TEMPORAL BONE ANATOMY
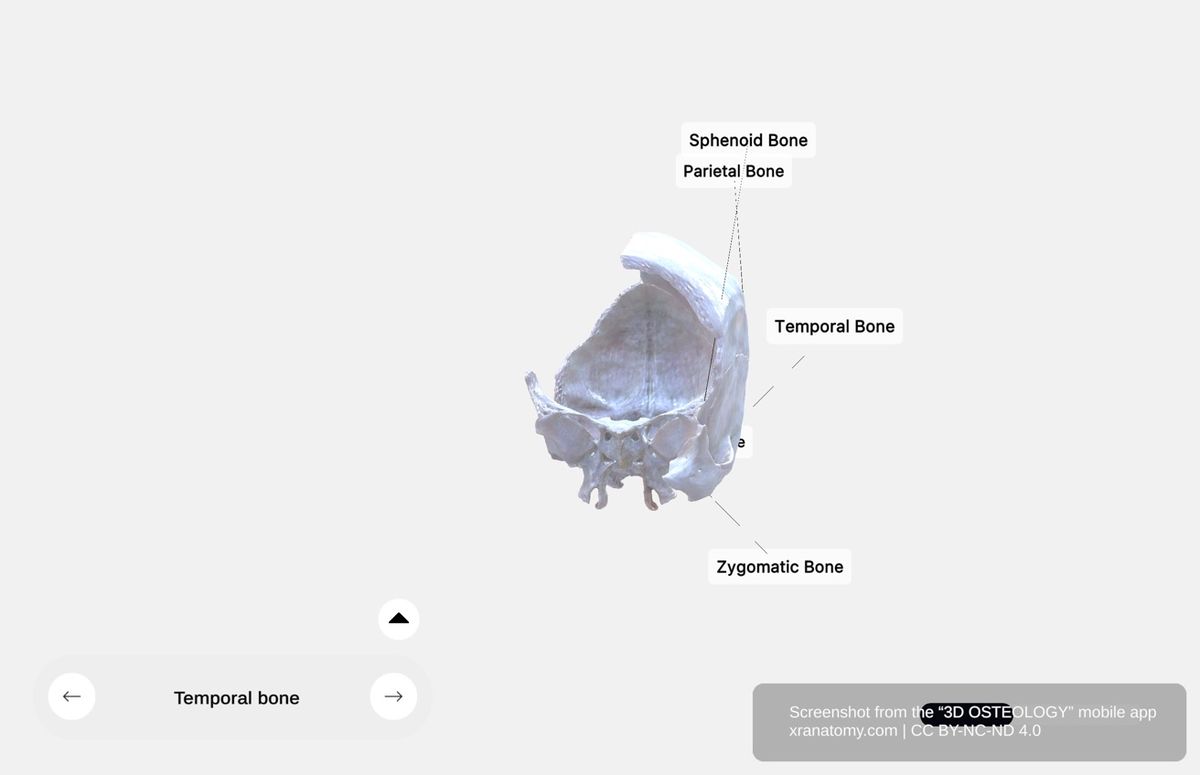
Temporal Bone - General Structure, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
The temporal bone sits on the lateral and basal aspects of your skull, right next to your external ears. It houses your hearing and balance organs, protects your inner ear structures, and contains the carotid canal that delivers blood to your brain. Understanding its three main parts helps you see how this single bone connects hearing, jaw movement, and cerebral blood supply.
In-Depth AR Atlas Available
Read the comprehensive anatomy description with AR illustrations and videos
Read AR Atlas →GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The temporal bone is a complex cranial bone situated on your skull's lateral and basal aspects. It is located adjacent to your external ears and supports your temporal region. The temporal bone contains structures for your hearing and balance and protects your inner ear organs. It articulates with surrounding cranial bones.
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS
Structural Components of the Temporal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
Parts of the Temporal Bone
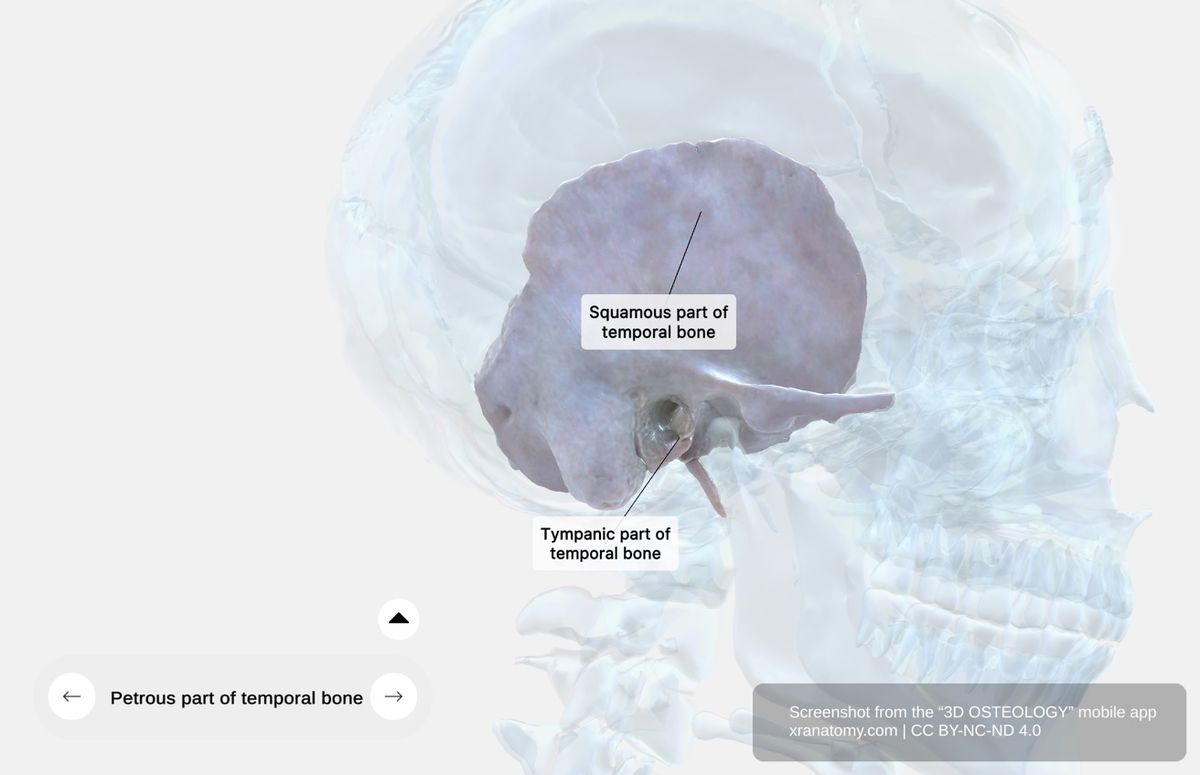
The temporal bone is an irregular bone composed of multiple distinct parts: the squamous part, the tympanic part, and the petromastoid part, which itself includes the petrous portion and the mastoid portion.
PETROUS PART
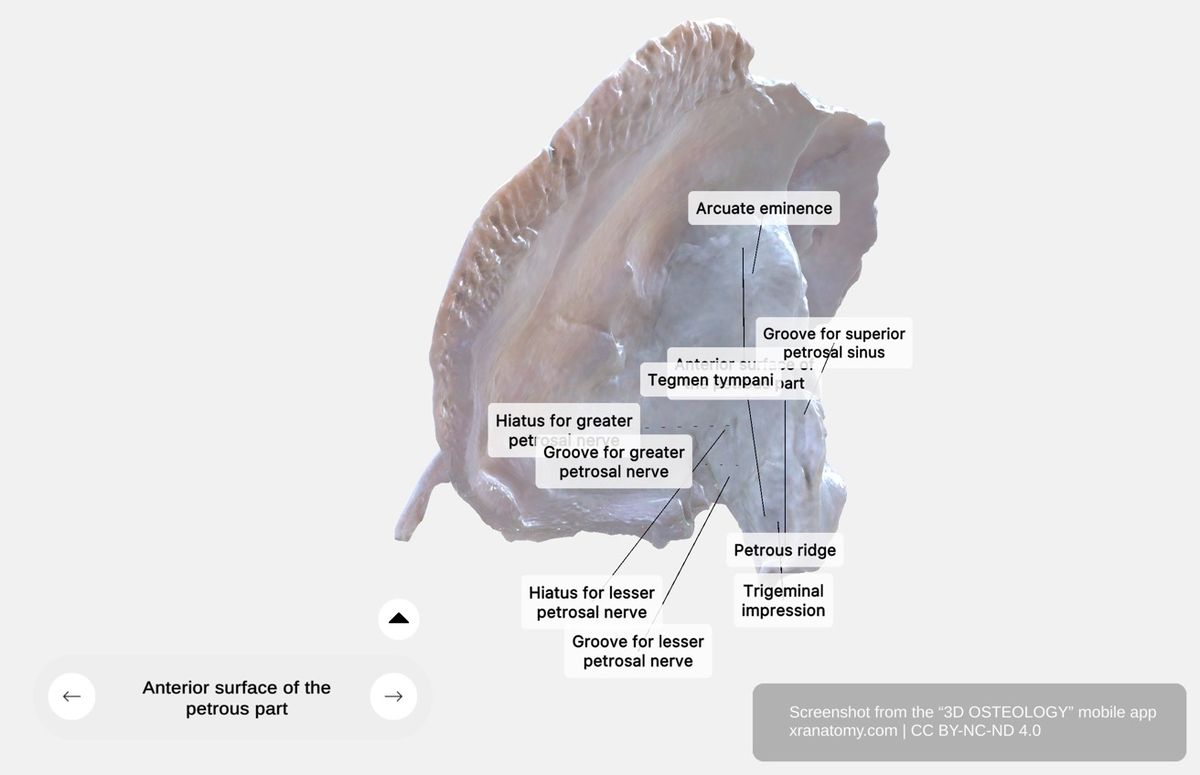
Petrous Part - Anterior Surface, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The petrous part contains several important regions and features. Superiorly, the general features describe its overall shape and density. The apex region articulates with adjacent cranial bones. The posterior border and mastoid features include the mastoid process, mastoid notch, occipital artery groove, and mastoid foramen. The inferior surface houses the carotid canal, and the musculotubal canal transmits structures for hearing and pressure equalization.
General Features
The petrous part is a pyramid-shaped region that contains an apex and a base. It presents three surfaces and three borders, with its base oriented laterally. It is among the densest bones in your body and houses your inner ear structures.
Apex Region

Petrous Part - Apex, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The petrous apex articulates with the greater wing of the sphenoid and the basilar portion of the occipital bone.
Posterior Border and Mastoid Features
The posterior border (occipital margin) articulates with the occipital bone. On the external surface of the posterior region, the mastoid process forms a prominent bony projection that serves as an attachment for your cervical muscles.
The mastoid notch is a groove inferior to the mastoid process and provides an attachment site for the digastric muscle posterior belly. The occipital artery groove sits posterior to the mastoid notch and accommodates the occipital artery during its cranial ascent.
The mastoid foramen is located posterior to the mastoid process. It transmits emissary veins and connects the sigmoid sinus to the posterior scalp.
Inferior Surface and Carotid Canal

Inferior Surface of the Petrous Part, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The carotid canal is a significant passageway in the petrous region. It begins on the inferior petrous surface and opens at the petrous apex. Its external opening is located medial to the jugular fossa, and its internal opening sits at the petrous apex. The carotid canal transmits the internal carotid artery to your cranial cavity and supplies your cerebral blood flow.
Musculotubal Canal
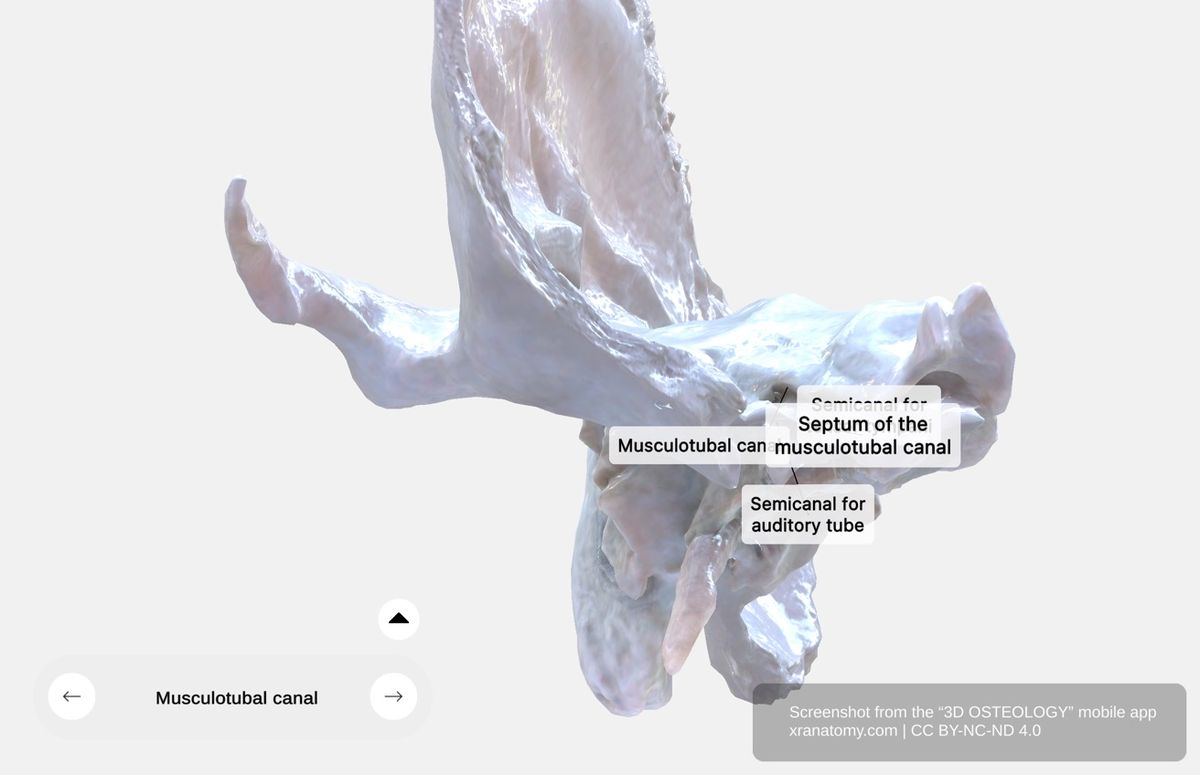
Musculotubal Canal, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The musculotubal canal is divided by a thin bony septum into two semicanals. The upper semicanal transmits the tensor tympani muscle. The lower semicanal accommodates your auditory tube, also termed the Eustachian tube, which connects your middle ear to your nasopharynx and equalizes pressure across your tympanic membrane. The canal opens into the tympanic cavity and is located anterior to the carotid canal external opening.
TYMPANIC PART
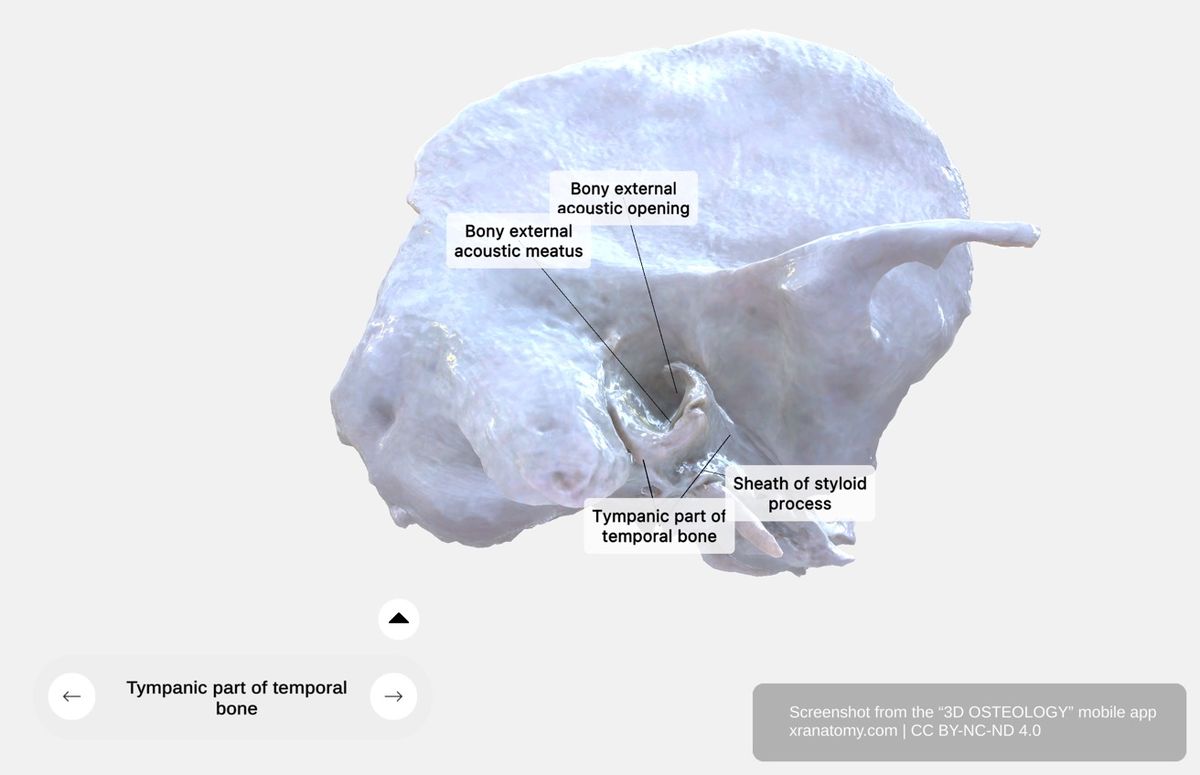
Tympanic Part of the Temporal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The tympanic part contains several sub-structures. Its general features describe the curved plate that forms the ear canal walls. The developmental aspects cover its growth from the neonatal tympanic ring. The external acoustic meatus section details the bony ear canal with its sulcus and notch, while the tympanic spines and styloid process describe the bony projections at its margins.
General Features
The tympanic part is a curved bony plate positioned anterior to the mastoid process. It forms the anterior wall, floor, and partial posterior wall of your external acoustic meatus.
Developmental Aspects
The tympanic part exists as a tympanic ring in neonates. It fuses with the squamous part shortly before birth and expands to form the mature tympanic part.
External Acoustic Meatus
The bony external acoustic opening marks the entrance to the meatus. The external acoustic meatus itself is an oval canal approximately 16 mm in length, formed by the tympanic and squamous parts.
The tympanic sulcus is a groove within the tympanic ring that provides the attachment site for your tympanic membrane circumference. The tympanic notch is a superior deficiency in the tympanic ring that allows the chorda tympani nerve to pass through.
Tympanic Spines and Styloid Process
The tympanic spines consist of the greater tympanic spine, an anterior ring projection, and the lesser tympanic spine, a posterior ring projection.
The styloid process sheath extends posteriorly from the carotid canal and encircles the styloid process. The styloid process itself is a slender bony projection that provides attachment for your lingual muscles and your pharyngeal ligaments.
SQUAMOUS PART
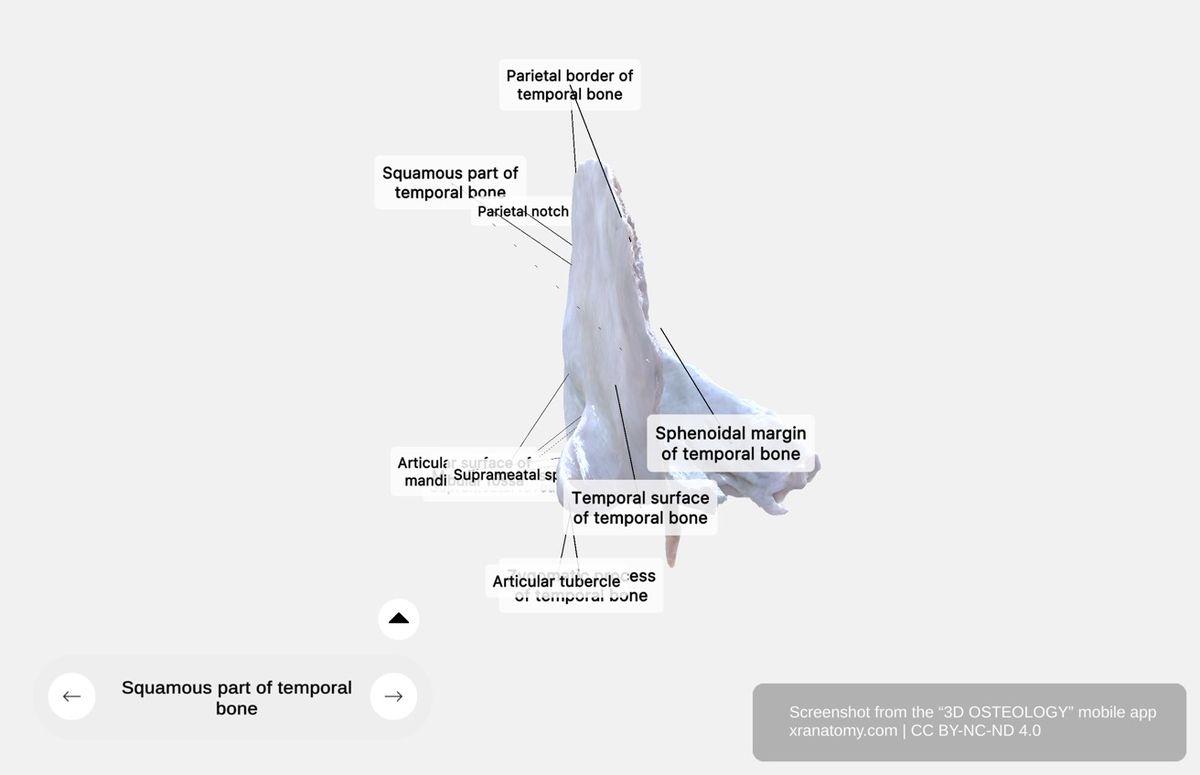
Squamous Part of the Temporal Bone, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The squamous part includes several groups of features. Its general features describe the thin flat portion. The surfaces section covers the temporal and cerebral surfaces. The borders and margins detail the superior border, parietal notch, and sphenoidal margin. The zygomatic process and related structures describe the arched projection and nearby landmarks, while the mandibular fossa section covers the temporomandibular joint contribution.
General Features
The squamous part is a thin flat portion located anterosuperiorly. It contributes to your temporal fossa.
Surfaces
The temporal surface is the outer aspect of the squamous part. It is smooth and convex and provides your temporalis muscle attachment.
The cerebral surface is the inner aspect. It has a concave configuration and accommodates your temporal lobe of the cerebrum. It contains grooves for middle meningeal vessels and shows impressions from cerebral gyri.
Borders and Margins
The superior border (parietal border) articulates with the parietal bone and forms part of the squamous suture. The parietal notch marks the angle between the parietal border and the mastoid superior border. The sphenoidal margin is located anteroinferiorly and articulates with the greater sphenoid wing.
Zygomatic Process and Related Structures
The zygomatic process is an arched projection that extends from the inferior squamous portion. It contributes to your zygomatic arch and connects with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
The supramastoid crest continues posteriorly from the root of the zygomatic process. The suprameatal fovea is a small depression located between the posterior wall of the external acoustic meatus and the posterior root of the zygomatic process. The suprameatal spine is an anatomical landmark near your external acoustic meatus.
Mandibular Fossa
The mandibular fossa is a concave depression located on the inferior squamous surface. It contributes to your temporomandibular joint and articulates with the mandibular condyle.
The articular surface forms the anterior portion of the mandibular fossa and contacts your mandible directly. The articular tubercle is a rounded eminence anterior to the fossa that prevents excessive posterior mandibular displacement when you open your jaw.
TEMPORAL BONE FISSURES
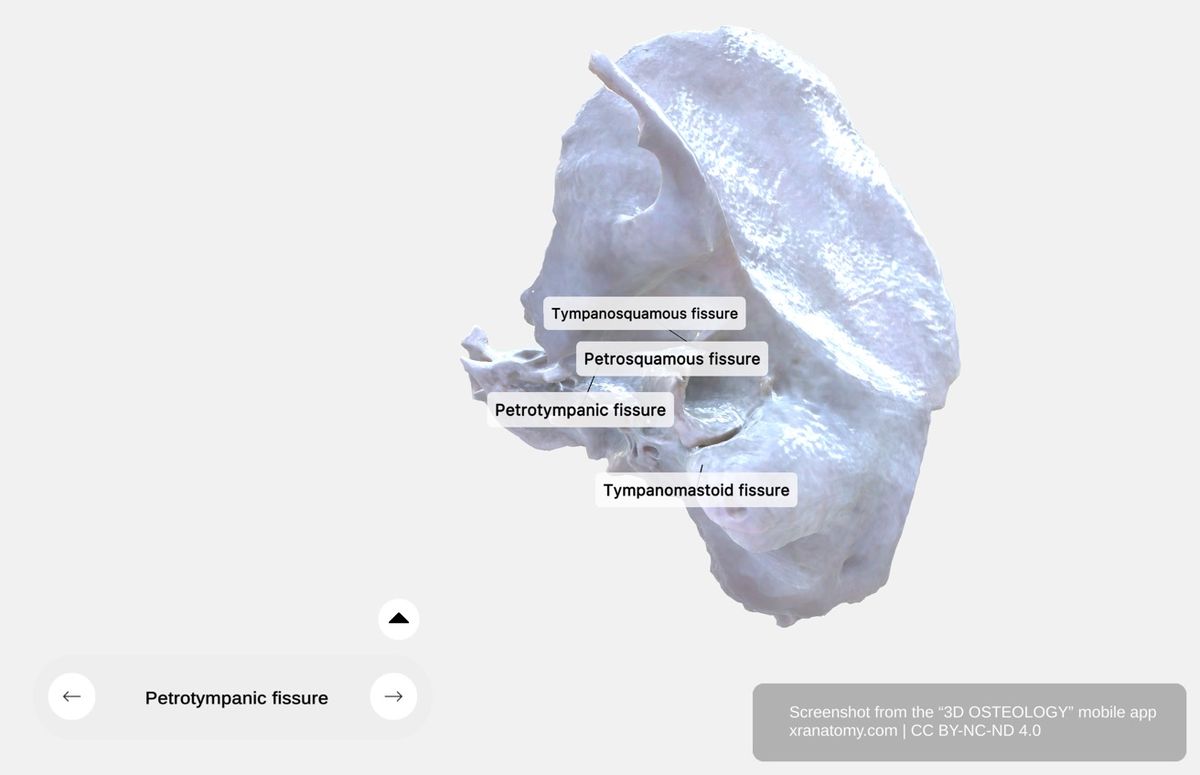
Temporal Bone Fissures, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The temporal bone fissures separate different bone parts and allow nerve and vessel passage. Four fissures define the boundaries between the temporal bone's components: the petrotympanic fissure, the petrosquamous fissure, the tympanosquamous fissure, and the tympanomastoid fissure.
Petrotympanic Fissure
The petrotympanic fissure is located between the mandibular fossa and the tympanic part. It sits posterior to the petrosquamous fissure.
Petrosquamous Fissure
The petrosquamous fissure is located anterior to the petrotympanic fissure. It separates the petrous from the squamous parts.
Tympanosquamous Fissure
The tympanosquamous fissure continues the petrosquamous and petrotympanic fissures laterally. It is located between the tympanic and squamous parts.
Tympanomastoid Fissure
The tympanomastoid fissure is formed by the posterior tympanic edge and the mastoid part.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What are the three main parts of the temporal bone?
Reveal Answer
The squamous part, the tympanic part, and the petromastoid part (which includes the petrous portion and the mastoid portion).
2. What does the carotid canal transmit, and where does it open?
Reveal Answer
The carotid canal transmits the internal carotid artery to your cranial cavity. It begins on the inferior petrous surface and opens at the petrous apex.
3. What structure prevents excessive posterior mandibular displacement when you open your jaw?
Reveal Answer
The articular tubercle, a rounded eminence anterior to the mandibular fossa.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you understand the temporal bone and its parts, the next page covers the Frontal Bone. You will explore the bone that forms your forehead, including its squamous part, orbital plates, nasal part, and frontal sinuses.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.