RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY AR ATLAS
Interactive 3D Version Available
Explore this anatomy in full 360° rotation with our interactive 3D viewer
View in 3D →TABLE OF CONTENTS
RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY
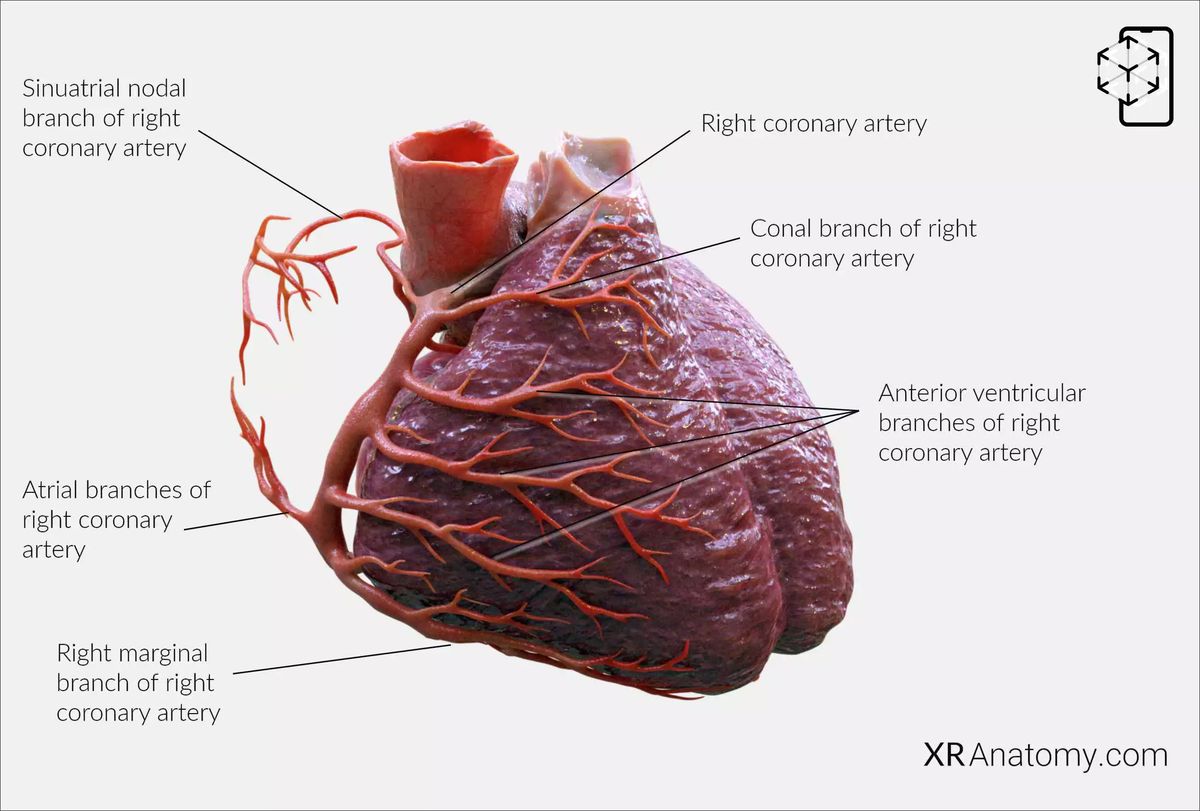
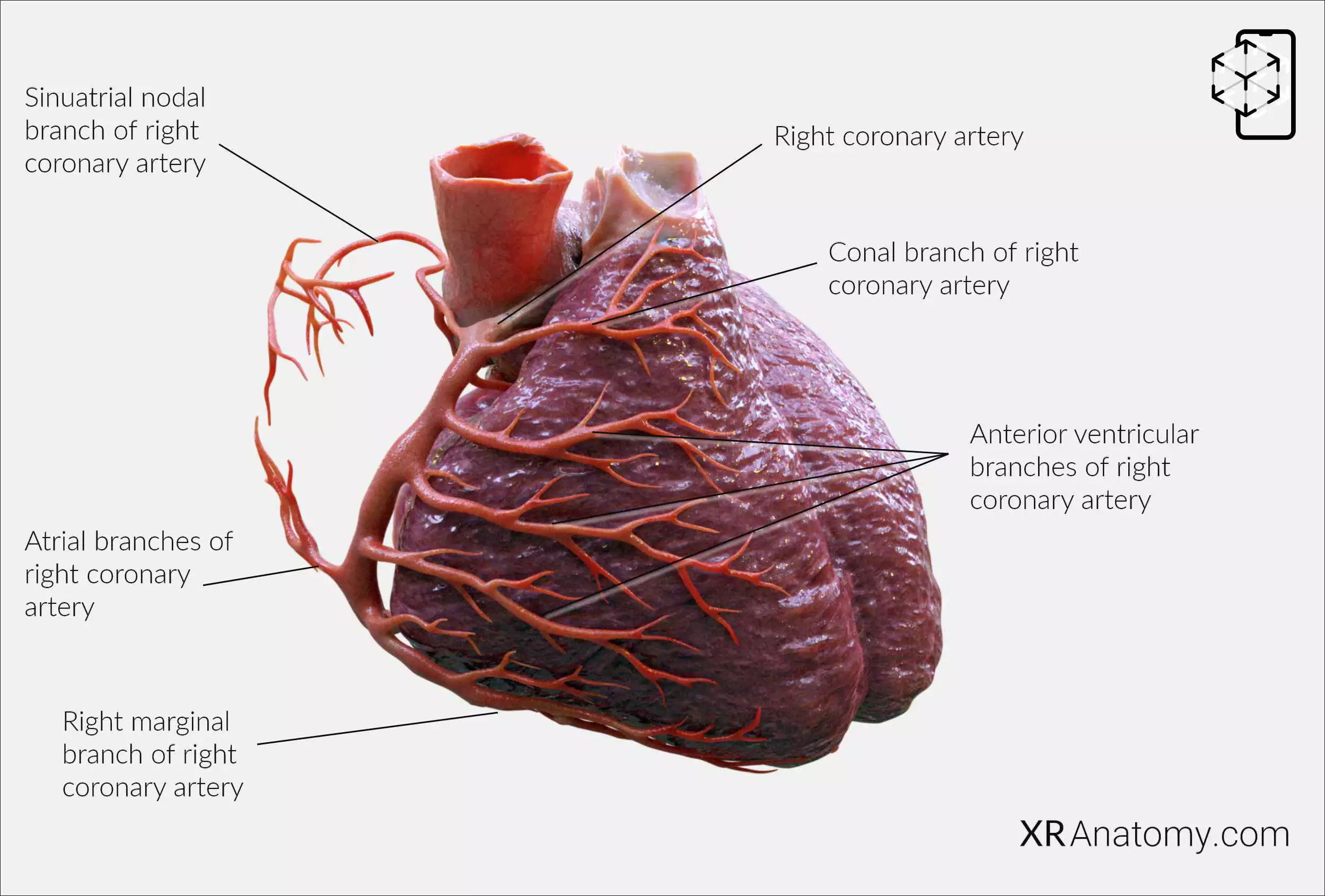
Right coronary artery: This is one of the two main vessels that branch off from the aorta. It originates from the right aortic sinus and follows a course along the atrioventricular groove. It generally supplies the right side of the heart. (1,2,3)
Conal branch of right coronary artery: Also known as the conus arteriosus artery, it runs towards the conus arteriosus or the right ventricular outflow tract, supplying blood to that region. (1,3)
Sinu-atrial nodal branch of right coronary artery: Typically supplies the sinoatrial node, the heart’s natural pacemaker. It encircles the superior vena cava in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction before reaching the sinoatrial (SA) node. (1,2,3)
Atrial branches of right coronary artery: These branches are typically responsible for supplying the right atrium. (2,3)
Anterior ventricular branches of right coronary artery: Branches that typically supply the anterior part of the right ventricle. (1,3)
Right marginal branch of right coronary artery: A significant branch that follows the margin of the heart to supply the outer right ventricular wall. (1,3)
INFERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR ARTERY

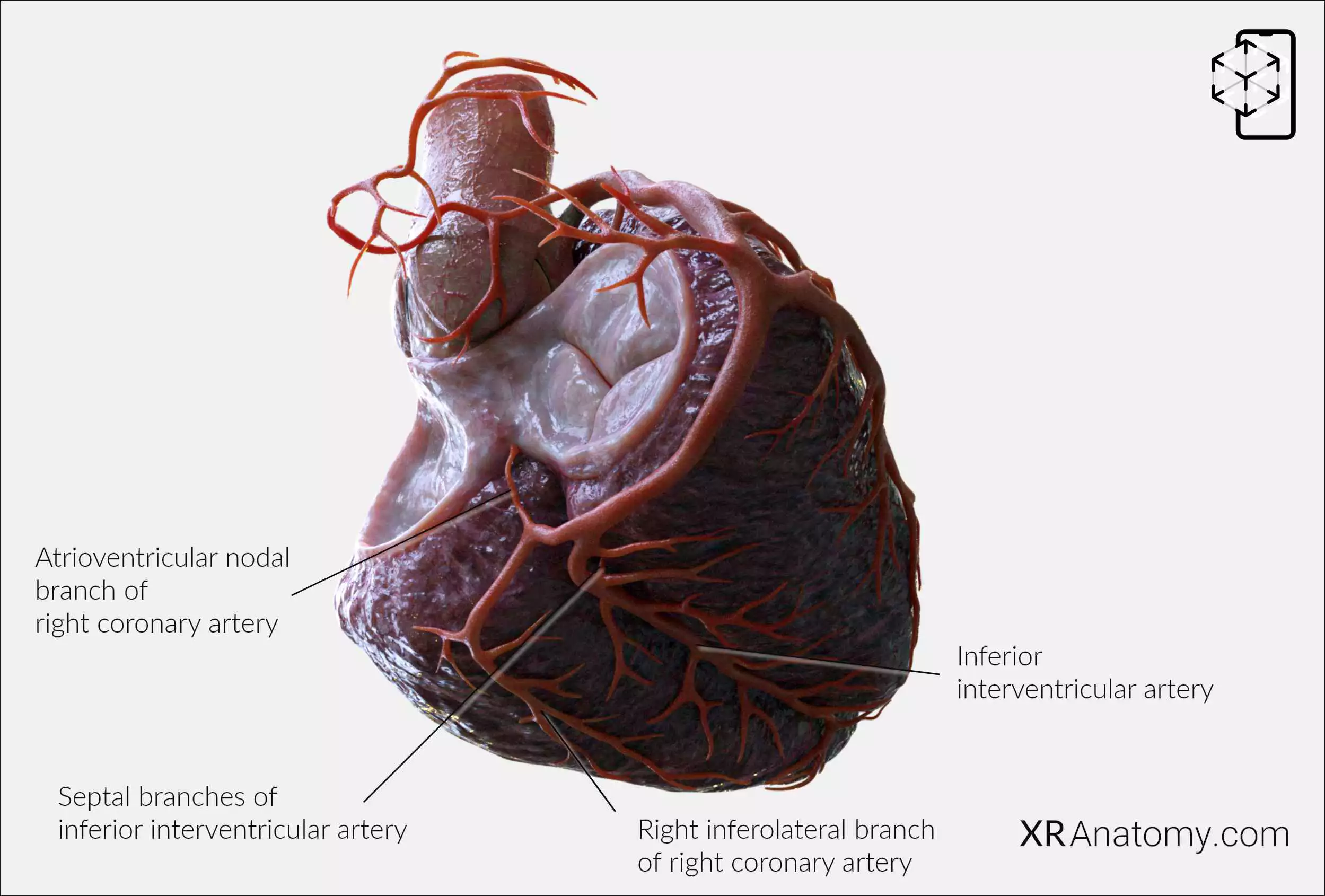
Inferior interventricular artery: Also known as the posterior descending artery, it usually runs along the inferior interventricular groove. Septal branches from this artery supply the ventricular septum. (2,3)
Septal branches of inferior interventricular artery: Arteries that originate from the inferior interventricular artery to supply the interventricular septum. (1,2,3)
Atrioventricular nodal branch of right coronary artery: In most cases, arises from the right coronary artery and supplies the AV node, a key component of the heart’s electrical conduction system. (2,3)
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Gray H, Lewis W. Angiology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918. p. 526–542.
2. Gosling JA, Harris PF, Humpherson JR, Whitmore I, Willan PLT. Human anatomy: color atlas and textbook. 6th ed. 2017. 45–58 p.
3. Anderson RH, Spicer DE, Hlavacek AM, Cook AC, Backer CL. (2013). Anatomy of the cardiac chambers. In Wilcox’s Surgical Anatomy of the Heart (4th ed., pp. 13–50). Cambridge University Press.
4. Fritsch H, Kuehnel W. Color Atlas of Human Anatomy. Vol. Volume 2, Color Atlas and Textbook of Human Anatomy. 2005. 10–42 p.
5. Moore K, Dalley A, Agur A. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Vol. 7ed, Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2014. 132–151 p.
6. Ho SYen. Anatomy for Cardiac Electrophysiologists: A Practical Handbook. Cardiotext Pub; 2012. 5–27 p.
7. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
8. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.