MAXILLA ANATOMY
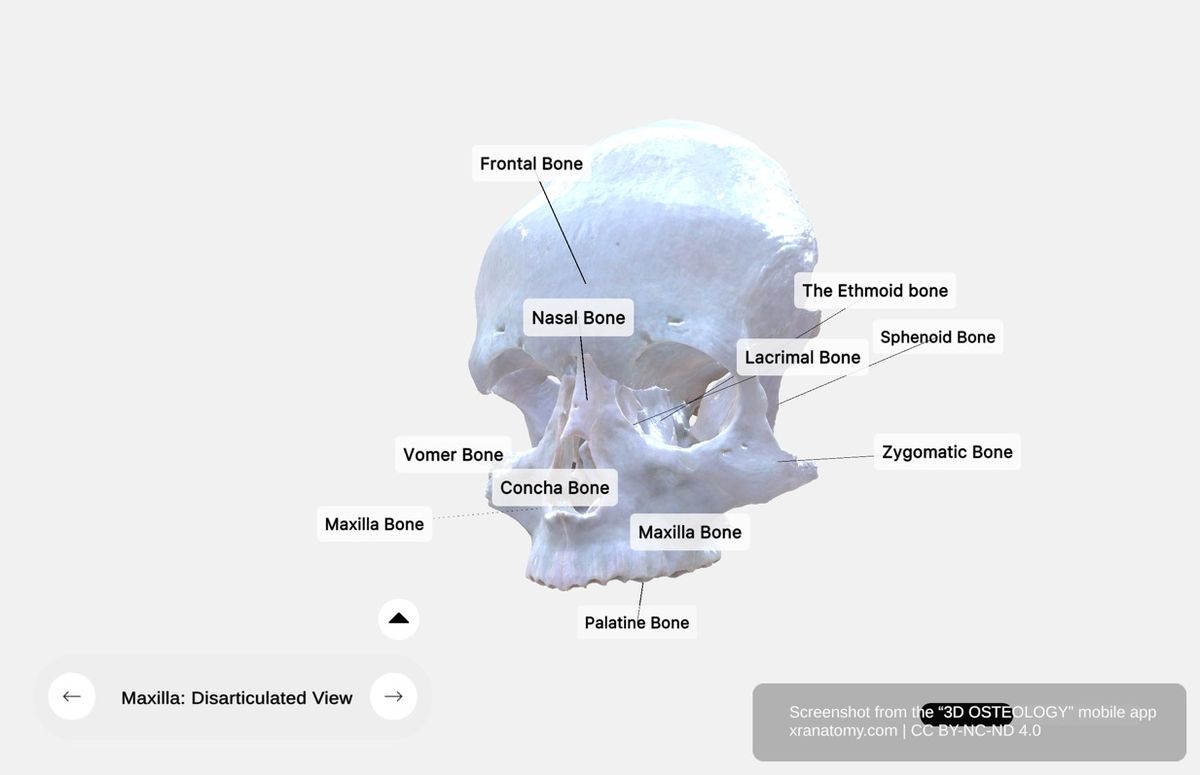
Maxilla - Disarticulated View, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The maxilla is the key bone of your facial skeleton, forming your upper jaw and contributing to the roof of your oral cavity, the orbital floor, and the walls of your nasal cavity. Understanding its body, four surfaces, and four processes helps you see how this single bone connects to 9 neighboring bones and supports structures essential for vision, breathing, and eating.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Overview of the Maxilla
The maxilla is a key bone of your facial skeleton. It forms your upper jaw and contributes to multiple anatomical regions: the roof of your oral cavity, the orbital floor, and the lateral and inferior walls of your nasal cavity.
Articulations
The maxilla articulates with 9 bones: the frontal bone, ethmoid bone, nasal bone, zygomatic bone, lacrimal bone, inferior nasal concha, palatine bone, vomer, and the contralateral maxilla.
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS
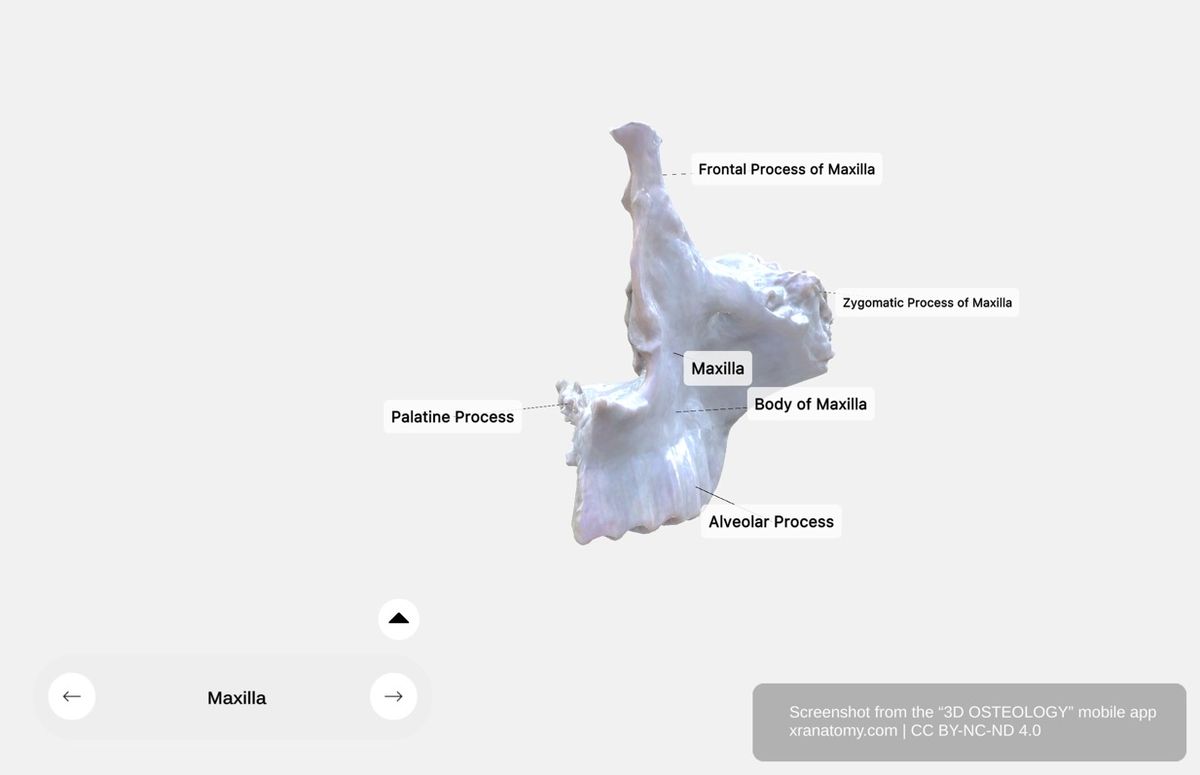
Maxilla - Structural Segments, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The maxilla consists of a central body and four projecting processes: the zygomatic process, frontal process, alveolar process, and palatine process.
BODY OF THE MAXILLA
The body is the central portion of the maxilla. It contains your maxillary sinus, a large pneumatic cavity that reduces your skull weight and contributes to your vocal resonance. The body features four distinct surfaces: the orbital surface, anterior surface, infratemporal surface, and nasal surface.
Orbital Surface

Orbital Surface of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The orbital surface is the superior aspect of the maxillary body, forming the orbital floor. It has a smooth triangular configuration and supports your ocular structures.
Infraorbital Groove and Canal
The orbital surface contains the infraorbital groove, which begins at the posterior border of the orbital surface and continues anteriorly as the infraorbital canal. These structures transmit the infraorbital nerve, the terminal branch of the maxillary nerve (V2, second division of your trigeminal nerve), and the infraorbital artery, a branch of the maxillary artery. The canal opens onto your facial surface at the infraorbital foramen, which provides sensory supply to the skin of your midface, upper lip, and lateral nose.
Maxillary Orbital Margin
The maxillary orbital margin forms the inferior orbital rim. It separates the orbital cavity from the facial surface.
Anterior Surface
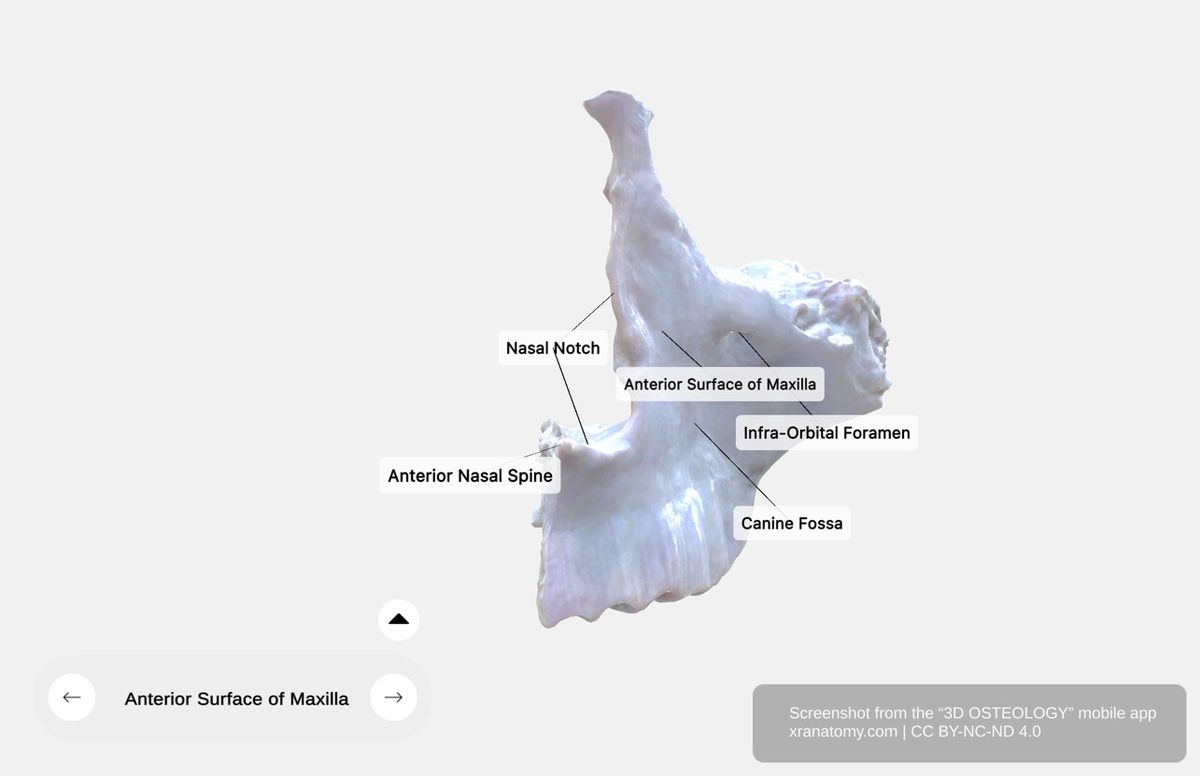
Anterior Surface of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The anterior surface faces forward and slightly lateral. It displays prominences corresponding to your tooth roots.
Canine Fossa
The canine fossa is a depression on the anterior surface, located inferior to the infraorbital foramen and positioned superior to your canine tooth roots.
Nasal Notch
The nasal notch is a deep concavity that contributes to the piriform aperture, the pear-shaped nasal opening.
Anterior Nasal Spine
The anterior nasal spine is a sharp projection formed by the union of the left and right maxillae. It is located at the inferior aspect of the nasal notch and provides attachment for your septal cartilage.
Infratemporal Surface
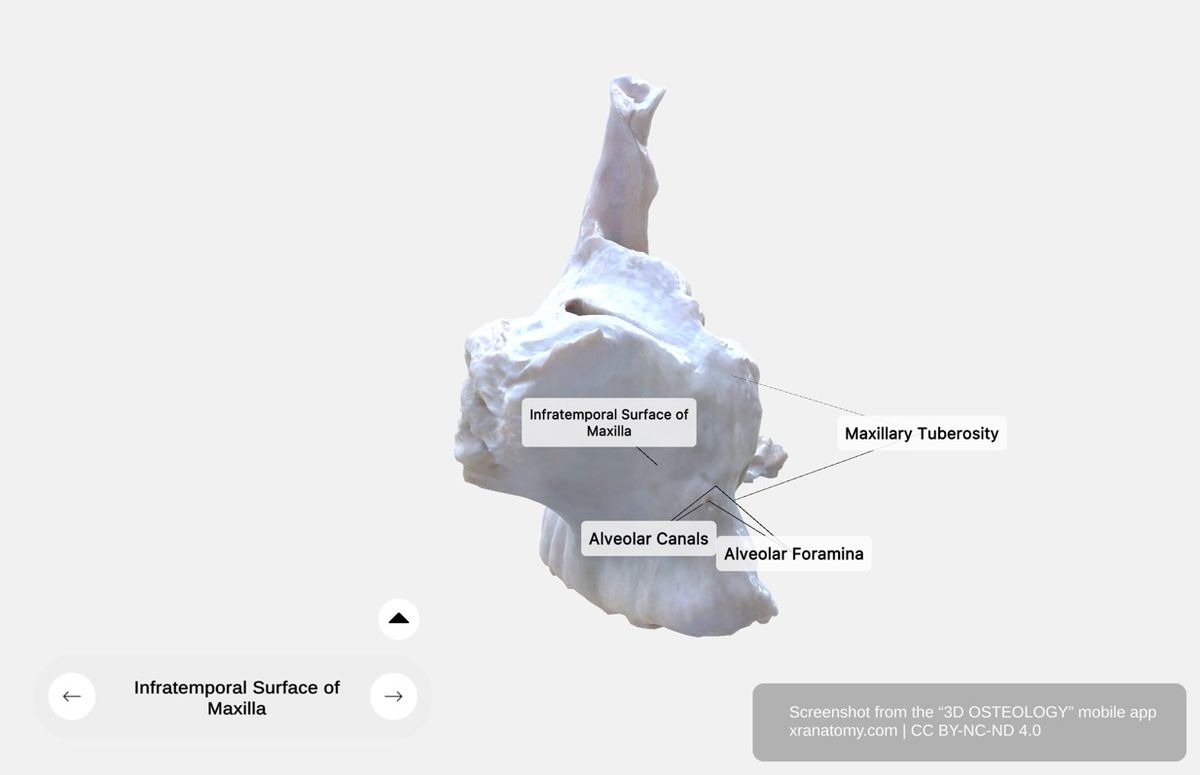
Infratemporal Surface of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The infratemporal surface is the posterior aspect of the maxillary body. It contributes to both the infratemporal fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa.
Maxillary Tuberosity
The maxillary tuberosity is a rounded eminence located posterior to your last molar. It serves as a muscular attachment site and is an important landmark in dental procedures.
Alveolar Foramina and Canals
The alveolar foramina and canals are openings on the infratemporal surface. They transmit the posterior superior alveolar nerves and posterior superior alveolar vessels, which supply your molar teeth.
Nasal Surface

Nasal Surface of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The nasal surface is the medial aspect of the maxillary body. It forms your lateral nasal cavity wall.
Lacrimal Groove
The lacrimal groove is a deep channel that combines with the lacrimal bone to form the nasolacrimal canal. This canal transmits the nasolacrimal duct, which drains your tears into your nasal cavity.
Conchal Crest
The conchal crest is a bony ridge that articulates with the inferior nasal concha and contributes to your lateral nasal wall.
Lacrimal Margin
The lacrimal margin articulates with the lacrimal bone and contributes to your medial orbital wall.
Maxillary Hiatus
The maxillary hiatus is a large irregular opening that leads into your maxillary sinus. It is partially covered by adjacent bones in life and lined by mucous membrane. The hiatus regulates your sinus airflow and drainage.
Greater Palatine Groove
The greater palatine groove is located near the posterior border of the nasal surface. It combines with the palatine bone to form the greater palatine canal, which transmits the greater palatine nerve and vessels that supply your hard palate.
FRONTAL PROCESS

Frontal Process of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The frontal process is an upward projection from the maxillary body. It articulates with the frontal bone, contributes to your lateral nasal boundary, and contributes to the medial orbital wall. Its key features include the anterior lacrimal crest, the lacrimal notch, and the ethmoidal crest.
Anterior Lacrimal Crest
The anterior lacrimal crest is a vertical ridge on the frontal process. It provides attachment for your lacrimal sac and your medial palpebral ligament, making it important for your lacrimal apparatus.
Lacrimal Notch
The lacrimal notch is a posterior indentation on the frontal process. It articulates with the lacrimal bone, completes the lacrimal fossa, and houses your lacrimal sac.
Ethmoidal Crest
The ethmoidal crest is an oblique ridge located on the frontal process. It articulates with the middle nasal concha of the ethmoid and contributes to your nasal cavity architecture.
ZYGOMATIC PROCESS

Zygomatic Process of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The zygomatic process is a lateral projection from the maxillary body. It articulates with the zygomatic bone and forms part of the infraorbital rim. This process contributes to your cheek prominence, maintains your facial contour, and provides muscular attachment sites.
PALATINE PROCESS
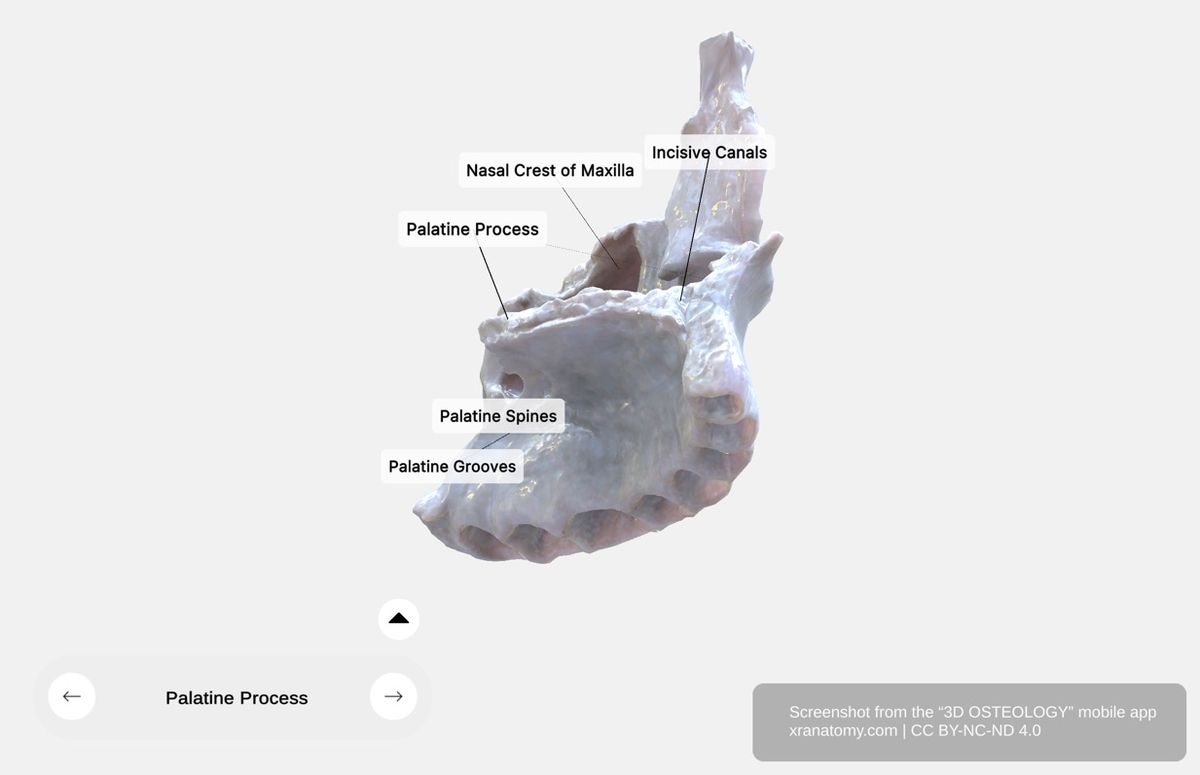
Palatine Process of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The palatine process is a medial projection from the maxillary body. It forms the anterior three-quarters of your hard palate and separates your oral and nasal cavities. It serves as your nasal cavity floor and your oral cavity roof, and it supports your upper dentition. Its key features include the nasal crest, the incisive canals, and the palatine grooves and spines.
Nasal Crest
The nasal crest is a midline ridge located where the left and right maxillae meet. It provides attachment for the vomer and contributes to your nasal septum.
Incisive Canals
The incisive canals are anterior passages that pass through the palatine process. They transmit nasopalatine nerves and branches of the greater palatine arteries. The canals open inferiorly at the incisive foramina, which are located posterior to your incisor teeth.
Palatine Grooves and Spines
The inferior surface of the palatine process features palatine grooves and palatine spines. These structures support your hard palate mucous membrane.
ALVEOLAR PROCESS

Alveolar Process of Maxilla, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The alveolar process is the inferior portion of the maxilla. It contains dental alveoli, the sockets for your upper teeth roots. This process is essential for your tooth anchorage and important for your mastication and speech. Its features include the alveolar arch, interalveolar septa, interradicular septa, alveolar yokes, and the incisive foramina.
Alveolar Arch
The alveolar arch is the curved free margin of the alveolar process. It follows your dental arcade contour.
Interalveolar Septa
The interalveolar septa are bony partitions that separate adjacent tooth sockets.
Interradicular Septa
The interradicular septa are present in multirooted teeth. They divide alveoli further and provide additional root support.
Alveolar Yokes
The alveolar yokes are external prominences that correspond to your tooth root positions and contribute to your upper jaw contour.
Incisive Foramina
The incisive foramina are midline openings located posterior to your incisors. They are important anatomical landmarks and transmit neurovascular structures to your anterior palate.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Name the four processes of the maxilla.
Reveal Answer
The frontal process, zygomatic process, palatine process, and alveolar process.
2. What structures does the infraorbital canal transmit, and where does it open onto the face?
Reveal Answer
The infraorbital canal transmits the infraorbital nerve (terminal branch of the maxillary nerve, V2) and the infraorbital artery (branch of the maxillary artery). It opens onto the facial surface at the infraorbital foramen, providing sensory supply to the midface, upper lip, and lateral nose.
3. What is the maxillary hiatus and what is its function?
Reveal Answer
The maxillary hiatus is a large irregular opening on the nasal surface of the maxillary body that leads into the maxillary sinus. It is partially covered by adjacent bones in life and lined by mucous membrane, and it regulates sinus airflow and drainage.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, explore the Vomer, a thin, flat bone that forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum. You will study its articulations, surfaces, and role in dividing the nasal cavity, with interactive 360-degree 3D views.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.