RIB ANATOMY

Rib - General Features, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
WHY THIS MATTERS
Your ribs are long, curved bones that connect posteriorly to your thoracic vertebrae and form the ribcage protecting your vital organs. Understanding each part of a rib, from the head and tubercle to the costal groove, helps you see how these bones articulate, house critical vessels and nerves, and give your chest wall its shape.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL FEATURES
Ribs are long, curved bones of your thoracic skeleton. They connect posteriorly to your thoracic vertebrae and form your ribcage. Each rib features distinct parts: the head, neck, body, tubercle, angle, and costal groove.
Head of Rib
The head is the rounded posterior portion of the rib connecting to your thoracic vertebrae. It contains two articular facets (superior and inferior) separated by the crest of the head (crista capituli). These facets articulate with two adjacent thoracic vertebrae. The crest provides stability for rib articulation.
Neck of Rib
The neck is the segment between the head and the tubercle. It features a roughened crest along the superior border. This crest serves as an attachment site for the superior costotransverse ligament, which stabilizes your rib's articulation with your vertebrae.
Body of Rib
The body is the long main portion of the rib, extending from the angle to the anterior end. It contains the costal groove along the inferior border. The costal groove houses and protects your intercostal vessels and nerve, which are crucial for your chest wall supply and sensation.
Tubercle of Rib
The tubercle sits at the junction of the rib's neck and body. It has two portions: an articular portion that articulates with the transverse process of your thoracic vertebra, and a non-articular portion that serves as an attachment site for ligaments.
Angle of Rib
The angle is the point where the rib changes direction, creating a bend. It marks the region where the rib begins to twist along its length.
Costal Groove
The costal groove runs along the inferior border of the rib's body. It guides and protects your intercostal vessels and nerve, ensuring efficient supply and sensation along your ribcage.
FIRST RIB
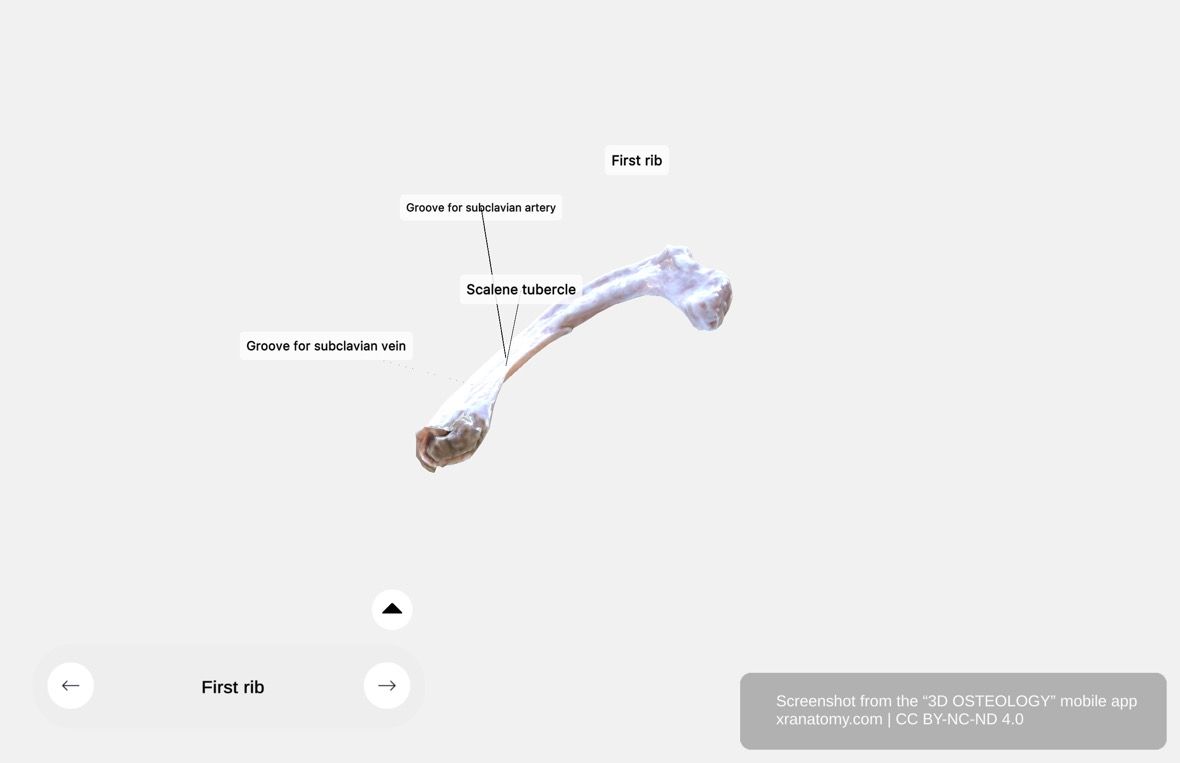
First Rib, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The first rib is the most curved and typically the shortest rib. Its shape is broad and flat, with surfaces angling upward and downward. It serves as a unique anatomical landmark in your thoracic cage. Key features on the first rib include the scalene tubercle, the groove for the subclavian artery, and the groove for the subclavian vein.
Scalene Tubercle
The scalene tubercle is a small bony prominence on the inner border of your first rib. It marks the end of a ridge on the upper surface and separates two grooves on the rib. It provides an attachment point for muscles involved in your neck movement.
Groove for Subclavian Artery
This groove sits just behind the scalene tubercle. It houses your subclavian artery and a nerve network essential for your arm function. The groove protects and routes these structures efficiently beneath the rib.
Groove for Subclavian Vein
This groove sits in front of the scalene tubercle. It holds your subclavian vein, which returns venous blood from your upper limb. The groove ensures your vein's protection and proper positioning.
SECOND RIB

Second Rib, Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
The second rib is approximately twice as long as the first rib, with a similar curvature. It is distinguished by a roughened tuberosity for the serratus anterior muscle.
Tuberosity for Serratus Anterior Muscle
The tuberosity for serratus anterior is a roughened area on the second rib. It serves as the anchor point for your serratus anterior muscle. This muscle facilitates movement of your shoulder blade, supports proper arm function, and stabilizes your shoulder.
FLOATING RIBS (ELEVENTH AND TWELFTH RIBS)
Floating Ribs (11th and 12th), Preview from the app. Download 3D OSTEOLOGY for full 3D control—multiple views, x-ray mode, and unlimited zoom.
Your floating ribs have free anterior ends that do not attach to your sternum. They terminate within your back musculature. They provide flexibility to your ribcage and are considered a subset of false ribs, as they do not contribute to your sternum's structure.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING
1. Name the six distinct parts of a typical rib.
Reveal Answer
Head, neck, body, tubercle, angle, and costal groove.
2. What structure on the first rib separates the groove for the subclavian artery from the groove for the subclavian vein?
Reveal Answer
The scalene tubercle. The groove for the subclavian artery sits just behind it, and the groove for the subclavian vein sits in front of it.
3. What distinguishes the floating ribs from other ribs?
Reveal Answer
The floating ribs (11th and 12th) have free anterior ends that do not attach to the sternum. They terminate within the back musculature.
WHAT'S NEXT
Now that you know the parts of a single rib, the next page covers the Sternum. You will explore the manubrium, sternal body, and xiphoid process, along with key landmarks like the jugular notch, sternal angle, and costal notches where your ribs attach anteriorly.
Review this page again in 3 days to reinforce what you have learned.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Henry G, Warren HL. Osteology. In: Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. p. 129–97.
2. Standring S, editor. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Essential Clinical Anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2015.