THORACIC SKELETON ANATOMY
Thoracic Skeleton - Overview, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
Your thoracic skeleton forms the protective cage around your chest. It shields your heart, lungs, and great vessels while giving your thoracic wall the flexibility it needs for breathing. Understanding how the ribs, sternum, thoracic vertebrae, and costal cartilages work together helps you see how your body balances protection with movement.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
THORAX OVERVIEW
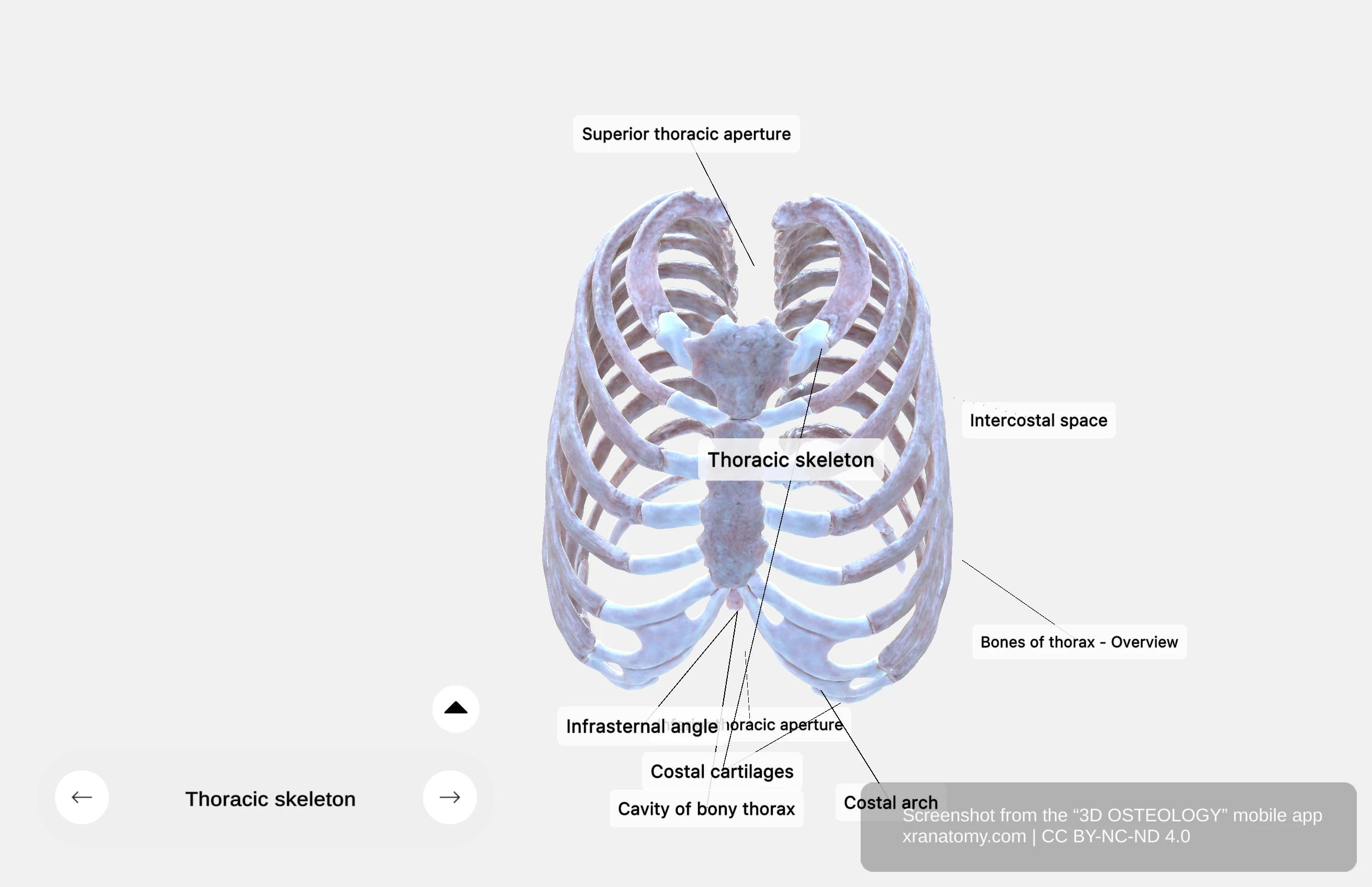
The thoracic cage is a structure made up of bones and cartilage that plays a vital role in protecting your thoracic organs like your heart, lungs, and great vessels. It is composed of the ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum, which together create a flexible yet sturdy framework crucial for your breathing. The thoracic cage forms a cavity that has two key openings. Below, you will explore the thoracic cage in detail, along with the thoracic cavity, superior thoracic aperture, and inferior thoracic aperture.
Thoracic Cage
Thoracic Cage, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The thoracic cage consists of bony and cartilaginous structures. It protects your vital organs: your heart, lungs, and great vessels. The cage is formed by your ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum, and it provides structural support and flexibility for your breathing.
Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity houses and protects your heart and lungs. It allows space for your lung expansion during respiration. The thoracic skeleton lines this cavity, providing protection and movement efficiency.
Superior Thoracic Aperture
The superior thoracic aperture is the upper opening of your thoracic cavity. It slopes downward and forward. Its boundaries include the first thoracic vertebra at the back, the manubrium of the sternum at the front, and the first ribs on each side. This opening allows passage of your trachea, esophagus, and major blood vessels.
Inferior Thoracic Aperture
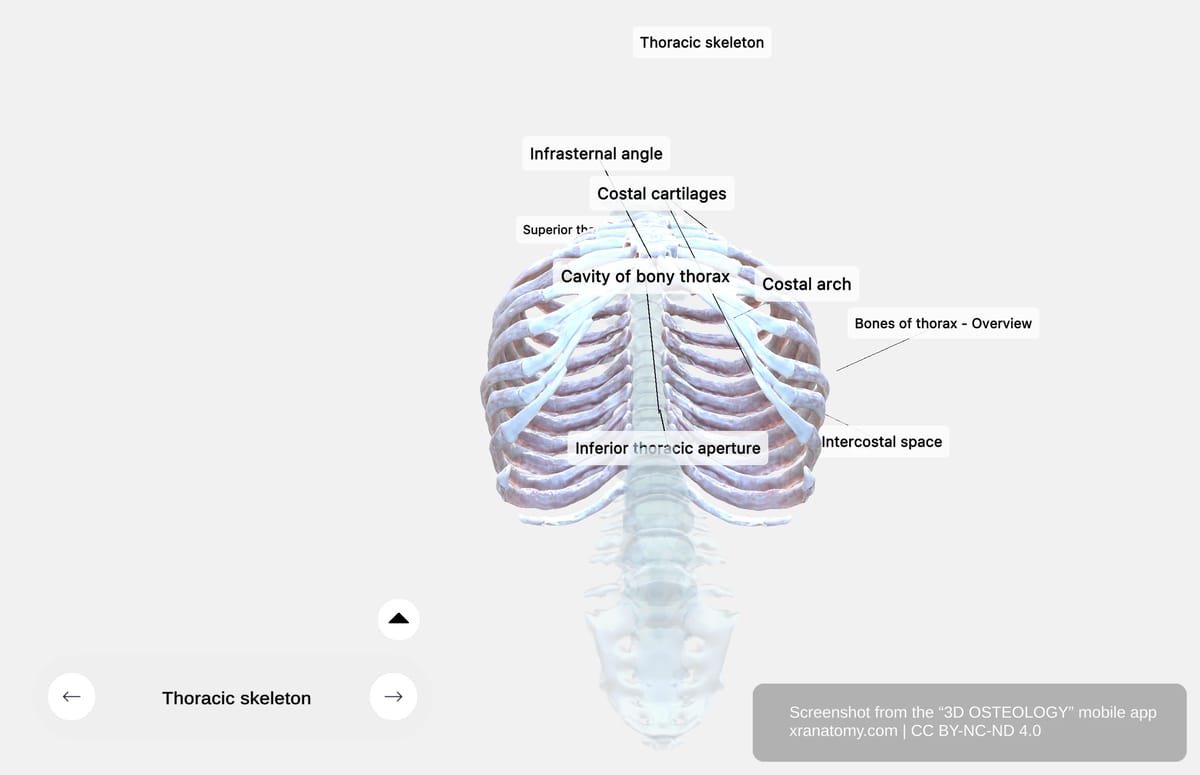
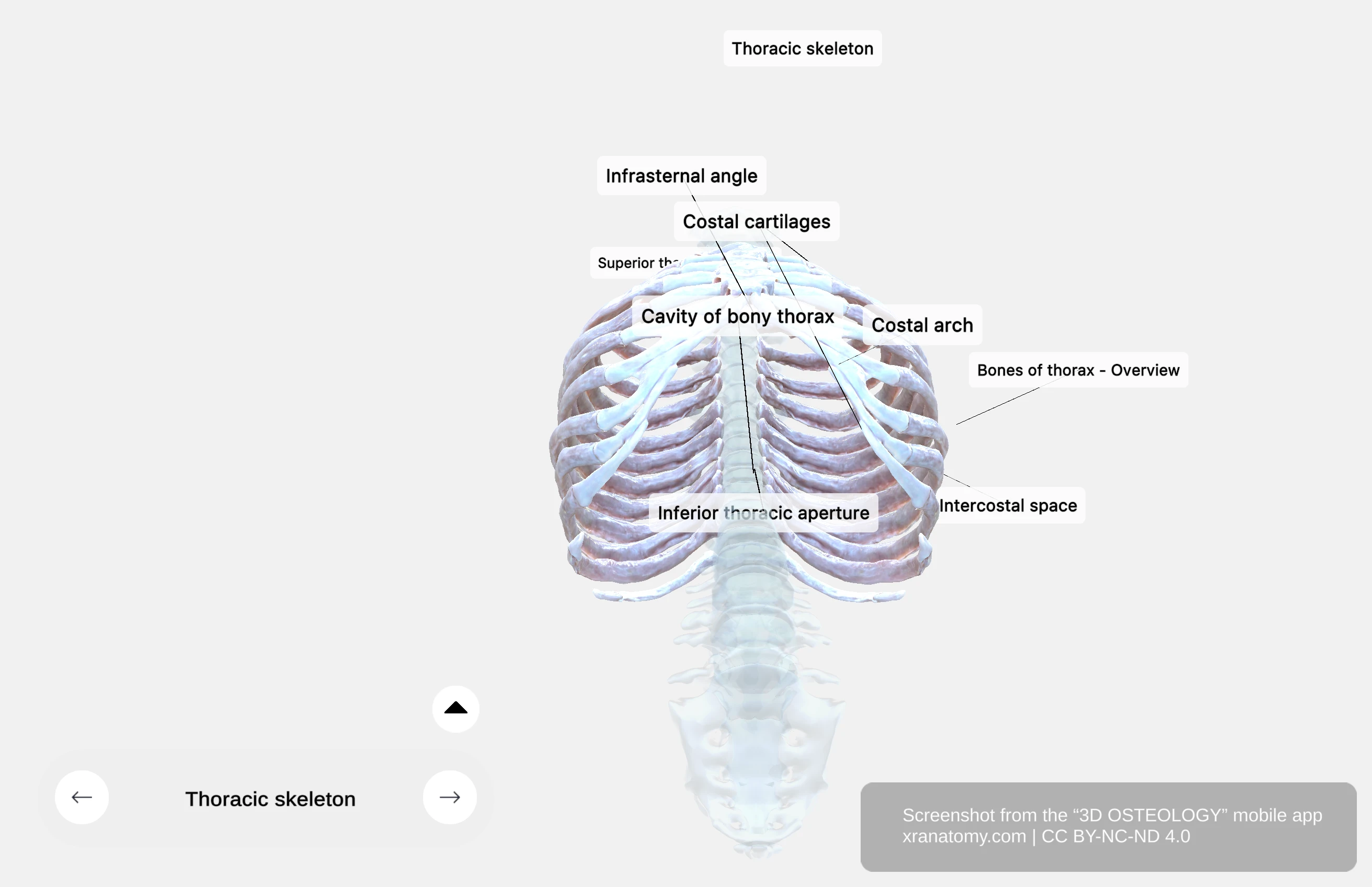
The inferior thoracic aperture is the lower opening of your thoracic cavity. Its boundaries include the twelfth thoracic vertebra posteriorly, the twelfth rib posterolaterally, the costal cartilages of ribs 7-10 forming the costal margin anterolaterally, and the xiphisternal joint anteriorly at the midline.
The infrasternal angle (subcostal angle) is the angle between the right and left costal margins at the xiphoid process. Your diaphragm seals this aperture, separating your thoracic cavity from your abdominal cavity.
THORACIC FEATURES
Your thorax features a well-designed framework that includes the costal arch for flexibility, intercostal spaces to facilitate rib movement, and the infrasternal angle as a key anatomical landmark. These structures work together to protect your vital organs and support efficient respiration through the expansion and contraction of your thoracic wall. Below, you will explore the thoracic skeleton bones, the infrasternal angle, costal cartilages, and intercostal spaces.
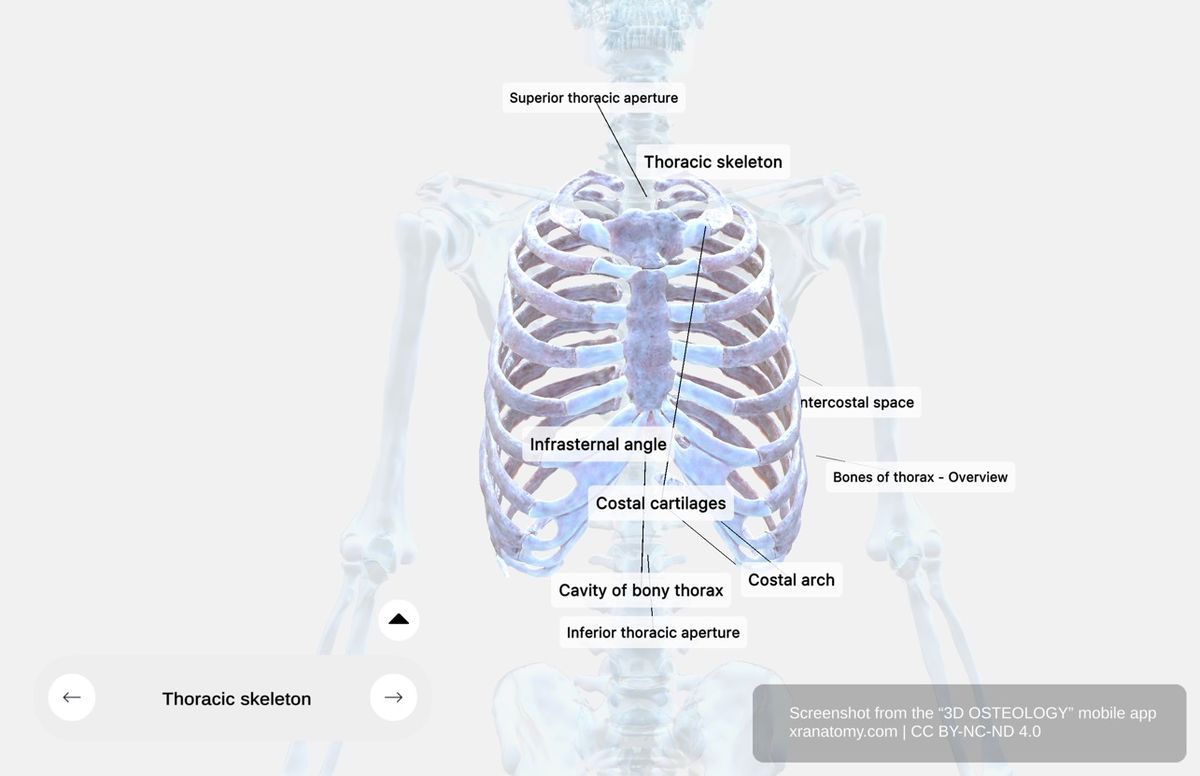
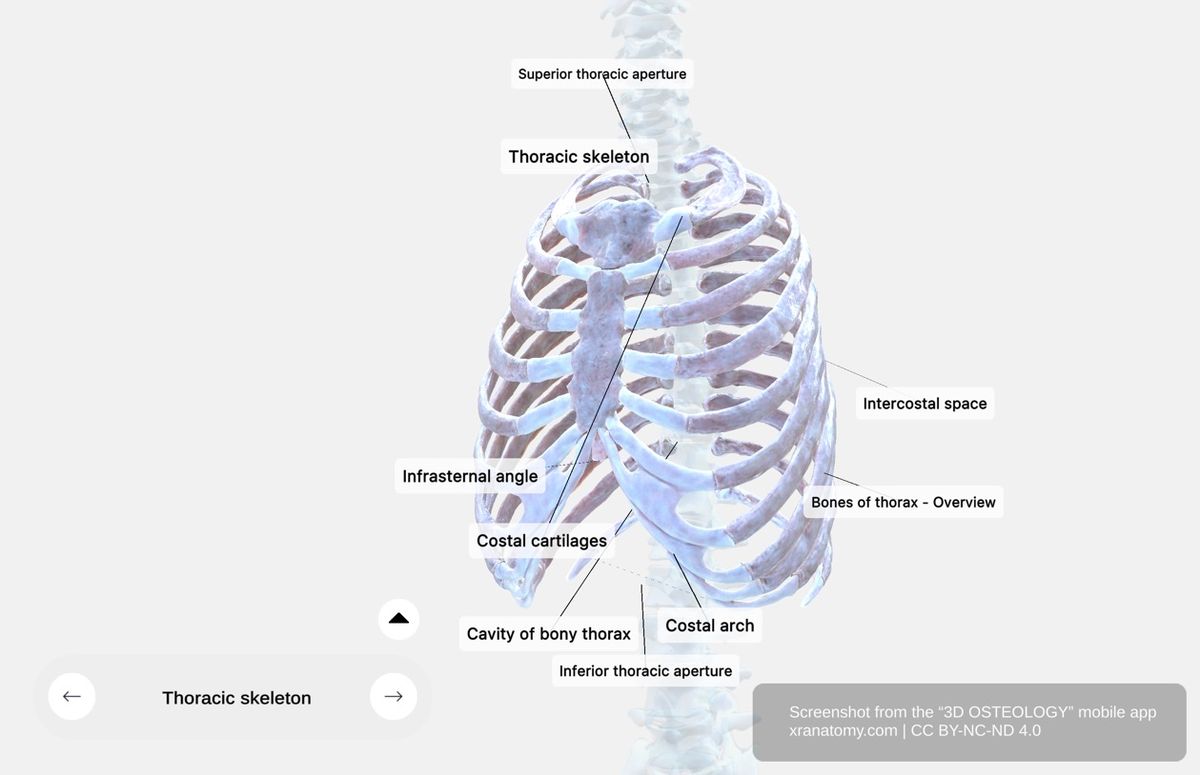
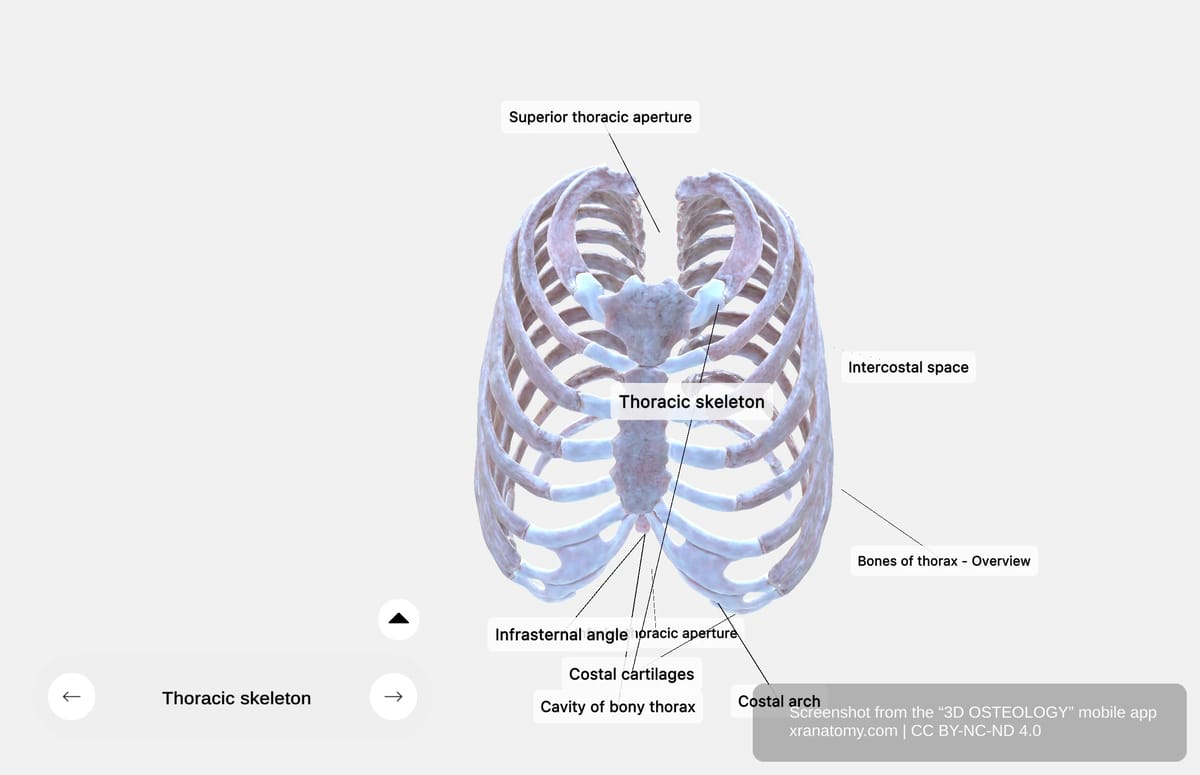
Thoracic Skeleton
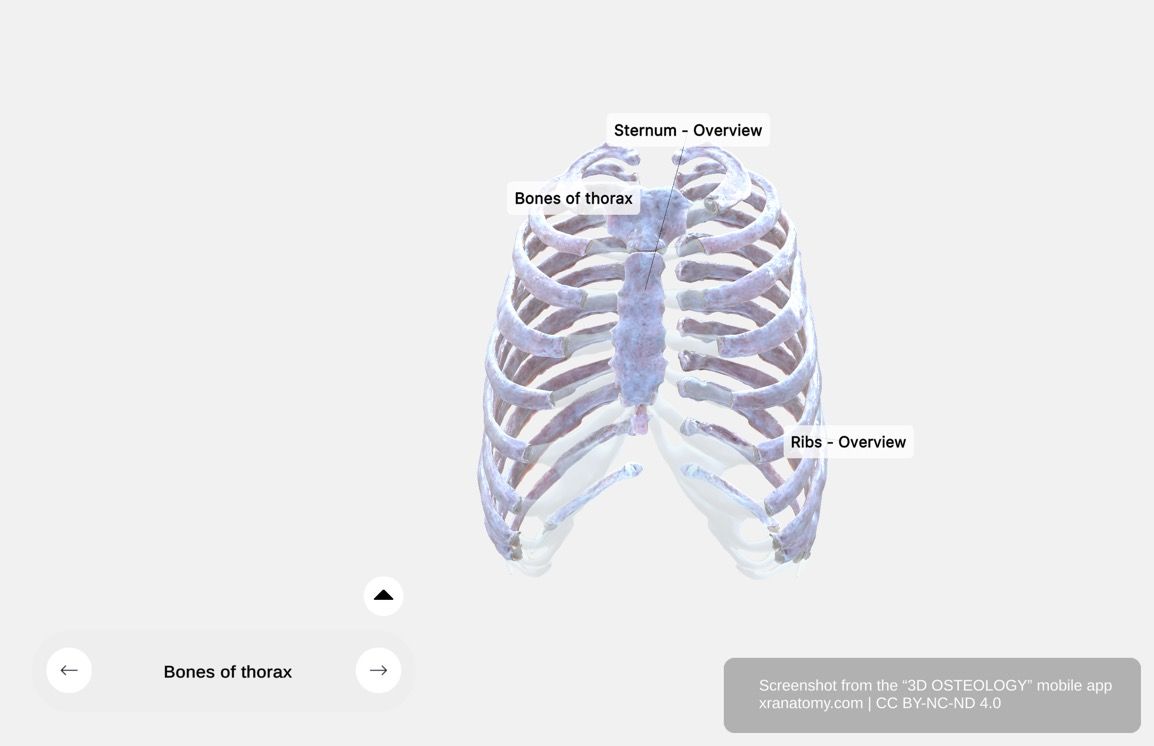
Bones of the Thorax, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The thoracic skeleton comprises the bones forming your thorax. These include the thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and sternum.
Your ribs consist of twelve pairs of elastic, curved bones. They attach posteriorly to your vertebral column and anteriorly to your sternum via costal cartilages. Your ribs provide structural support, protect your thoracic organs, and enable respiration through their mobility.
The sternum is a long, flat bone in the center of your anterior thoracic wall. It provides structural support and articulates with your clavicles (collarbones) and the first seven pairs of ribs via costal cartilages.
Infrasternal Angle
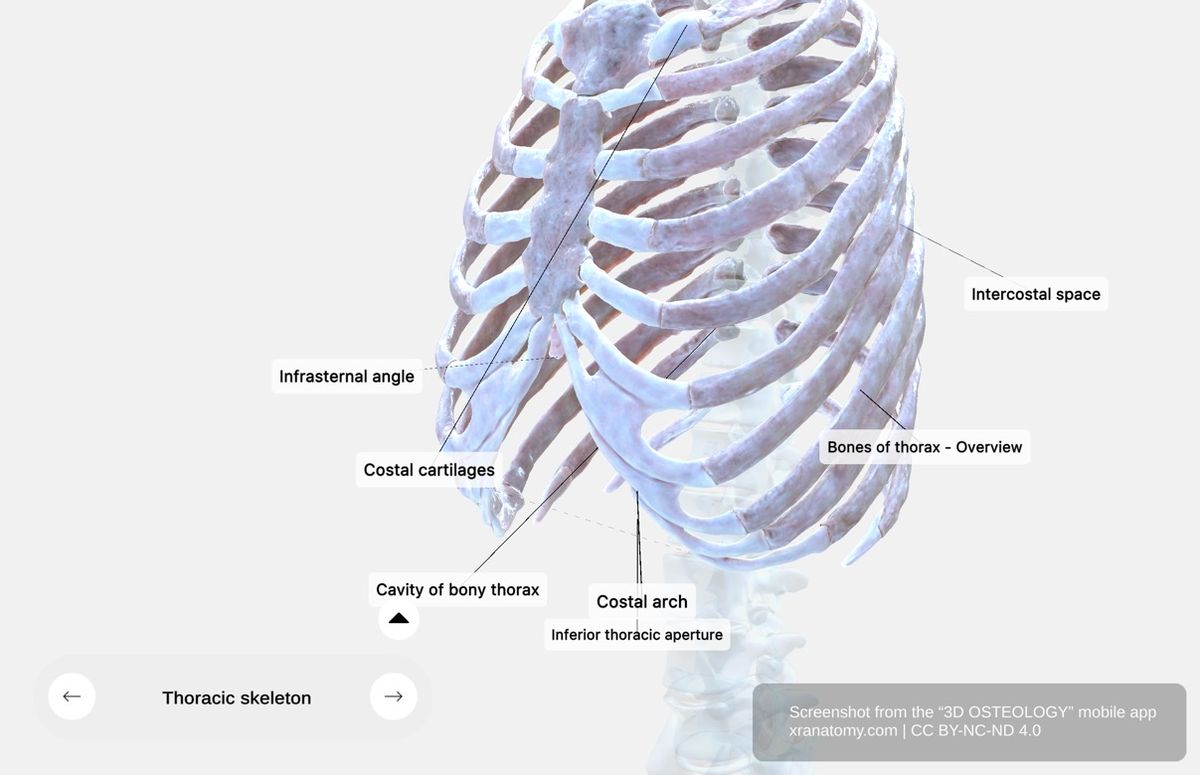
Infrasternal Angle, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The infrasternal angle is the angle formed at your xiphoid process where the lower rib cage edges meet. It serves as an anatomical landmark for diaphragm access.
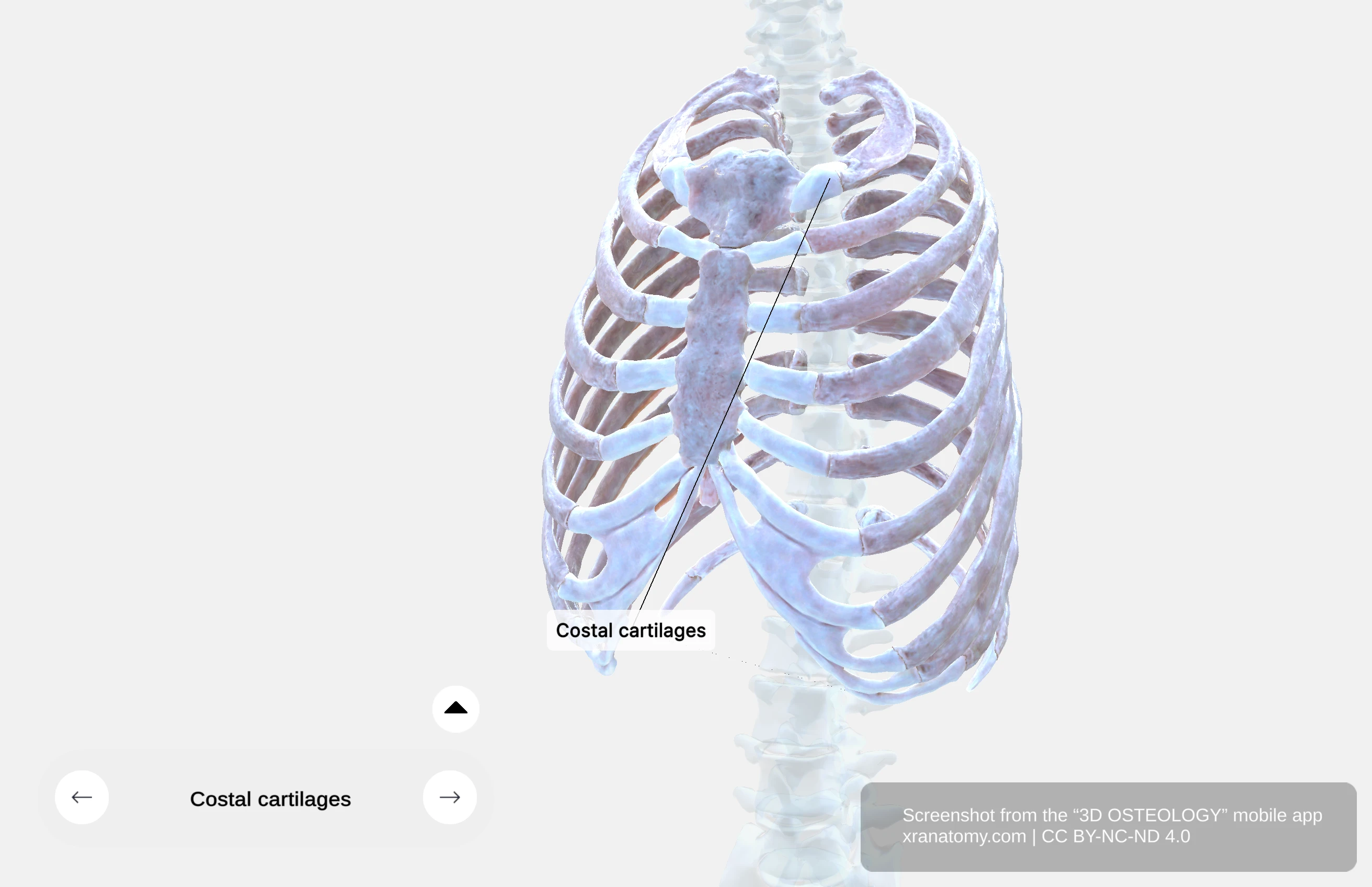
Costal Cartilages
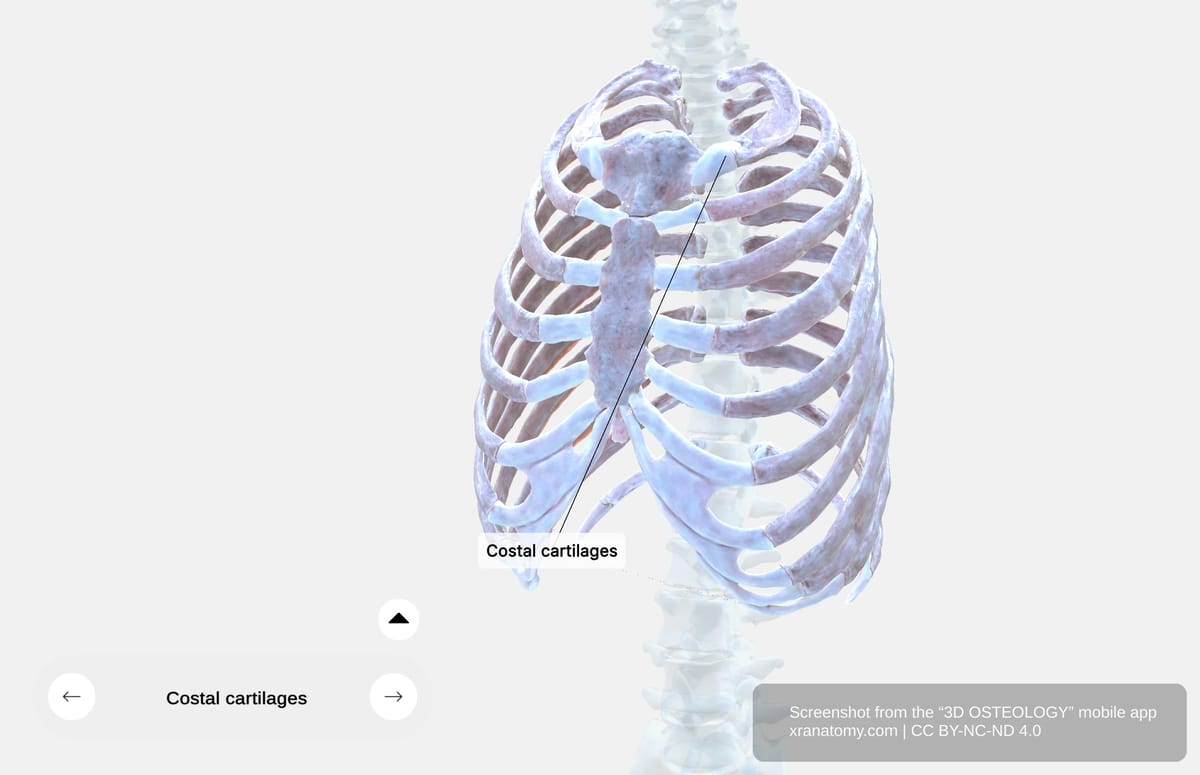
Costal cartilages are made of hyaline cartilage connecting your ribs to your sternum or to each other. They provide flexibility to your thoracic wall for respiration.
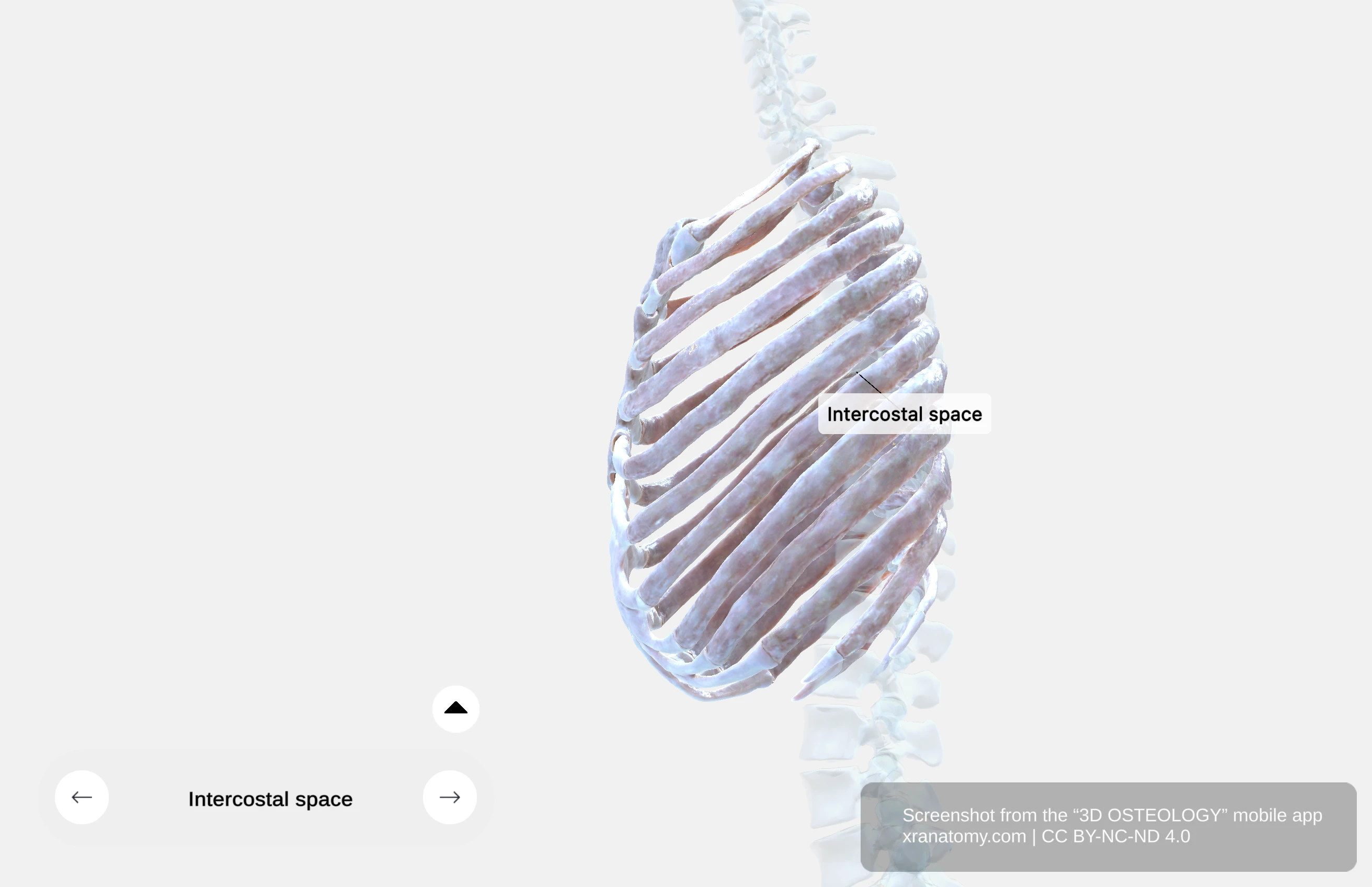
Intercostal Spaces
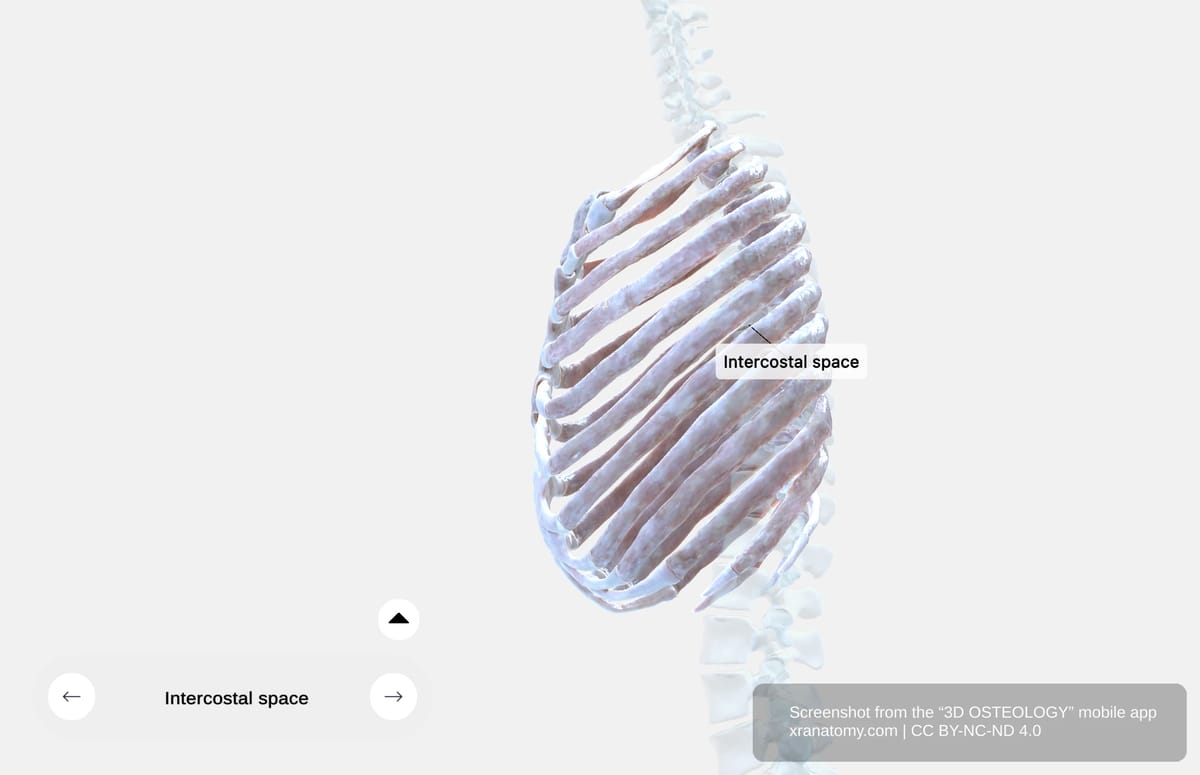
Intercostal spaces are the spaces between adjacent ribs and their costal cartilages. There are eleven spaces on each side. They contain intercostal muscles, membranes, and neurovascular bundles.
These spaces allow your rib movement during respiration and aid in your thoracic cavity expansion and contraction.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. What three bones make up the thoracic cage?
Reveal Answer
The ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum.
2. Name the boundaries of the superior thoracic aperture.
Reveal Answer
The first thoracic vertebra (back), the manubrium of the sternum (front), and the first ribs (sides).
3. How many intercostal spaces are there on each side, and what do they contain?
Reveal Answer
Eleven spaces on each side. They contain intercostal muscles, membranes, and neurovascular bundles.
WHAT'S NEXT
Next, you will explore the Rib Cage. You will learn how the twelve pairs of ribs are classified into true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs, and how the costal arch and costal cartilages contribute to the structure of your thorax.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.