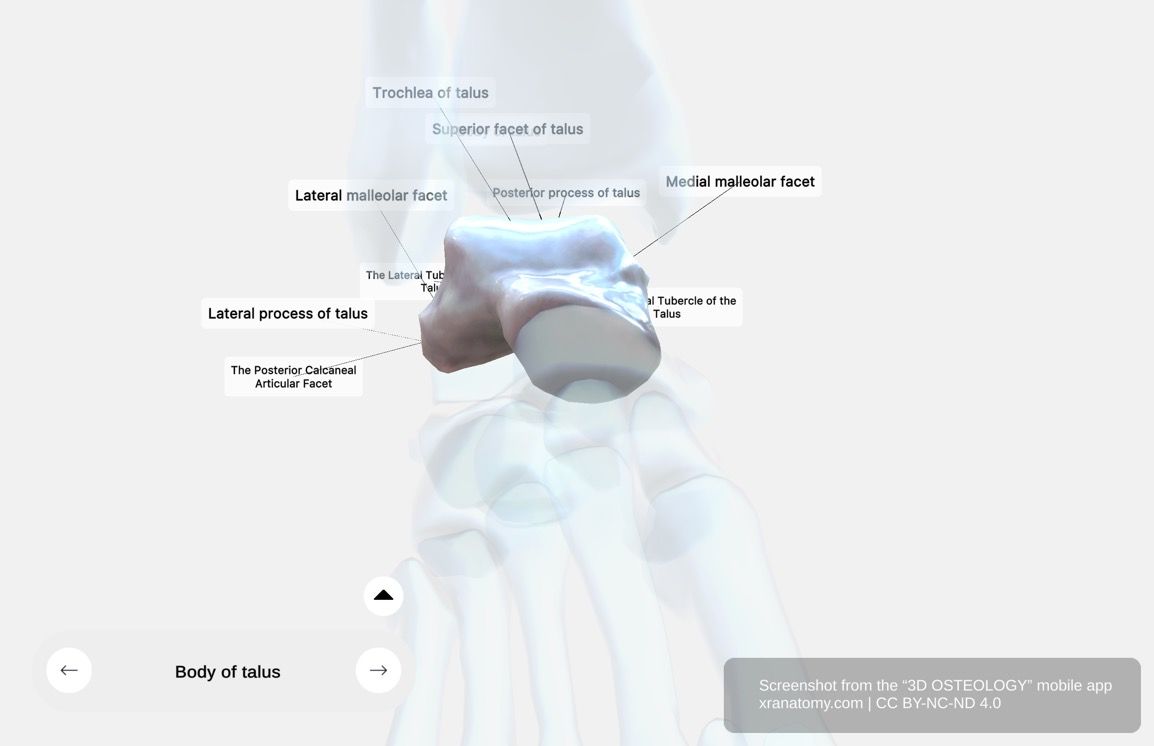
The body of the talus is the cuboidal posterior part of the bone. Its dorsal surface features the trochlea, which articulates with your tibia and fibula. The lateral surface provides an attachment site for the anterior talofibular ligament. The posterior surface is traversed by a sulcus that accommodates the tendon of your flexor hallucis longus. Key features include the superior facet, the lateral and medial malleolar facets, the lateral process, the posterior process with its two tubercles, the sulcus for the flexor hallucis longus, and the posterior calcaneal articular facet.
Trochlea
The trochlea is an articular eminence on the dorsal surface of the body. It articulates with your tibia and is broader in front than behind. Its surface is convex from front to back and slightly concave from side to side.
Superior Facet
The superior facet sits on the dorsal surface of the trochlea. It articulates with your tibia and forms the upper surface of your ankle joint.
Lateral Malleolar Facet
The lateral malleolar facet sits on the trochlea of the talus. It articulates with the lateral malleolus of your fibula and contributes to lateral stability of your ankle joint.
Lateral Process
The lateral process is a rough, triangular eminence on the lateral side of the talus. It serves as an attachment point for the lateral talocalcaneal ligament and stabilizes your subtalar joint.
Medial Malleolar Facet
The medial malleolar facet sits on the medial aspect of the trochlea. It articulates with the medial malleolus of your tibia and contributes to medial stability of your ankle joint.
Posterior Process
The posterior process extends backward from the talus. A sulcus traverses it for the tendon of your flexor hallucis longus. It contains two tubercles. The lateral tubercle is more prominent and provides attachment for the posterior talofibular ligament; when detached, it is referred to as the os trigonum. The medial tubercle provides attachment for the medial talocalcaneal ligament.
Sulcus for the Tendon of Flexor Hallucis Longus
This sulcus sits on the posterior process. It allows passage of the tendon towards your big toe.
Posterior Calcaneal Articular Facet
The posterior calcaneal articular facet sits on the plantar surface of the talus body. It is a large, oval-shaped facet that articulates with the calcaneus. It forms part of the talocalcaneal joint and supports transfer of your body weight to your heel.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What are the three main parts of the talus?
Reveal Answer
The head, neck, and body.
2. What structure does the sulcus tali help form, and what fills it?
Reveal Answer
Together with the sulcus calcanei, the sulcus tali forms the sinus tarsi, which is filled with the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament.
3. What are the two tubercles of the posterior process, and what attaches to each?
Reveal Answer
The lateral tubercle (more prominent, attachment for the posterior talofibular ligament; when detached called the os trigonum) and the medial tubercle (attachment for the medial talocalcaneal ligament).
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, explore the Calcaneus, the largest tarsal bone that forms your heel. You will study the calcaneal tuberosity, sustentaculum tali, talar articular surfaces, and tarsal sinus.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.