ETHMOID BONE ANATOMY
Ethmoid Bone - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The ethmoid bone sits between your orbital cavities and forms part of your anterior cranial fossa, nasal cavity, and medial orbital walls. Understanding its cribriform plate, perpendicular plate, and ethmoidal labyrinths helps you see how one delicate bone supports your sense of smell, separates your nasal passages, and protects your orbital contents.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The ethmoid is an unpaired cuboid-shaped bone located between your orbital cavities. It forms part of your anterior cranial fossa, contributes to your nasal cavity structure, and participates in the medial orbital wall.
Articulations
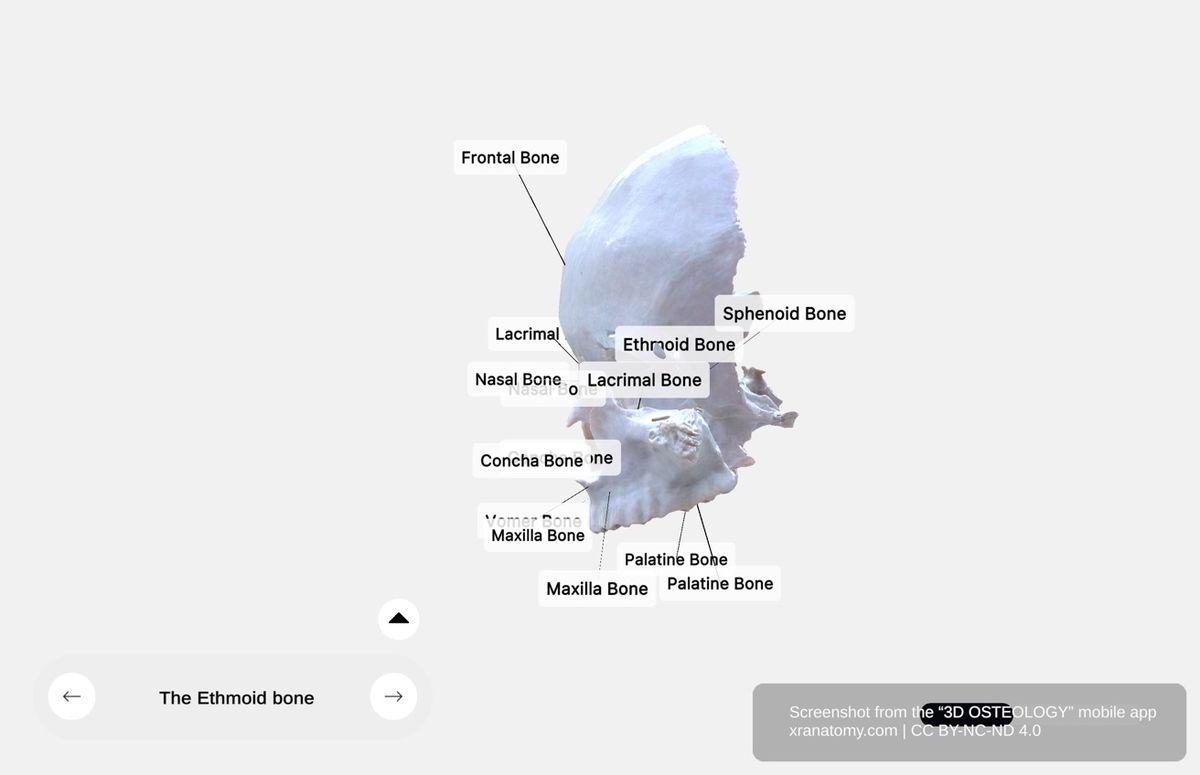
Ethmoid Bone - Articulations, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The ethmoid bone articulates with eight bones: the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, vomer, inferior nasal conchae, palatine bones, lacrimal bones, nasal bones, and maxillae.
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS
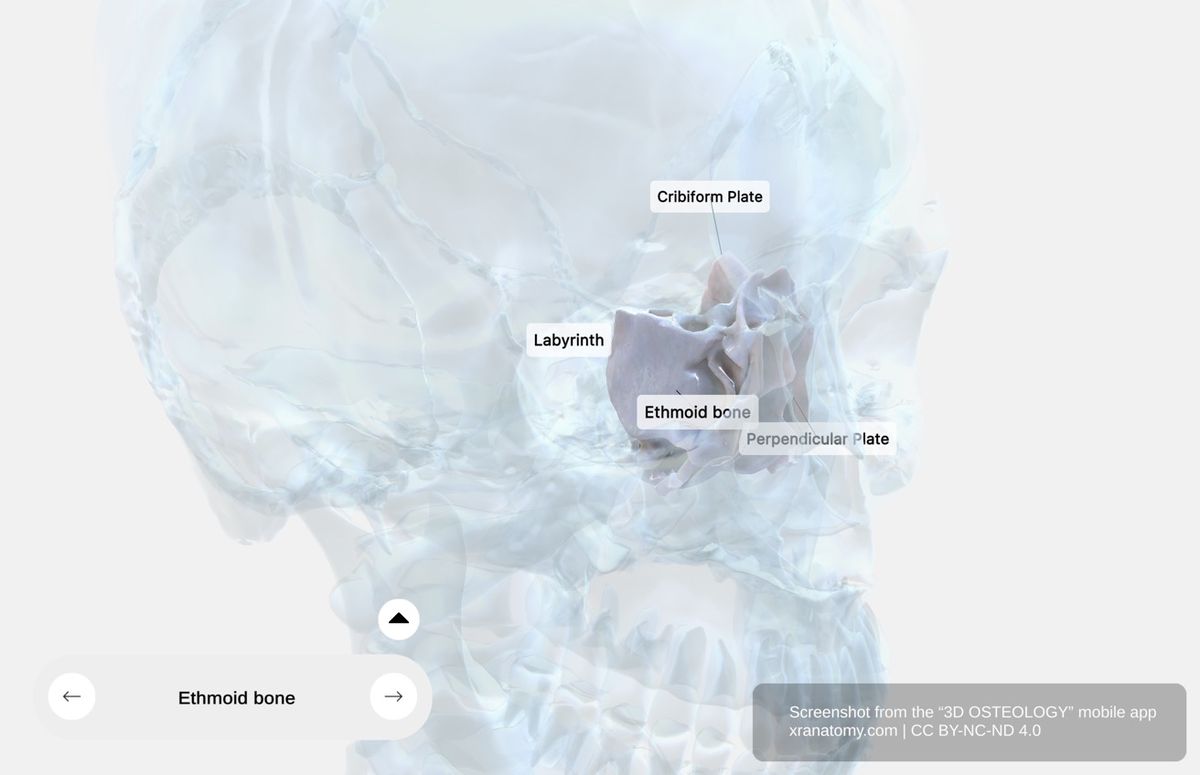
The ethmoid bone is composed of four main parts: the cribriform plate, the perpendicular plate, and two ethmoidal labyrinths. Despite being lightweight, it is fragile and delicate in structure.
CRIBRIFORM PLATE
Cribriform Plate, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
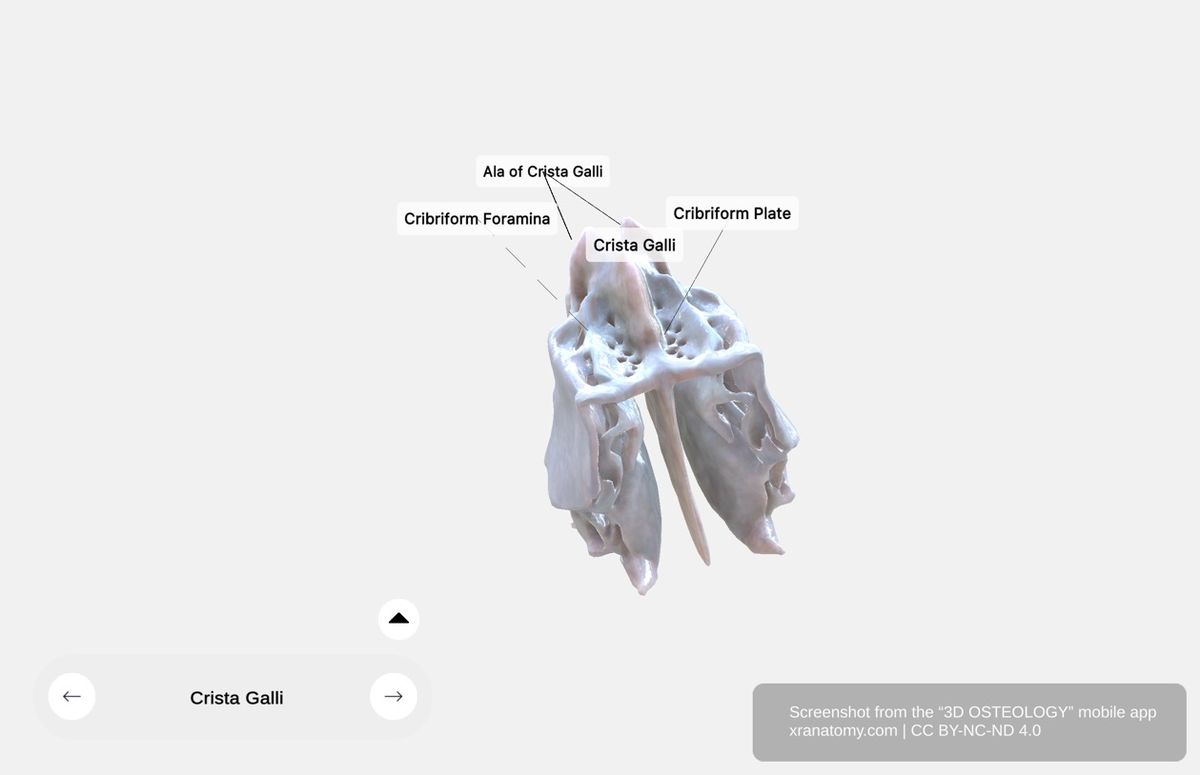
The cribriform plate is the horizontal portion of the ethmoid bone. It occupies the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone, features a deeply grooved surface, and provides support for your olfactory bulb. Its key sub-structures include the cribriform foramina, the crista galli, and the ala of crista galli.
Cribriform Foramina
The cribriform foramina are numerous small perforations in the cribriform plate. They allow passage of olfactory nerve fibers, connecting your nasal cavity to your brain and enabling your sense of smell.
Crista Galli
The crista galli is a vertical bony projection arising from the midline of the cribriform plate. It serves as the attachment point for the falx cerebri, the membrane that separates your cerebral hemispheres.
Ala of Crista Galli
The ala of crista galli are paired extensions that flank the anterior border of the crista galli. They articulate with the frontal bone and provide additional stability to the ethmoid.
PERPENDICULAR PLATE
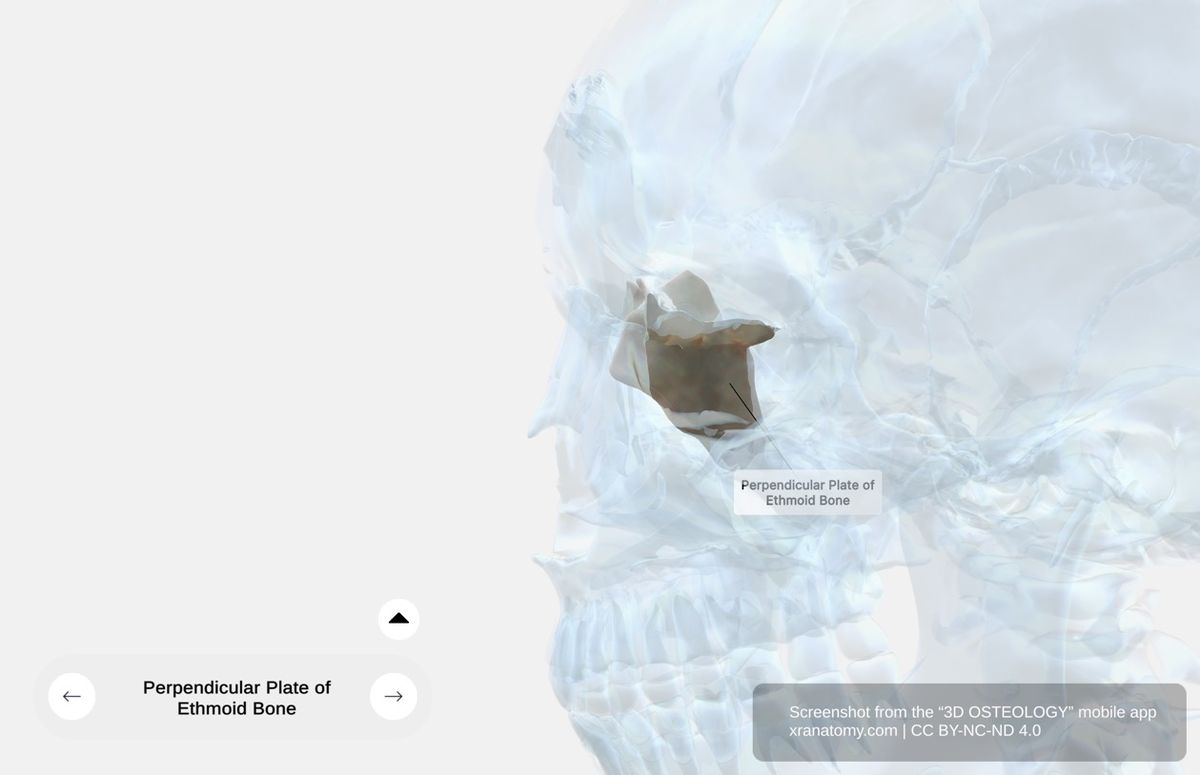
Perpendicular Plate, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The perpendicular plate is a thin vertical bony lamina that descends from the inferior surface of the cribriform plate. It forms the superior portion of your nasal septum, dividing your nasal cavity into left and right halves. Inferiorly it articulates with the vomer, and anteriorly it articulates with the septal cartilage.
The perpendicular plate supports your nasal structure and contributes to proper airflow through your nasal passages.
ETHMOIDAL LABYRINTH

Ethmoidal Labyrinth, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The ethmoidal labyrinths are two lateral masses flanking the perpendicular plate. They are composed of thin-walled air-filled cavities and contain the ethmoidal cells (ethmoidal sinuses). Their key sub-structures include the ethmoidal cells, the orbital plate, the ethmoidal bulla, the uncinate process, the semilunar hiatus, and the ethmoidal infundibulum.
Ethmoidal Cells
The ethmoidal cells are grouped into three categories.
| Cell Group | Location | Covering |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior cells | Front of the labyrinth | Lacrimal bone |
| Middle cells | Between anterior and posterior groups; contribute to the medial orbital wall | Orbital plate of ethmoid |
| Posterior cells | Back of the labyrinth | Orbital plate |
Orbital Plate
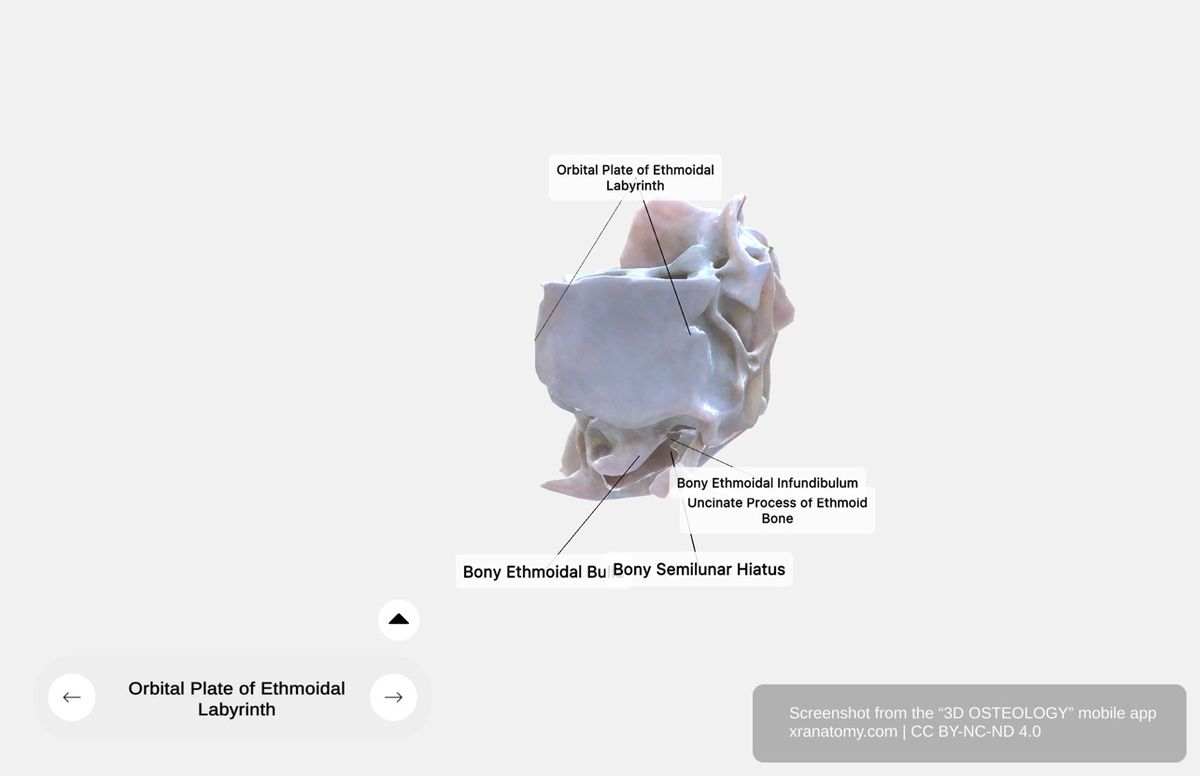
Orbital Plate (Lamina Papyracea), Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The orbital plate is a thin smooth bony sheet that covers the middle and posterior ethmoidal cells. It forms a significant portion of your medial orbital wall.
Ethmoidal Bulla
The ethmoidal bulla is a prominent rounded elevation formed by the middle ethmoidal cells.
Uncinate Process
The uncinate process is a curved lamina located anterior to the ethmoidal bulla. It descends posteroinferiorly and articulates with the ethmoidal process of the inferior nasal concha.
Semilunar Hiatus
The semilunar hiatus is a crescent-shaped groove located between the uncinate process and the ethmoidal bulla. It leads into the ethmoidal infundibulum.
Ethmoidal Infundibulum
The ethmoidal infundibulum is a connecting passage that opens into the middle nasal meatus. It facilitates drainage of your frontal sinus and your maxillary sinus.
NASAL CONCHAE
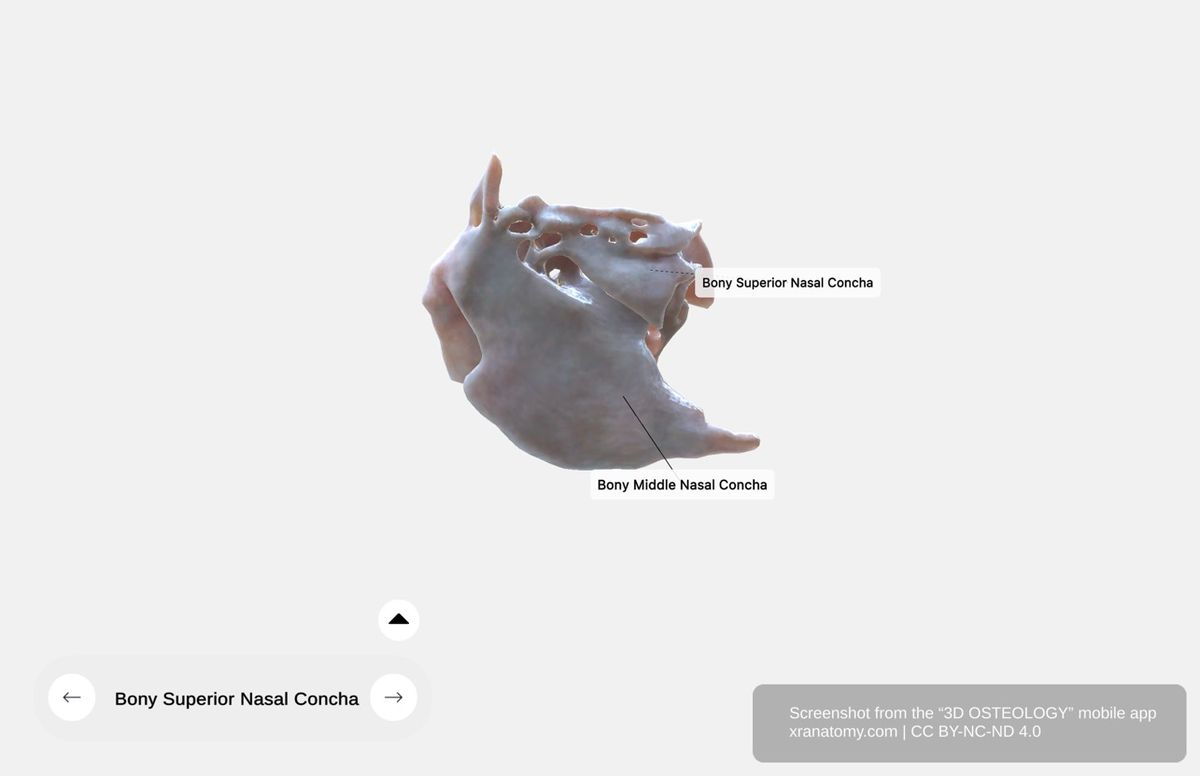
Nasal Conchae, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The ethmoid bone gives rise to two nasal conchae: the superior nasal concha and the middle nasal concha. Both extend from the medial surface of the ethmoidal labyrinth into the nasal cavity.
Superior Nasal Concha
The superior nasal concha is a thin curved bony plate extending from the medial surface of the ethmoidal labyrinth. It is the smallest and most superior concha and forms the upper boundary of the superior nasal meatus.
Middle Nasal Concha
The middle nasal concha is a thin curved bony plate extending from the medial surface of the ethmoidal labyrinth. It is larger than the superior concha and projects from the inferior border of the labyrinth. It forms part of your lateral nasal cavity wall.
Functions of Conchae
The nasal conchae increase the surface area within your nasal passages. They enhance warming, promote humidification, and improve filtration of the air you inhale.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Name the four main parts of the ethmoid bone.
Reveal Answer
Cribriform plate, perpendicular plate, and two ethmoidal labyrinths.
2. What passes through the cribriform foramina, and what function does this enable?
Reveal Answer
Olfactory nerve fibers pass through the cribriform foramina, connecting the nasal cavity to the brain and enabling the sense of smell.
3. What is the crista galli, and what attaches to it?
Reveal Answer
The crista galli is a vertical bony projection arising from the midline of the cribriform plate. The falx cerebri attaches to it, separating the cerebral hemispheres.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, explore the Maxilla, the largest bone of your face. You will study its body, orbital surface, anterior and infratemporal surfaces, nasal surface, and four processes (frontal, zygomatic, palatine, alveolar) with interactive 360° 3D views.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.